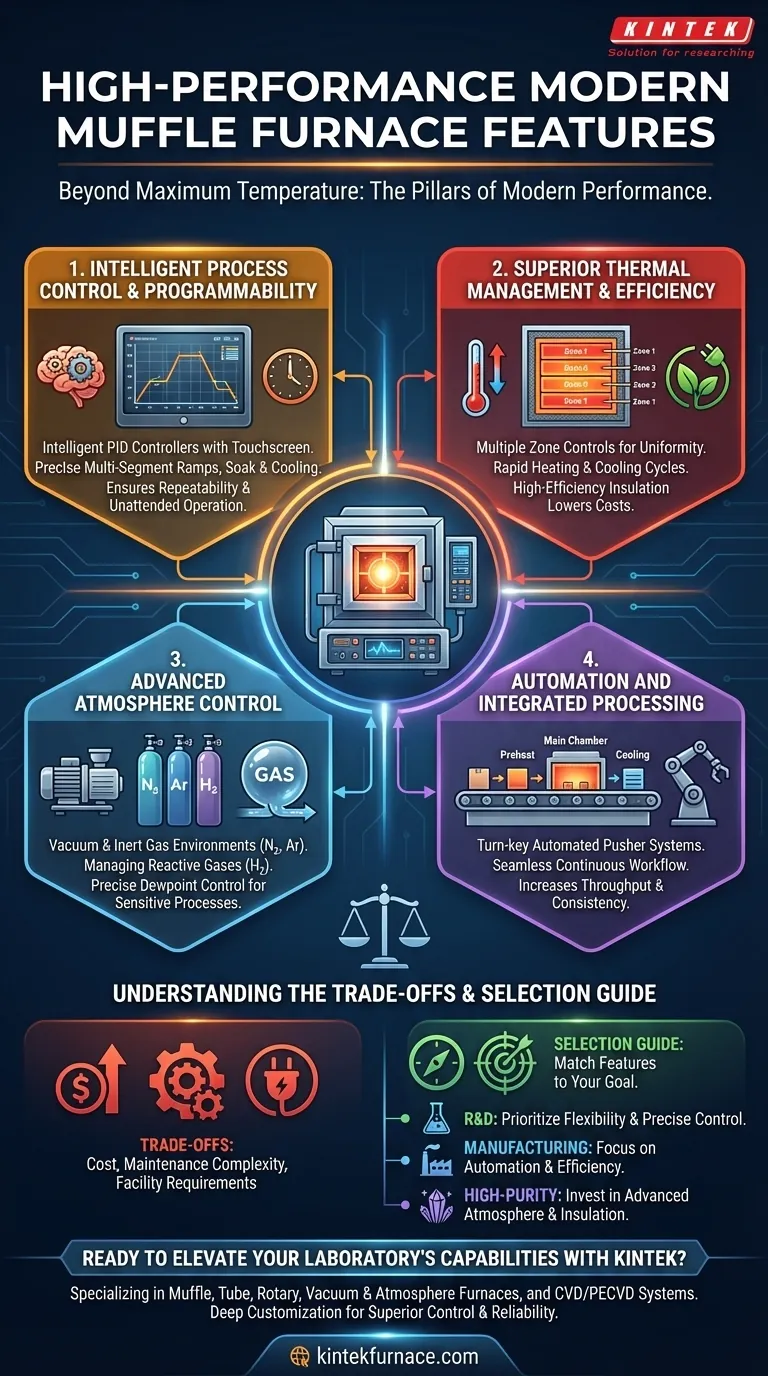
At its core, a high-performance modern muffle furnace is defined by features that provide precise and repeatable control over the entire thermal process. Beyond simply reaching high temperatures, these furnaces incorporate intelligent process controllers, advanced thermal management for speed and uniformity, sophisticated atmosphere control systems, and integrated automation for continuous operation.
The leap from a standard furnace to a high-performance one is not about achieving higher temperatures, but about gaining absolute control over the processing environment. This control—over temperature ramps, atmosphere, and material handling—is what enables superior quality, repeatability, and efficiency.

Beyond Maximum Temperature: The Pillars of Modern Performance
The value of a modern furnace is measured by its ability to execute a complex, multi-stage process flawlessly every time. This capability rests on several key technological pillars that work in concert.
Intelligent Process Control & Programmability
The "brain" of the furnace is its controller. Basic units may only hold a setpoint, but high-performance models offer complete command over the thermal profile.
Intelligent PID controllers with touchscreen interfaces are now standard. These systems allow operators to program precise, multi-segment heating rates, soak times, and cooling rates, ensuring process repeatability and enabling unattended operation.
This programmability is critical for applications like annealing or ceramic firing, where the rate of temperature change is just as important as the peak temperature itself.
Superior Thermal Management & Efficiency
Performance is directly tied to how well a furnace manages heat. This involves not just generating heat, but also controlling it uniformly and using it efficiently.
Multiple zone controls are essential for ensuring temperature uniformity across a large chamber or a long process tube. By using several independent heating zones and sensors, the furnace can compensate for heat loss and guarantee the entire workload experiences the same thermal conditions.
Features like rapid heating and cooling cycles are achieved through low thermal mass insulation and high-power heating elements, such as silicon carbide. This dramatically increases throughput and allows for processes like quenching. Modern insulation also significantly boosts energy efficiency, lowering long-term operational costs.
Advanced Atmosphere Control
Many advanced material processes cannot be performed in ambient air. High-performance furnaces isolate the workload and allow for precise management of the internal atmosphere.
This can range from creating a vacuum to remove reactive gases, to introducing specific process gases like nitrogen or argon for an inert environment that prevents oxidation.
For more reactive processes, systems can manage reducing atmospheres with gases like hydrogen or control low or high dewpoint levels. This capability is fundamental for operations like brazing, sintering, and metallizing.
Automation and Integrated Processing
For industrial-scale production, manual loading and unloading is a major bottleneck. High-performance systems integrate automation to create a seamless, continuous workflow.
Turn-key automated pusher systems are a prime example. These systems automatically move parts through different furnace sections, such as a preheat section or a binder removal section, before they enter the main heating chamber.
This level of automation not only increases throughput but also enhances process consistency by eliminating the variability of manual handling.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Complexity vs. Capability
While advanced features provide powerful capabilities, they also introduce practical considerations that must be weighed.
Cost and Maintenance
Unsurprisingly, furnaces with sophisticated controls, multi-zone heating, and advanced atmosphere systems carry a higher initial investment. They also involve more complex components that can increase maintenance requirements and operating skill level.
Process Specificity
A furnace highly optimized for one specific task, such as hydrogen brazing, may be less flexible for general-purpose thermal processing. The design choices that make it excel in one area may be limitations in another.
Facility Requirements
High-performance furnaces often have significant infrastructure needs. High power draws may require electrical service upgrades, while the use of process gases, especially flammable ones like hydrogen, demands strict safety protocols, specialized plumbing, and proper ventilation.
Selecting the Right Features for Your Application
The ideal furnace configuration depends entirely on your primary objective. Focus on the features that directly support your most critical process outcomes.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Prioritize precise PID programmable controllers and flexible atmosphere options to accommodate a wide range of experimental parameters.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: Emphasize automation features like pusher systems, multi-zone control for uniformity, and energy efficiency to minimize operational costs.
- If your primary focus is high-purity materials or sensitive processes: Invest in advanced atmosphere control systems (vacuum, inert gas) and high-quality insulation to guarantee process isolation and purity.
Choosing the right furnace is about matching its capabilities to your specific process goals, ensuring every feature serves a direct purpose.
Summary Table:
| Feature Category | Key Components | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligent Process Control | PID controllers, touchscreen interfaces | Precise temperature programming, repeatability, unattended operation |
| Thermal Management | Multiple zone controls, rapid heating/cooling, energy-efficient insulation | Uniform heating, high throughput, reduced operational costs |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum systems, inert gas handling (e.g., nitrogen, argon), hydrogen compatibility | Oxidation prevention, process isolation for sensitive applications |
| Automation | Pusher systems, integrated processing sections | Increased throughput, consistency, reduced manual handling |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with a high-performance furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, delivering superior control, efficiency, and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a furnace to your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















