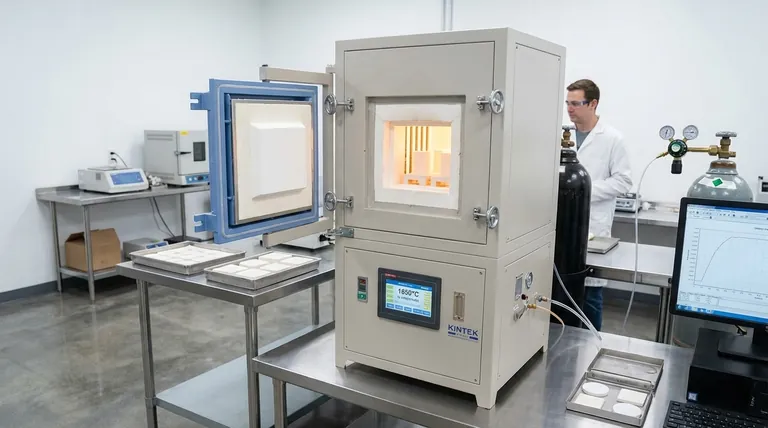
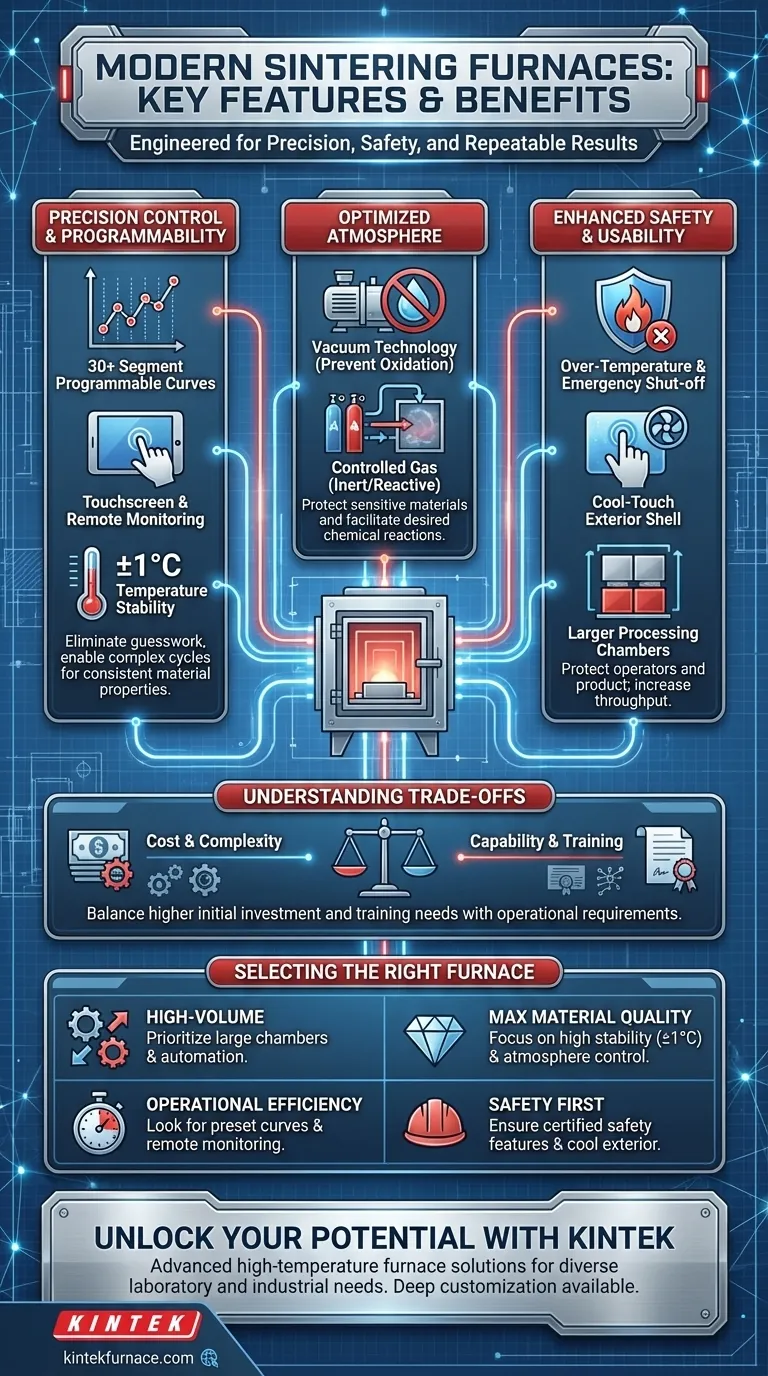
At their core, modern sintering furnaces are defined by features that deliver precise environmental control and enhanced safety. Key advancements include highly programmable control systems, vacuum and controlled atmosphere capabilities, and robust, automated safety mechanisms to protect both operators and the product. These features work in concert to ensure uniform heating, prevent oxidation, and create highly repeatable results for materials ranging from dental ceramics to industrial components.
Modern furnace technology has shifted from simply applying heat to precisely engineering the entire thermal process. The goal is no longer just to reach a target temperature, but to control every variable—from atmosphere to heating rate—to achieve specific, predictable material properties.

Precision Control and Programmability
The brain of a modern furnace is its control system. These systems are designed to eliminate guesswork and enable complex, multi-stage processes that are perfectly repeatable.
Programmable Sintering Curves
Modern furnaces feature 30-segment (or more) programmable controls, allowing users to define intricate heating, soaking, and cooling cycles.
Many units come with preset sintering curves for common materials like zirconia, saving time and reducing the risk of programming errors.
Advanced Control Systems
Operations are often managed through a 7-inch (or larger) color touchscreen, providing an intuitive interface for monitoring and programming.
Intelligent control systems with remote monitoring capabilities allow technicians to oversee processes from a distance, simplifying operation and enabling continuous production workflows.
Uniform Temperature Stability
Superior insulation and advanced heating elements ensure exceptional temperature stability, often within ±1°C of the setpoint. This uniformity is critical for achieving consistent material density and preventing structural defects.
Optimizing the Sintering Atmosphere
The environment inside the furnace is just as important as the temperature. Modern furnaces provide exceptional control over the internal atmosphere to prevent contamination and facilitate desired chemical reactions.
Vacuum Technology
The ability to pull a vacuum is a key feature for preventing oxidation. By removing oxygen before the heating cycle begins, the furnace protects sensitive materials from discoloration and degradation of their mechanical properties.
Controlled Atmospheres
Beyond a vacuum, many furnaces allow for the introduction of specific gases. This is crucial for materials that require an inert (like argon) or reactive atmosphere to achieve their final characteristics.
Enhancing Safety and Usability
As furnaces become more powerful and complex, integrated safety and user-centric design have become paramount.
Built-in Safety Mechanisms
Over-temperature protection automatically cuts power if the furnace exceeds a safe limit, preventing damage to the unit and the product.
Systems also include emergency shut-off buttons and, in some cases, gas leak detection sensors to ensure the complete safety of the operating environment during high-temperature processing.
User-Focused Design
Modern designs often feature a double-layer cooling shell or fan-assisted cooling, keeping the external surface temperature low (often below 50°C) to prevent operator burns.
Larger processing chambers are now common, increasing throughput and productivity without a proportional increase in the furnace's footprint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While advanced features offer significant benefits, they also introduce practical considerations that must be weighed.
Cost vs. Capability
More sophisticated features, such as advanced atmospheric controls or larger chambers, directly correlate with a higher initial investment. It's crucial to match the furnace's capabilities to the actual processing requirements to avoid overspending.
Complexity and Training
While touchscreens simplify operation, the underlying programmability is more complex. Unlocking the full potential of a 30-segment controller or a multi-gas system requires proper operator training to prevent errors.
Maintenance Considerations
A furnace with advanced electronics, vacuum pumps, and gas flow controllers has more potential points of failure than a simple kiln. Consider the availability of technical support and the cost of maintaining these sophisticated components over the long term.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Choosing a furnace requires aligning its features with your primary goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Prioritize furnaces with larger chambers and features that support continuous or automated batch processing.
- If your primary focus is maximum material quality: Invest in a system with the highest degree of temperature stability (±1°C) and advanced atmosphere or vacuum control.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Look for advanced programmable controllers with preset curves and remote monitoring to minimize manual intervention and human error.
- If your primary focus is safety: Ensure the furnace includes certified safety features like over-temperature protection, emergency shut-off, and a cool-to-touch exterior shell.
Ultimately, the right furnace is a tool precisely matched to the demands of your material and the goals of your operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Precision Control | 30+ segment programmable curves, ±1°C stability, touchscreen interface |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum and gas options for oxidation prevention and material quality |
| Safety Mechanisms | Over-temperature protection, emergency shut-off, cool exterior |
| Usability | Larger chambers, remote monitoring, preset curves for efficiency |
Unlock the full potential of your sintering processes with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need precise temperature control, enhanced safety, or tailored designs for materials like ceramics, KINTEK delivers reliable performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our sintering furnaces can elevate your lab's productivity and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance



















