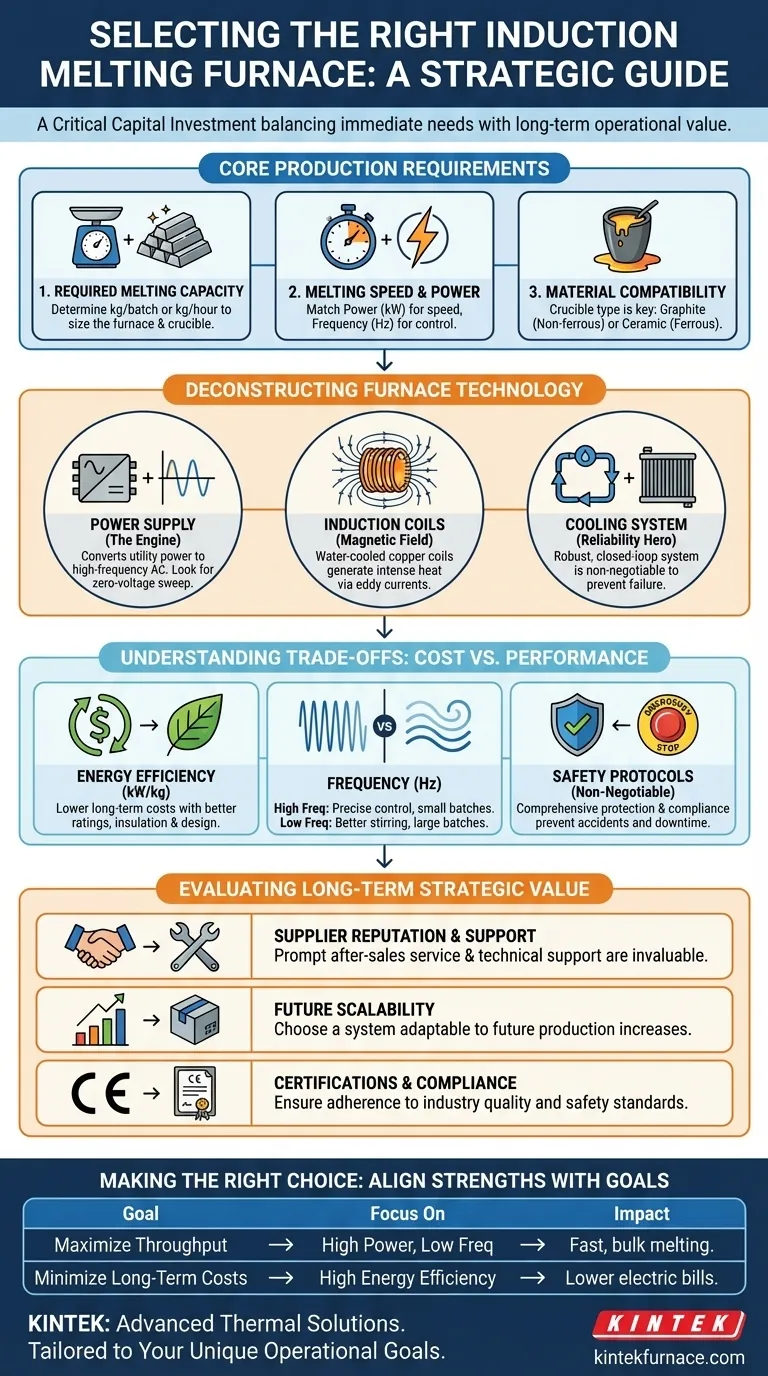
Selecting the right induction furnace is a critical capital investment. The most important factors to consider are your required melting capacity, the necessary speed of your melts, the specific materials you will be processing, and the overall energy efficiency of the system. These primary criteria dictate the furnace's power, frequency, and crucible type, forming the foundation of your decision.
Beyond the basic specifications, the optimal choice hinges on a holistic assessment of your entire operational ecosystem. True value is found by balancing initial purchase price against long-term energy costs, safety protocols, and the strategic value of supplier support and future scalability.

Defining Your Core Production Requirements
The first step is to quantify your operational needs with precision. The furnace must be sized to meet your current and anticipated production demands without being excessively oversized, which leads to inefficiency.
Calculating Your Required Melting Capacity
Your required capacity is the amount of metal, by weight, that you need to melt in a single batch or over a specific time frame (e.g., kilograms per hour). This directly determines the physical size of the furnace and its crucible.
Matching Power and Frequency to Melting Speed
Melting speed is a function of the furnace's power rating (kW) and its operating frequency (Hz). A higher power rating delivers more energy into the charge, resulting in faster melting times.
Frequency plays a more nuanced role. Lower frequencies (below 1 kHz) are better for stirring and melting larger batches of metal, while higher frequencies (up to 1100 kHz) are more efficient for smaller batches and specialty alloys, offering precise control.
Ensuring Material and Crucible Compatibility
The type of metal you are melting dictates the required crucible material. Graphite crucibles are common for non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper, while ceramic crucibles are necessary for ferrous metals like steel and iron due to their higher melting points and different chemical interactions.
Deconstructing the Furnace Technology
Understanding the key components of an induction furnace reveals how it achieves its performance and where potential points of failure lie.
The Power Supply: The Engine of the Furnace
The power supply is the heart of the system. It converts standard 50/60 Hz utility power into the high-frequency AC current that energizes the induction coils. Modern power supplies with zero-voltage sweep software allow for efficient and frequent start-ups, which is crucial for dynamic production environments.
The Induction Coils: Generating the Magnetic Field
Water-cooled copper coils generate the intense, alternating magnetic field that induces eddy currents within the metal charge, causing it to heat and melt. The design and integrity of these coils are paramount for efficient energy transfer.
The Cooling System: The Unsung Hero of Reliability
An induction furnace generates immense heat, not just in the metal but in the electronics and coils. A robust, closed-loop water cooling system is non-negotiable. It prevents overheating, protects critical components, and is essential for consistent, long-term operation. Insufficient cooling is a primary cause of furnace failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Performance
A cheap furnace is rarely the most economical choice. The initial purchase price is only one part of the total cost of ownership.
The Energy Efficiency Equation
Energy consumption is the single largest operational cost. Look for furnaces with clear energy efficiency ratings (kW per kg/lb of metal melted). Improved insulation, optimized coil design, and advanced power modulation can significantly reduce electricity bills over the furnace's lifetime.
High Frequency vs. Low Frequency
There is a direct trade-off here. High-frequency furnaces offer precise control for small, clean melts but are less effective at stirring large volumes. Low-frequency furnaces excel at creating a strong stirring action, which is ideal for homogenizing alloys in large batches, but they are less controlled for smaller quantities.
The Hidden Costs of Inadequate Safety
Skimping on safety is a catastrophic mistake. A quality furnace must include comprehensive protection mechanisms: automatic shut-offs, over-current and over-voltage protection, and emergency stops. Compliance with industry safety standards protects your operators and prevents costly accidents and downtime.
Evaluating Long-Term Strategic Value
Your furnace selection is a long-term partnership with both the equipment and its manufacturer.
Supplier Reputation and After-Sales Support
A supplier's reputation is a direct indicator of product quality and reliability. Investigate their track record, customer testimonials, and the availability of prompt after-sales service and technical support. When a problem occurs, the speed and quality of support are invaluable.
Planning for Future Expansion
Consider your business's growth trajectory. A furnace that can be scaled or is part of an adaptable system can accommodate future increases in production demand. This foresight prevents the need for a complete and costly replacement down the line.
The Importance of Certifications and Compliance
Ensure the furnace meets key industry and regional certifications, such as CE (for Europe). These standards are not just bureaucratic hurdles; they are a baseline guarantee of quality, safety, and operational integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
To simplify your decision, align the furnace's strengths with your primary business goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Prioritize a high-power, lower-frequency system with a large capacity crucible to melt bulk material quickly.
- If your primary focus is melting diverse, small batches of specialty alloys: A high-frequency furnace offers the best control, cleanliness, and efficiency for your application.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operational costs: Scrutinize the energy efficiency ratings (kW/kg) and invest in superior insulation and cooling, even if the initial cost is higher.
- If your primary focus is operational safety and reliability: The supplier's reputation, robust safety features, and available support network should be your top criteria.
A well-chosen furnace is not just a piece of equipment; it is a strategic asset that drives the efficiency and profitability of your entire melting operation.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations | Impact on Choice |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Capacity | Required kg/batch or kg/hour | Determines furnace size and crucible |
| Melting Speed | Power rating (kW) and Frequency (Hz) | Higher power = faster melts; Frequency affects stirring and control |
| Material Compatibility | Type of metal (ferrous/non-ferrous) | Dictates crucible type (graphite vs. ceramic) |
| Energy Efficiency | kW per kg of metal melted | Major driver of long-term operational costs |
| Supplier Support | After-sales service, technical support, and reputation | Critical for reliability and minimizing downtime |
Ready to select the right induction furnace for your specific needs?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced thermal solutions. Our team will work with you to analyze your core production requirements—from capacity and speed to material compatibility and energy efficiency—ensuring your furnace is a strategic asset that drives profitability.
Contact KINTROL today to discuss your project and discover how our expertise and deep customization capabilities can deliver a solution precisely tailored to your unique operational goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















