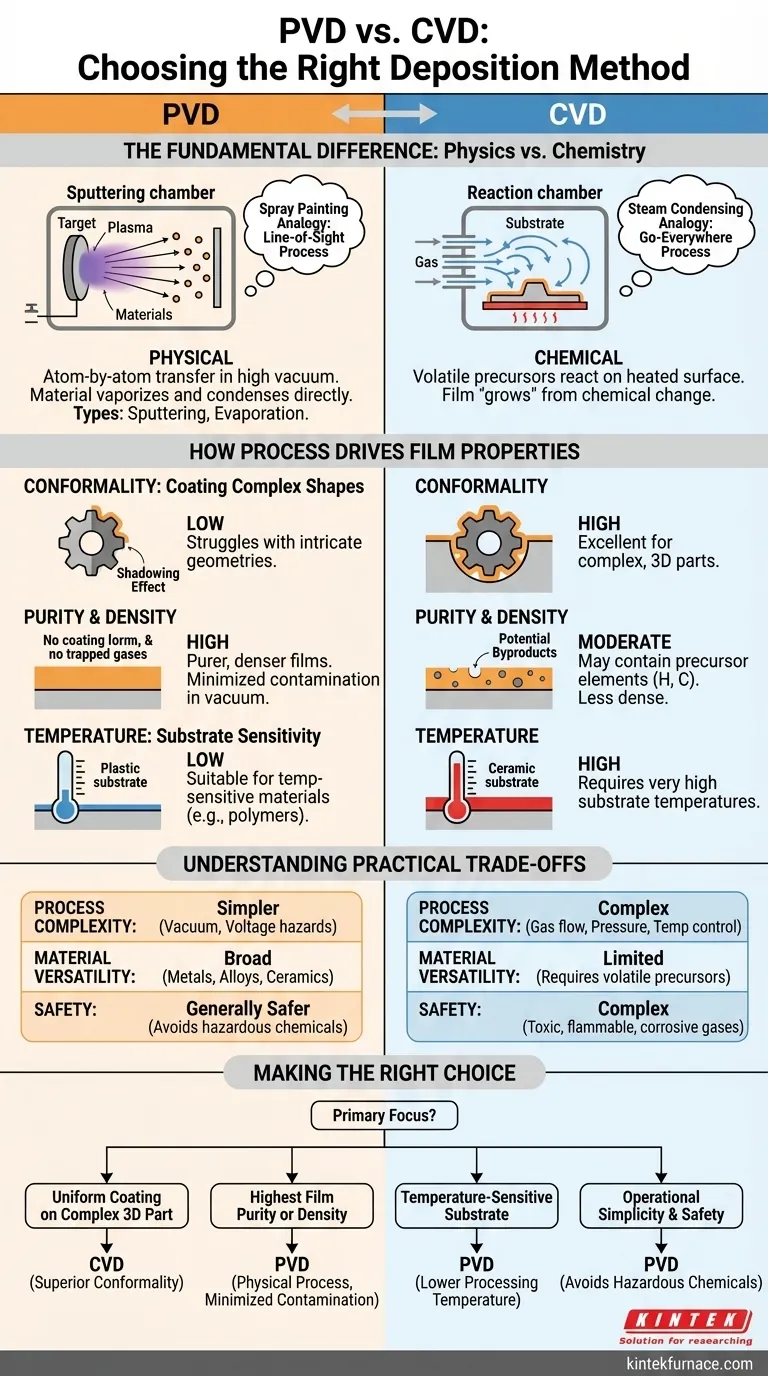
When choosing between PVD and CVD, your decision hinges on three core factors: the material being deposited, the physical geometry of the part you are coating, and the specific properties required of the final film. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a physical, line-of-sight process, while Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a chemical, gas-based process. This fundamental difference dictates which method is right for your application.
The choice is not about which method is universally "better," but which one aligns with your project's most critical requirement. PVD excels at creating exceptionally pure, dense films on simpler surfaces. CVD excels at coating complex, three-dimensional shapes with a uniform layer.
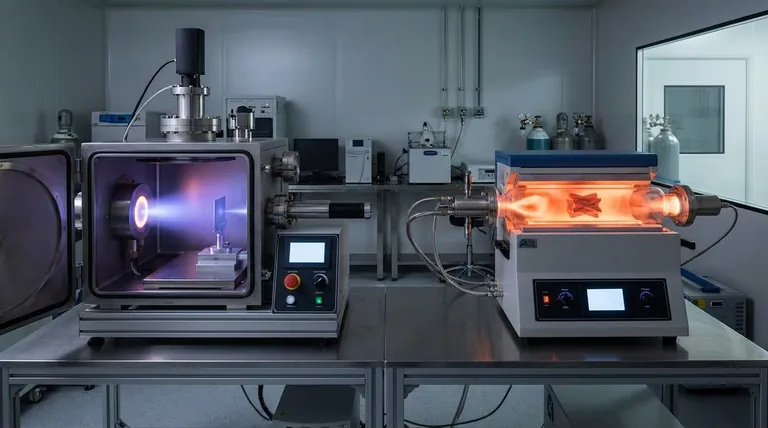

The Fundamental Difference: Physics vs. Chemistry
Understanding how each process works is the key to selecting the right one. They operate on entirely different principles, which directly impacts the characteristics of the final coating.
PVD: A Physical, "Line-of-Sight" Process
Physical Vapor Deposition is an atom-by-atom transfer process that occurs in a high-vacuum environment. Material from a solid source is vaporized, travels in a straight line through the vacuum, and condenses onto the substrate.
Think of it like spray painting. The paint only coats the surfaces it can directly see. This method is physical—no chemical reactions take place to form the film. The two main types are sputtering and evaporation.
CVD: A Chemical, "Go-Everywhere" Process
Chemical Vapor Deposition uses volatile chemical precursors—specialty gases—that are introduced into a reaction chamber. When these gases contact the heated substrate, a chemical reaction occurs, causing a solid film to "grow" on the surface.
This is more like steam condensing on a cold window. The water vapor is in the air and can reach every surface, no matter how complex, before it condenses. The film is the product of a chemical change.
How Process Drives Film Properties
The "line-of-sight" nature of PVD versus the "go-everywhere" nature of CVD creates distinct advantages and disadvantages in the final film.
Conformality: Coating Complex Shapes
CVD is the clear winner for conformality. Because the precursor gases flow around the part before reacting, CVD can deposit a highly uniform coating inside deep trenches, holes, and on intricate 3D geometries.
PVD struggles with this. Due to its line-of-sight nature, it creates a "shadowing" effect, where features not directly facing the source material receive little or no coating.
Purity and Density: The Impact of Byproducts
PVD generally produces purer and denser films. The process occurs in a high vacuum, minimizing the chance of atmospheric gases getting trapped in the film. Because it is a direct physical transfer, there are no chemical byproducts to cause contamination.
CVD films can be very pure, but the chemical reactions can sometimes leave behind unwanted elements from the precursor gases (like hydrogen or carbon). This can result in a less dense film with potential impurities.
Temperature: Substrate Sensitivity
PVD is often better for temperature-sensitive materials. While some PVD processes require heat, many can be performed at or near room temperature. This makes it ideal for coating plastics, polymers, or other substrates that cannot withstand high heat.
CVD almost always requires very high substrate temperatures (often several hundred degrees Celsius) to provide the energy needed to drive the chemical reactions.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
Beyond the film itself, the processes have different operational requirements that impact cost, safety, and versatility.
Process Complexity and Safety
PVD systems are mechanically and operationally simpler. The primary hazards relate to high voltage and vacuum systems.
CVD is significantly more complex. It requires precise control of gas flow, pressure, and temperature. Furthermore, many chemical precursors used in CVD are highly toxic, flammable, or corrosive, demanding extensive safety protocols and infrastructure.
Material Versatility
Both methods are highly versatile but in different ways. PVD can deposit nearly any metal, alloy, or ceramic that can be made into a solid "target" for sputtering or evaporation.
CVD is limited to materials for which a suitable volatile chemical precursor gas exists and can be safely handled. However, for materials like silicon, diamond, and silicon nitride, CVD is the dominant and most effective industrial method.
Deposition Rate
Deposition rates are highly dependent on the specific material and application. CVD can achieve extremely high growth rates for certain materials (like thick silicon films), making it cost-effective for high-volume manufacturing. For other applications, especially thin decorative or metallic films, PVD can be faster.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your deposition method based on the single most important outcome you need to achieve for your component.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex 3D part uniformly: CVD is almost always the superior choice due to its excellent conformality.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity or density: PVD is the preferred method, as its physical process in a vacuum minimizes contamination.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive substrate (like a polymer): PVD offers a significant advantage with its lower processing temperature options.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity and avoiding hazardous chemicals: PVD is a more straightforward and generally safer process to implement.
Understanding these core principles transforms the choice from a guess into a strategic engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Factor | PVD | CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Conformality | Low (line-of-sight) | High (uniform on complex shapes) |
| Film Purity | High (minimal contamination) | Moderate (potential byproducts) |
| Temperature | Low (suitable for sensitive substrates) | High (requires heated substrate) |
| Process Safety | Simpler (hazards: vacuum, voltage) | Complex (hazards: toxic gases) |
| Material Versatility | Broad (metals, alloys, ceramics) | Limited (requires volatile precursors) |
Struggling to choose the right deposition method for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to ensure precise performance for your experiments. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your coating processes and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What are the drawbacks of CVD compared to PECVD? Key Limitations for Your Lab



















