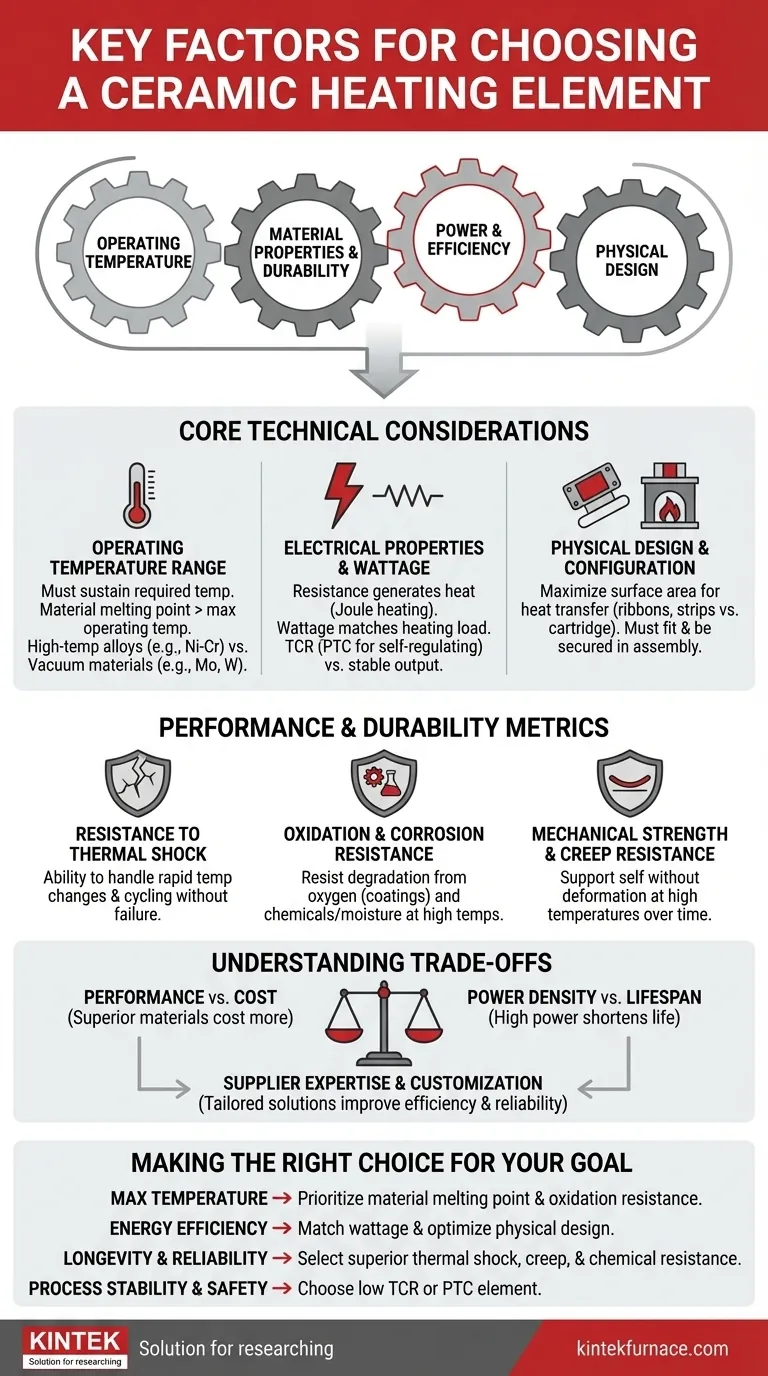
To choose the right ceramic heating element, you must evaluate four primary factors. These are the required operating temperature range, the element's material properties and durability, its power requirements and efficiency, and its physical design as it relates to your specific application.
The optimal choice is not the most powerful or advanced element, but the one whose technical specifications and physical design most closely match the precise demands of your system. A mismatch in any key area leads to inefficiency, premature failure, or inadequate performance.

Core Technical Considerations
Selecting the correct heating element begins with a clear understanding of the fundamental technical requirements. These properties dictate how the element will perform under load and within its intended environment.
Operating Temperature Range
The most critical factor is the temperature the element must achieve and sustain. The element’s material composition must have a melting point significantly higher than its maximum operating temperature to ensure stability and a long service life.
Different ceramic and metallic materials are suited for different heat ranges. For example, nickel-chromium alloys are common for high-temperature air heating, while materials like molybdenum or tungsten are used in vacuum furnaces for even higher temperatures.
Electrical Properties and Wattage
The element's electrical resistance is what generates heat when a current is applied (Joule heating). This resistance is determined by the material's inherent resistivity and its physical dimensions, particularly its cross-sectional area.
Wattage, or power output, must be carefully matched to the heating load. An undersized element will fail to reach the target temperature, while an oversized one is inefficient and can be harder to control.
Also, consider the temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR). A low TCR provides stable heat output as the element's temperature changes, which is ideal for precise process control. A high positive TCR (PTC) is useful for self-regulating heaters that reduce their power output as they get hotter, preventing overheating.
Physical Design and Configuration
The shape and size of the heating element directly impact heat transfer efficiency. The goal is to maximize the surface area that radiates or conducts heat to the target.
For instance, wide ribbons or strips are often used in vacuum furnaces to maximize radiant surface area. In contrast, a compact cartridge heater is designed for insertion into drilled holes to provide concentrated conductive heat. The element must physically fit and be properly secured within your assembly.
Performance and Durability Metrics
Beyond initial performance, an element's ability to withstand its operating environment over time is crucial for reliability and reducing downtime.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Ceramic materials can be susceptible to cracking when subjected to rapid temperature changes. Thermal shock resistance is a measure of an element’s ability to handle fast heating and cooling cycles without mechanical failure, a critical factor in applications with frequent on/off cycles.
Resistance to Oxidation and Corrosion
At high temperatures, most materials react with oxygen in the air, a process called oxidation. This degrades the element and leads to failure. High-quality elements often incorporate materials resistant to oxidation or are protected by a surface layer, such as a silicon or aluminum oxide coating.
If the element will be exposed to chemicals or moisture, its corrosion resistance is equally important for ensuring a long operational life.
Mechanical Strength and Creep Resistance
A heating element must be strong enough to support itself without deforming at high temperatures. This property, known as creep resistance, prevents the element from sagging, stretching, or breaking under its own weight over thousands of hours of operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element involves balancing competing factors. Being aware of these trade-offs is essential for making a practical, cost-effective decision.
Performance vs. Cost
High-performance materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments are invariably more expensive. You must weigh the need for superior durability and performance against the project's budget.
Power Density vs. Element Lifespan
Operating an element at its maximum rated wattage (high power density) provides more heat but also puts more stress on the material. This significantly shortens its operational lifespan. For applications requiring long-term reliability, it is often wise to use a slightly larger or more capable element run below its maximum limit.
Supplier Expertise and Customization
A low-cost, off-the-shelf part may seem appealing, but a knowledgeable supplier can be a valuable partner. A good manufacturer can provide technical guidance and customized solutions tailored to your specific voltage, wattage, and dimensional needs, ultimately improving efficiency and reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Align your selection criteria with your single most important objective to simplify your decision.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature: Prioritize the element's material composition, ensuring its melting point and oxidation resistance are well above your target operating temperature.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Match the element's wattage precisely to your heating requirements and choose a physical design that maximizes heat transfer to your target.
- If your primary focus is longevity and reliability: Select for superior thermal shock resistance, creep resistance, and chemical durability, even if it entails a higher upfront cost.
- If your primary focus is process stability and safety: Choose an element with a low temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) for stable output or a PTC element for inherent self-regulating properties.
By systematically evaluating your application against these technical factors, you can confidently select an element that delivers reliable and efficient performance.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature Range | Material melting point, stability, and suitability for high temperatures |
| Electrical Properties | Resistance, wattage, temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) for efficiency |
| Physical Design | Shape, size, surface area for heat transfer and fit in assembly |
| Durability Metrics | Thermal shock resistance, oxidation/corrosion resistance, mechanical strength |
| Trade-offs | Performance vs. cost, power density vs. lifespan, supplier customization |
Need a custom heating solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for improved efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















