The effectiveness of degassing in vacuum annealing hinges on a precise interplay of four key parameters. These are the process temperature, the level of vacuum achieved, the duration of the operation, and the inherent physical and chemical properties of the material and the gases dissolved within it. Properly controlling these variables is the difference between a successful purification and a failed attempt.
The core challenge of degassing is not just applying heat and vacuum. It is about strategically using temperature to energize trapped gas atoms and using a high vacuum to create a powerful pressure gradient that forces them out of the material.
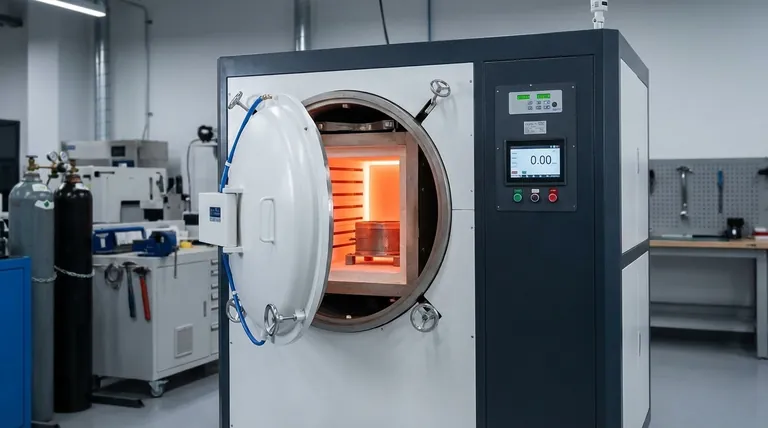

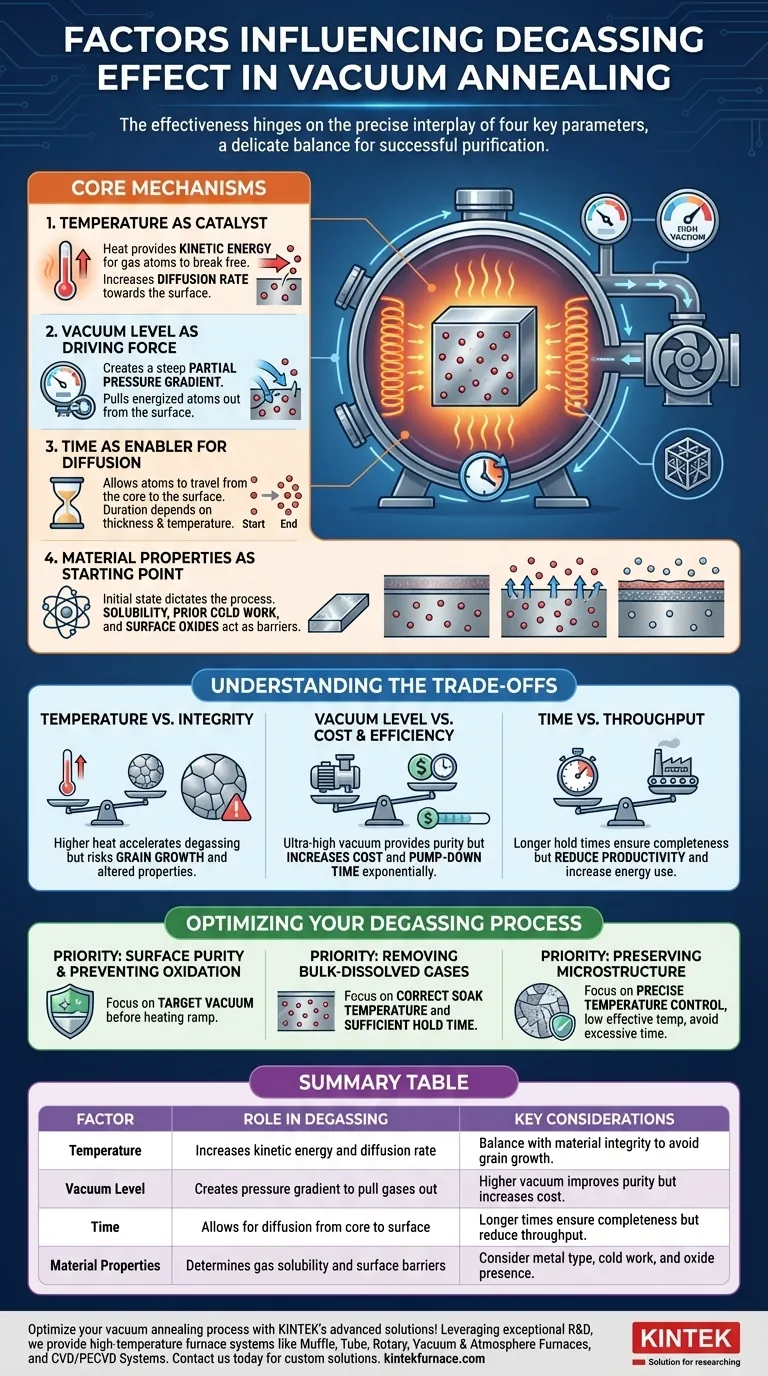
The Core Mechanisms of Degassing
To control the outcome, you must first understand the role each factor plays in the physical process of removing trapped gases from a solid material.
Temperature as the Catalyst
Heat provides the necessary kinetic energy for gas atoms (like hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen) to break free from the metallic lattice where they are trapped.
Higher temperatures also dramatically increase the diffusion rate of these atoms, allowing them to move more freely through the material's structure toward the surface.
Vacuum Level as the Driving Force
A high vacuum significantly lowers the pressure in the annealing chamber. This creates a steep partial pressure gradient between the material's interior (high concentration of gas) and the surrounding environment (low concentration of gas).
This pressure difference is the fundamental driving force that pulls the energized gas atoms out once they reach the material's surface, where they are then removed by the vacuum pumps.
Time as the Enabler for Diffusion
Degassing is not instantaneous. It requires sufficient time for the gas atoms to travel from the core of the component to its surface.
The required duration depends directly on the material's thickness, its temperature, and the specific gas being removed. Thicker parts or lower temperatures demand longer hold times to achieve complete degassing.
Material Properties as the Starting Point
The initial state of your material dictates the entire process. Factors like the type of metal, prior cold work, and the presence of alloys determine the solubility of different gases.
Furthermore, stable metal oxides on the surface can act as a barrier, preventing gas from escaping. A key function of the vacuum is to prevent new oxides from forming during the heating process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a vacuum annealing cycle is an exercise in balancing competing factors. Pushing one variable to its extreme often has negative consequences for another.
Temperature vs. Material Integrity
While higher temperatures accelerate degassing, excessive heat can be destructive. It can cause unwanted grain growth, which alters mechanical properties, or lead to undesirable phase changes in the alloy. The goal is to find a temperature high enough for diffusion but low enough to preserve the desired microstructure.
Vacuum Level vs. Cost and Efficiency
Achieving an ultra-high vacuum (UHV) provides the cleanest environment but comes at a significant cost in both equipment and time. The required pump-down time increases exponentially as you target higher vacuums. You must balance the need for surface purity against operational costs and throughput.
Time vs. Throughput
A longer hold time ensures more complete gas removal, especially from the core of thick components. However, every extra minute spent in the furnace reduces overall productivity and increases energy consumption. The cycle time must be long enough to meet quality standards but short enough to remain economically viable.
Optimizing Your Degassing Process
Your specific goal will determine which process variable you should prioritize.
- If your primary focus is surface purity and preventing oxidation: Prioritize achieving the target vacuum level before you begin ramping up the furnace temperature.
- If your primary focus is removing bulk-dissolved gases (like hydrogen): Prioritize achieving the correct soak temperature and allowing for sufficient hold time to enable full diffusion.
- If your primary focus is preserving a specific microstructure: Prioritize precise temperature control, using the lowest effective temperature and avoiding excessively long hold times.
By mastering these variables, you transform vacuum annealing from a simple heating process into a precise tool for material purification.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role in Degassing | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Increases kinetic energy and diffusion rate of gases | Balance with material integrity to avoid grain growth |
| Vacuum Level | Creates pressure gradient to pull gases out | Higher vacuum improves purity but increases cost |
| Time | Allows for diffusion from core to surface | Longer times ensure completeness but reduce throughput |
| Material Properties | Determines gas solubility and surface barriers | Consider metal type, cold work, and oxide presence |
Optimize your vacuum annealing process with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing degassing efficiency and material purity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements and boost your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















