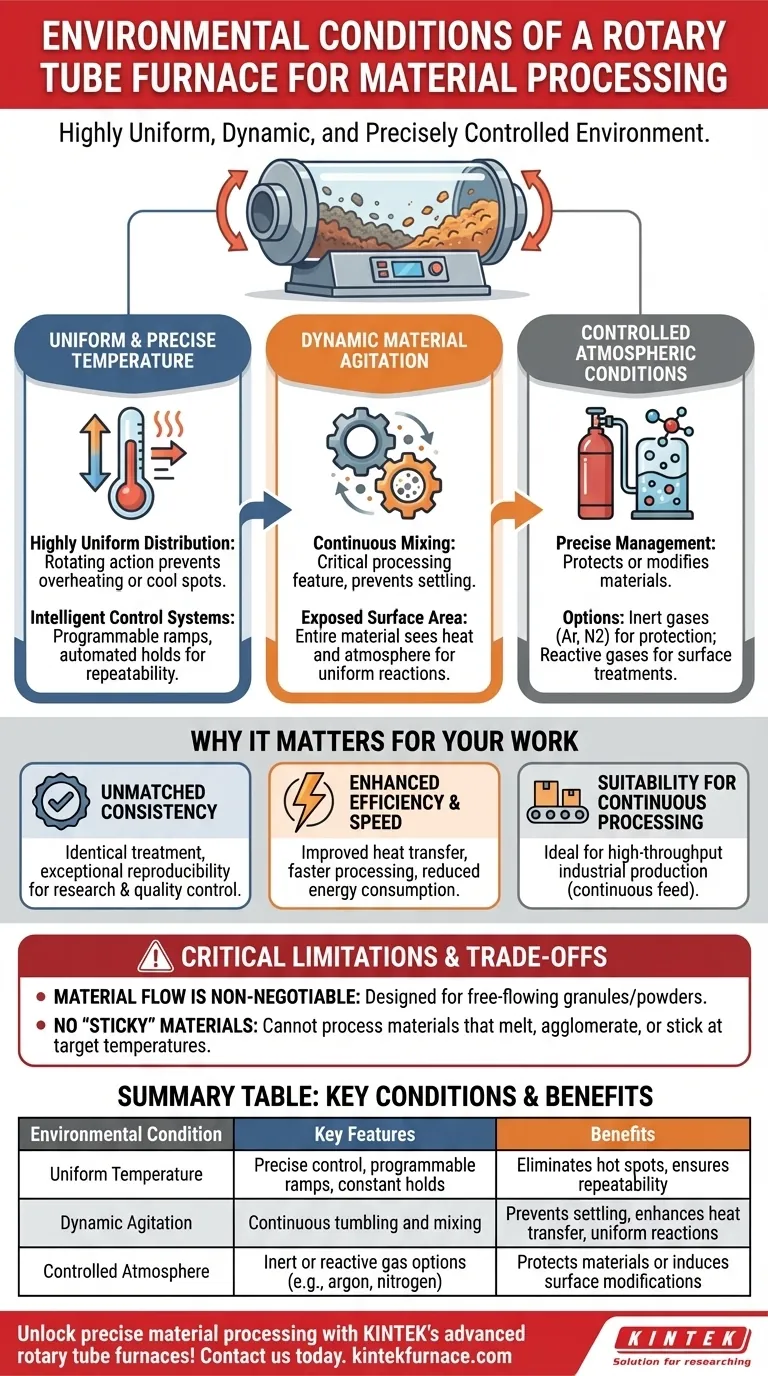
At its core, a rotary tube furnace provides a highly uniform, dynamic, and precisely controlled environment for processing materials. This environment is primarily defined by its exceptional temperature stability and its ability to regulate the internal atmosphere, all while continuously agitating the material.
The unique value of a rotary tube furnace comes from its rotation. This constant tumbling action ensures every particle of the material is exposed to the same temperature and atmospheric conditions, eliminating inconsistencies and hot spots common in static furnaces.
The Pillars of the Processing Environment
To understand if this furnace is right for your work, you must grasp the three key environmental conditions it creates and controls. These factors work in tandem to deliver consistent results.
Uniform and Precise Temperature
The primary condition is highly uniform temperature distribution. The rotating action constantly tumbles the material, preventing any single part of the sample from overheating or remaining too cool.
This is coupled with intelligent temperature control systems. These systems allow for high-precision regulation, programmable heating ramps, and automated constant temperature holds, ensuring your process is repeatable.
Dynamic Material Agitation
Unlike a static furnace where materials can settle or sinter together, a rotary furnace provides continuous mixing. This agitation is not just a side effect; it's a critical processing feature.
This constant movement guarantees that the entire surface area of the material is exposed to the heat and the furnace atmosphere. It prevents settling and segregation of particles, which is vital for achieving uniform reactions and treatments.
Controlled Atmospheric Conditions
The furnace atmosphere is a crucial variable that can be precisely managed. You can create specific conditions to achieve different outcomes.
This allows you to either protect the material from unwanted reactions, such as oxidation, by using an inert gas like argon or nitrogen. Alternatively, you can introduce reactive gases to induce specific surface modifications like carburizing or nitriding.
Why This Environment Matters for Your Work
The controlled environment of a rotary tube furnace directly translates into significant advantages for material synthesis and treatment.
Unmatched Process Consistency
Because every particle is treated identically, the furnace delivers exceptional consistency and reproducibility. This is critical for scientific research where results must be validated and for industrial production where quality control is paramount.
Enhanced Efficiency and Speed
The tumbling action dramatically improves heat transfer efficiency. By constantly exposing new surfaces to the heat source, materials reach the target temperature faster, leading to shorter processing times and reduced energy consumption.
Suitability for Continuous Processing
The design of a rotary tube furnace is inherently suited for continuous or semi-continuous operation. Granular or powdered materials can be fed into one end and collected at the other, making it an ideal choice for high-throughput production environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a rotary tube furnace is not a universal solution. Its primary limitations are mechanical and material-dependent.
Material Flow is Non-Negotiable
The single most important limitation is the type of material you can process. The furnace is designed exclusively for granular or particulate materials that can flow freely when hot. Examples include powders, small pellets, and grains of metals, ceramics, or carbon.
The Problem with "Sticky" Materials
You cannot use a rotary tube furnace for materials that melt, agglomerate, or become sticky at your target processing temperature. Doing so will cause the material to clump together, coat the furnace walls, and completely halt the uniform tumbling action, destroying the process.
Mechanical Complexity
Compared to a simple static tube or box furnace, a rotary furnace has more moving parts, including the rotation mechanism and seals. While modern designs are durable, this added complexity can introduce potential maintenance considerations over the long term.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching your material and process goals to the equipment's core capabilities.
- If your primary focus is uniform treatment of powders or granules: A rotary tube furnace is the superior choice for preventing hot spots and ensuring every particle is processed identically.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput, continuous production: The design of a rotary furnace is ideal for feeding material through for efficient, ongoing industrial processing.
- If your primary focus is treating solid objects or materials that become sticky: A static box or tube furnace is the correct and necessary tool for your application.
By understanding its unique environmental controls and limitations, you can leverage the rotary tube furnace to achieve exceptionally consistent and efficient material processing results.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Condition | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Uniform Temperature | Precise control, programmable ramps, constant holds | Eliminates hot spots, ensures repeatability |
| Dynamic Agitation | Continuous tumbling and mixing | Prevents settling, enhances heat transfer, uniform reactions |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Inert or reactive gas options (e.g., argon, nitrogen) | Protects materials or induces surface modifications |
Unlock precise material processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve consistent results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the role of rotary tube furnaces in the energy sector? Boost Efficiency in Biomass and Battery Material Processing
- What are the advantages of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Material Processing
- In what environments are rotary tube furnaces considered indispensable? Essential for Uniform Thermal Processing
- What level of process control do rotary tube furnaces provide? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing for Uniform Results
- What optional features enhance the processing capabilities of rotary tube furnaces? Boost Efficiency with Advanced Customizations



















