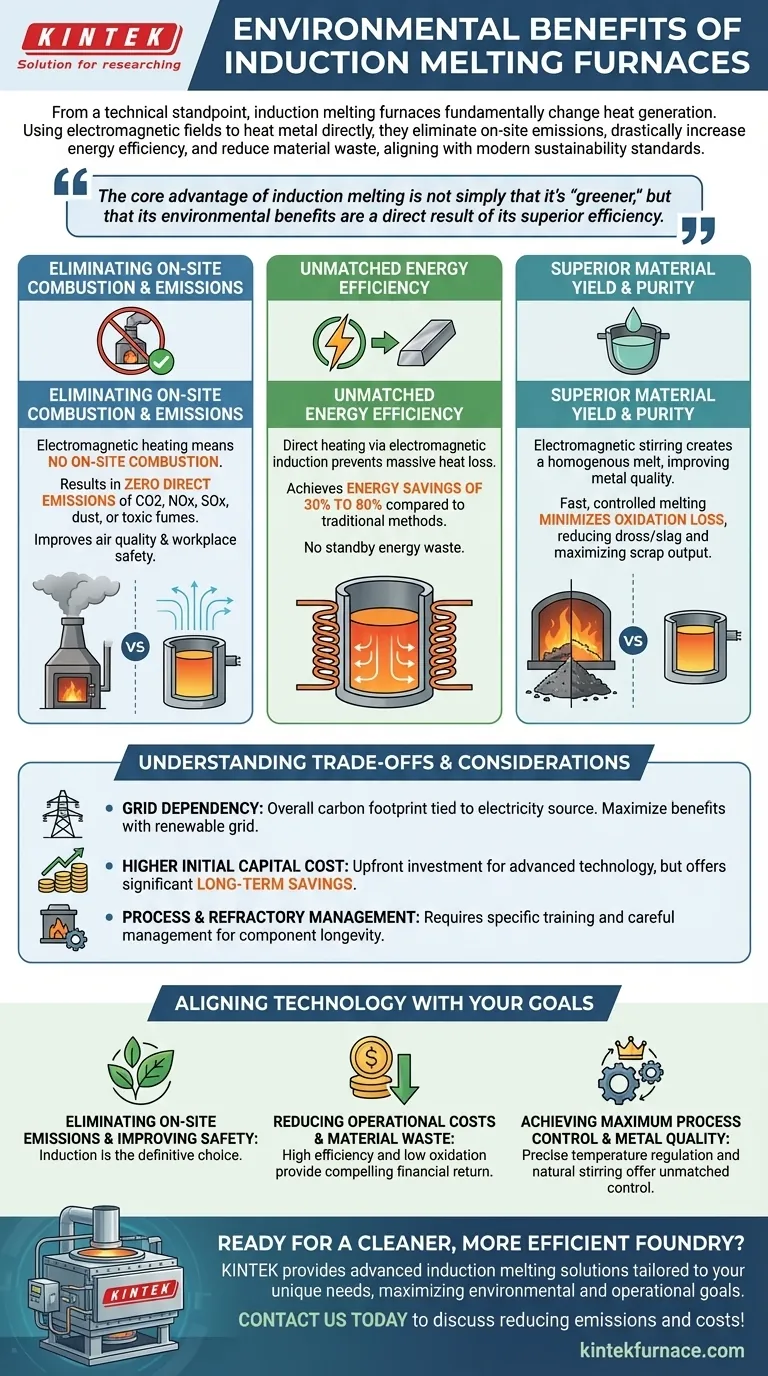
From a technical standpoint, induction melting furnaces provide their primary environmental benefits by fundamentally changing how heat is generated. Unlike traditional fuel-fired furnaces that rely on combustion, induction uses electromagnetic fields to heat the metal directly, eliminating on-site emissions, drastically increasing energy efficiency, and reducing material waste. This clean, precise method aligns with modern sustainability standards while simultaneously improving operational performance.
The core advantage of induction melting is not simply that it's "greener," but that its environmental benefits are a direct result of its superior efficiency. By eliminating combustion and heating only the target material, it inherently consumes less energy, produces less waste, and creates a safer work environment.

The Core Principles of Environmental Performance
The environmental case for induction technology is built on three foundational pillars: the elimination of combustion, superior energy conversion, and a significant reduction in material loss.
Eliminating On-Site Combustion and Emissions
Traditional furnaces burn fossil fuels (like coke, oil, or natural gas) to generate heat, releasing greenhouse gases and pollutants directly into the atmosphere.
Induction furnaces are powered by electricity. The heating process is electromagnetic, meaning there is no on-site combustion. This results in zero direct emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), dust, or toxic fumes at the facility.
This not only helps meet stringent environmental regulations but also dramatically improves air quality and safety for employees on the foundry floor.
Unmatched Energy Efficiency
Energy consumption is a critical factor in both cost and environmental impact. Induction technology excels here by directly targeting the energy where it is needed.
The electromagnetic field induces an electric current within the metal itself, causing it to heat rapidly from the inside out. This avoids the massive heat loss seen in conventional furnaces, which must first heat the entire chamber and the crucible before transferring that heat to the charge.
This direct heating method, combined with the ability to power on and off instantly, results in energy savings of 30% to 80% compared to traditional methods. There is no energy wasted keeping the furnace at a standby temperature between melts.
Superior Material Yield and Purity
Waste in a foundry is not just discarded material; it represents lost energy, time, and resources.
The electromagnetic stirring action inherent to the induction process creates a homogenous, uniform melt, which improves the final metal quality. More importantly, the fast, controlled melting process minimizes oxidation loss, meaning less of your valuable metal turns into dross or slag.
By preserving more of the raw material, induction furnaces reduce the total amount of scrap waste generated and maximize the output from each charge, which is especially beneficial when melting and recycling scrap metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
No technology is without its specific context and limitations. An objective assessment requires acknowledging the trade-offs associated with induction melting.
The Grid Dependency Factor
While induction furnaces produce zero on-site emissions, their overall carbon footprint is tied to the source of their electricity. The environmental benefit is maximized when the facility is powered by a grid with a high percentage of renewable or low-carbon energy sources.
If the local grid relies heavily on fossil fuels like coal, the emissions are effectively outsourced from the foundry to the power plant, not entirely eliminated.
Higher Initial Capital Cost
Induction furnace systems often require a higher upfront capital investment compared to some conventional furnace types. The advanced power supplies (like IGBT systems) and copper coils represent a significant cost.
However, this must be evaluated from a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) perspective. The significant long-term savings from reduced energy consumption, lower material loss, and decreased maintenance often provide a strong return on the initial investment.
Process and Refractory Management
The intense, localized heating that makes induction so efficient also requires careful management of the refractory lining. Improper charging or temperature control can lead to localized hotspots and accelerated wear on the crucible.
Operators require specific training to manage the process effectively and ensure the longevity of the furnace components.
Aligning Technology with Your Environmental Goals
Choosing the right melting technology depends on prioritizing your organization's specific operational, financial, and environmental objectives.
- If your primary focus is eliminating on-site emissions and improving workplace safety: Induction is the definitive choice, as its combustion-free process completely removes localized air pollutants and significantly reduces ambient noise and heat.
- If your primary focus is reducing operational costs and material waste: The high energy efficiency and low oxidation loss of induction offer a compelling financial and environmental return on investment over the equipment's lifecycle.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum process control and metal quality: The precise temperature regulation and natural stirring action of induction furnaces provide an unmatched level of control for producing clean, homogenous alloys.
Ultimately, adopting induction melting is a strategic investment in a more efficient, precise, and sustainable operational future.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Benefit | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Zero On-Site Emissions | Eliminates direct CO2, NOx, SOx, and toxic fume release. |
| High Energy Efficiency | Saves 30-80% energy by directly heating metal, not the chamber. |
| Superior Material Yield | Reduces oxidation loss and waste, maximizing output from scrap. |
Ready to invest in a cleaner, more efficient foundry? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced induction melting solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our expertise in high-temperature furnace technology ensures you get a system that maximizes your environmental and operational goals. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you reduce emissions and costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity



















