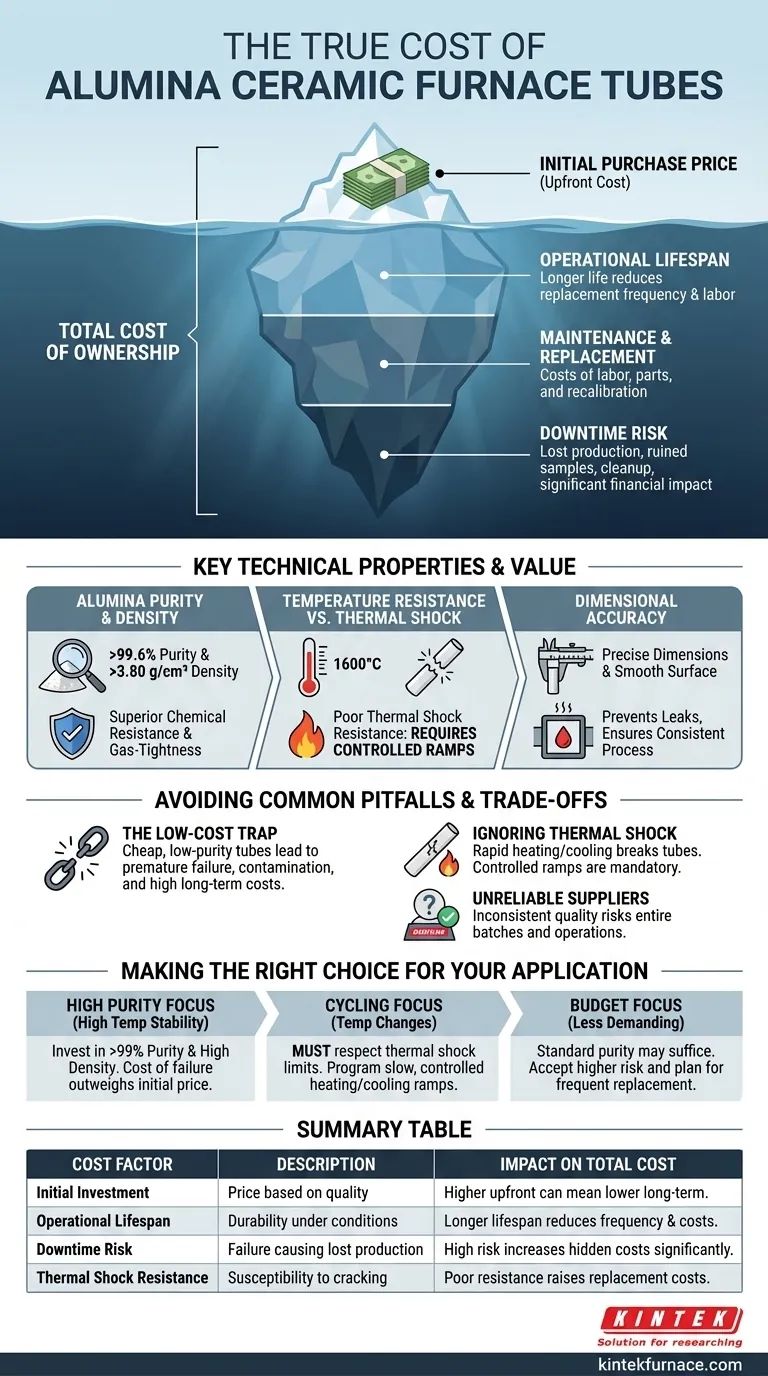
Considering the cost of an alumina furnace tube requires looking far beyond the initial purchase price. The true cost is a combination of the upfront investment, the tube's expected operational lifespan, potential maintenance requirements, and the significant hidden cost of process downtime should the tube fail prematurely.
The most critical mistake is equating "low price" with "low cost." The total cost of ownership is the only metric that matters, where the technical specifications of the tube directly determine its long-term value and protect you from expensive failures.

Beyond the Price Tag: Unpacking Total Cost of Ownership
To make a sound financial decision, you must analyze how the tube's quality impacts your entire operation over time. The initial price is often the smallest part of the equation.
The Initial Investment: What Are You Paying For?
The sticker price of an alumina tube is directly linked to its material quality and manufacturing precision.
Higher costs are associated with higher alumina purity (often above 99.6%), greater material density, and tighter dimensional tolerances. These attributes require more refined raw materials and advanced manufacturing processes, but they are what deliver superior performance.
Operational Lifespan and Durability
A more expensive, high-purity tube often results in a lower long-term cost simply because it lasts longer.
Its superior resistance to high temperatures and chemical corrosion means it can withstand demanding process conditions without degrading. This reduces the frequency of replacements and the associated labor costs.
The Hidden Cost of Downtime
This is often the most significant and overlooked expense. A catastrophic tube failure mid-process can be incredibly costly.
Costs here include not just the replacement tube but also lost production time, ruined product or research samples, and the labor hours required for cleanup and re-calibration of your furnace system.
Key Technical Properties That Drive Long-Term Cost
The performance characteristics of the tube are what ultimately determine its total cost of ownership. Understanding this link is crucial for making a smart investment.
Alumina Purity and Density
Specifications like >99.6% alumina content and a bulk density of >3.80 g/cm² are indicators of high quality.
High purity ensures excellent chemical inertness, preventing the tube from reacting with your process atmosphere or samples. High density contributes to better mechanical strength and gas-tightness, preventing leaks that could compromise your results.
Temperature Resistance vs. Thermal Shock
Alumina offers exceptional performance at continuous high temperatures, often up to 1600°C.
However, it has notoriously poor thermal shock resistance. This means rapid heating or cooling will cause it to crack. A tube failure caused by thermal shock leads to immediate replacement costs and significant downtime.
Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Finish
A tube with precise dimensions ensures a proper seal within your furnace system. Poorly fitting components can lead to atmosphere leaks, energy loss, and inconsistent process conditions.
A smooth internal surface finish is easier to clean and less likely to trap contaminants, which is critical for high-purity applications where even trace impurities can ruin a batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Choosing the wrong tube for your application is the most common path to escalating costs.
The Low-Cost Tube Trap
Purchasing a cheap, low-purity alumina tube for a demanding, high-temperature application is a classic mistake. While it saves money upfront, it almost guarantees premature failure, process contamination, and ultimately higher costs through frequent replacement and lost production.
Ignoring Thermal Shock Limitations
Many users break tubes by attempting to heat or cool their furnace too quickly to save time. This operational error directly negates the high-temperature benefits of alumina and turns a durable component into a fragile, disposable one. Controlled temperature ramps are not optional; they are a core operational requirement.
Overlooking Supplier Reliability
Inconsistent quality from a less reputable supplier is a hidden risk. A single bad tube from an unreliable batch can disrupt your work for days, invalidating research or ruining valuable product. A trustworthy supplier delivers predictable and repeatable quality, which is essential for stable operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the most cost-effective tube, align the material specifications with your specific operational demands.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability and process purity: Invest in a high-purity (>99%), high-density tube, as the cost of contamination or failure far outweighs the initial price difference.
- If your primary focus is running cycles with significant temperature changes: You must respect alumina's poor thermal shock resistance by programming slow, controlled heating and cooling ramps into your process.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront capital for a less demanding, lower-temperature process: A standard-purity tube may suffice, but you must accept the higher risk of a shorter lifespan and plan for more frequent replacement.
Ultimately, a well-informed decision balances initial cost against the predictable performance and long-term reliability your process requires.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Description | Impact on Total Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Price based on purity, density, and manufacturing precision | Higher upfront cost can lead to lower long-term expenses |
| Operational Lifespan | Durability under high temperatures and corrosion | Longer lifespan reduces replacement frequency and costs |
| Downtime Risk | Potential for failure causing lost production and cleanup | High risk increases hidden costs significantly |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Susceptibility to cracking from rapid temperature changes | Poor resistance raises replacement and downtime costs |
Ready to optimize your furnace tube investment? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Don't let hidden costs derail your projects—contact us today to discuss how our reliable alumina tubes can enhance your process efficiency and reduce total cost of ownership!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















