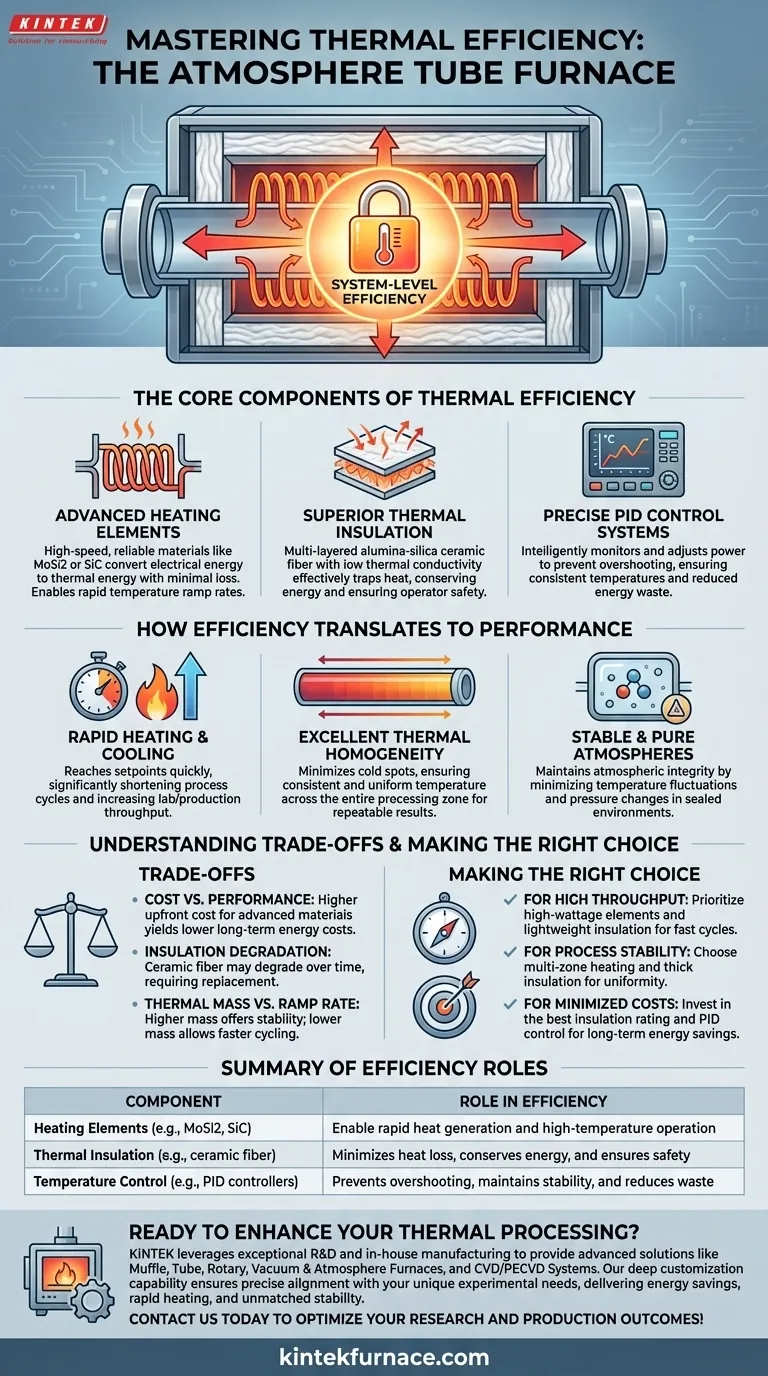
The high heating efficiency of an atmosphere tube furnace is the direct result of a system-level design that combines advanced heating technology with high-performance thermal insulation. These two elements work together to generate heat quickly, deliver it precisely to the workpiece, and, most importantly, prevent it from escaping. This synergy enables rapid temperature ramp rates and exceptional stability while minimizing wasted energy.
True efficiency in a tube furnace is not just about reducing energy costs; it is the core enabler of the precise, repeatable thermal processing required for advanced materials research and manufacturing. It achieves this by delivering heat exactly where it's needed and keeping it there.
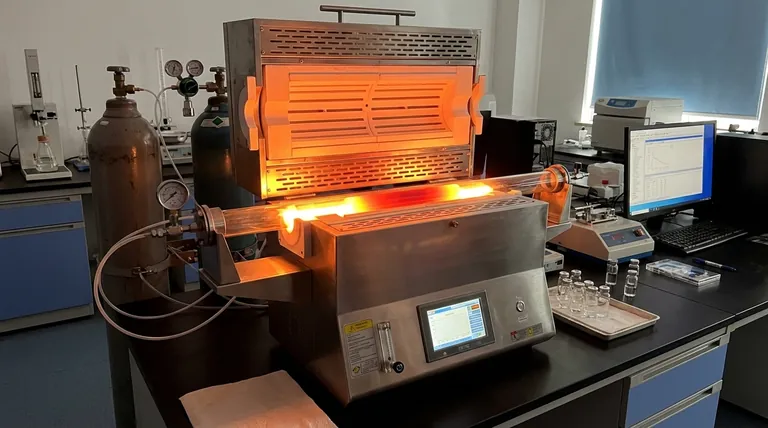

The Core Components of Thermal Efficiency
The remarkable efficiency of a modern atmosphere tube furnace isn't accidental. It stems from the careful selection and integration of several key components, each playing a critical role in managing thermal energy.
Advanced Heating Element Technology
Most high-performance tube furnaces utilize electric resistance heating. The material used for these heating elements is crucial for both the speed and ceiling of temperature ranges.
Common materials like Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) or Silicon Carbide (SiC) are chosen for their ability to heat up extremely fast and operate reliably at very high temperatures. They efficiently convert electrical energy into thermal energy with minimal loss.
Superior Thermal Insulation
The most significant factor in preventing heat loss is the furnace's insulation. Modern furnaces use multi-layered, high-purity alumina-silica ceramic fiber insulation.
This material has exceptionally low thermal conductivity, meaning it is extremely effective at trapping heat within the furnace chamber. This not only conserves energy but also keeps the external casing of the furnace cool to the touch, ensuring operator safety.
Precise Temperature Control Systems
Efficiency is wasted without control. Furnaces use sophisticated PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers coupled with temperature sensors (thermocouples).
A PID controller continuously monitors the chamber temperature and intelligently adjusts the power sent to the heating elements. This prevents the furnace from overshooting its target temperature, a common source of both energy waste and inconsistent experimental results.
How Efficiency Translates to Performance
High thermal efficiency is not just an abstract benefit. It directly produces the tangible performance characteristics that make these furnaces essential tools for science and industry.
Rapid Heating and Cooling
Because heat is generated quickly by the elements and retained effectively by the insulation, the furnace can reach its setpoint temperature in a very short amount of time. This significantly shortens process cycles and increases laboratory or production throughput.
Excellent Thermal Homogeneity
A highly efficient, well-insulated chamber minimizes "cold spots." This results in excellent thermal homogeneity, meaning the temperature is consistent and uniform across the entire processing zone of the tube. This is critical for ensuring a sample or workpiece is treated evenly, leading to reliable and repeatable outcomes.
Stable and Pure Atmospheres
Atmosphere tube furnaces are designed to control the gaseous environment around a sample. A well-sealed and thermally stable chamber is essential for maintaining the purity of the inert or reactive gas inside. Inefficient designs with temperature fluctuations can cause pressure changes that compromise atmospheric integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly desirable, achieving maximum efficiency involves balancing several design and operational factors.
Cost vs. Performance
Higher-quality insulation materials and more advanced heating elements significantly increase the initial purchase price of a furnace. This upfront investment, however, is often returned through lower long-term energy costs and the value of higher-quality, repeatable results.
Insulation Degradation
Over many heating and cooling cycles, ceramic fiber insulation can slowly degrade, becoming more brittle and less effective. This gradual reduction in efficiency is a long-term operational cost, as the insulation may eventually require replacement to restore peak performance.
Thermal Mass vs. Ramp Rate
A furnace with extremely thick, dense insulation has a high thermal mass. It will be exceptionally stable at a set temperature and very energy-efficient during long processes. However, it may heat up and, particularly, cool down more slowly. The design is always a trade-off between stability and the speed of thermal cycling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application will determine which aspects of efficiency are most critical for your success.
- If your primary focus is high throughput: Prioritize a furnace with high-wattage heating elements and efficient, lightweight insulation to achieve the fastest possible heating and cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is process stability and uniformity: Look for furnaces with multi-zone heating capabilities and thick, high-density ceramic fiber insulation to ensure exceptional thermal homogeneity for sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational costs: Invest in a furnace with the best possible insulation rating and a modern PID controller to reduce long-term energy consumption, even if the initial cost is higher.
Understanding these principles of thermal efficiency empowers you to select and operate your furnace for optimal results and long-term value.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Heating Elements (e.g., MoSi2, SiC) | Enable rapid heat generation and high-temperature operation |
| Thermal Insulation (e.g., ceramic fiber) | Minimizes heat loss, conserves energy, and ensures safety |
| Temperature Control (e.g., PID controllers) | Prevents overshooting, maintains stability, and reduces waste |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with a high-efficiency furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering energy savings, rapid heating, and unmatched stability. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your research and production outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















