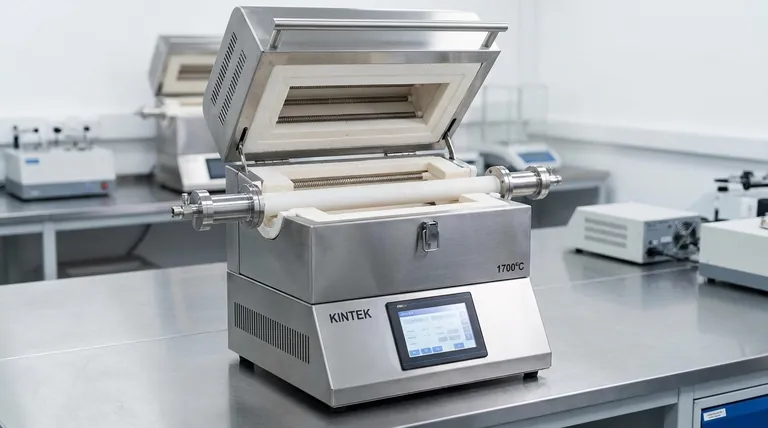
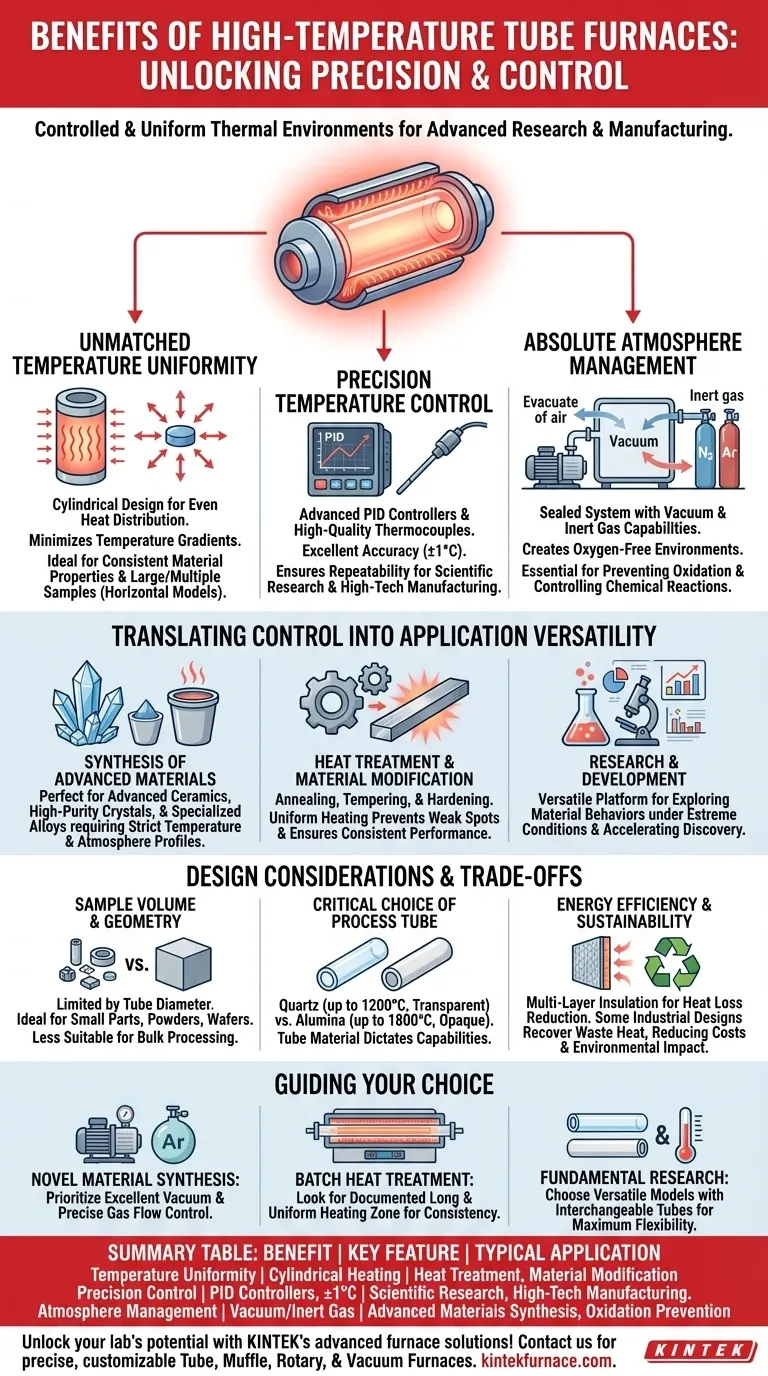
At their core, high-temperature tube furnaces provide an exceptionally controlled and uniform thermal environment. Their primary benefits stem from this principle, offering unparalleled precision in temperature accuracy, uniform heat distribution across a sample, and the ability to strictly manage the atmospheric conditions during processing.
The true value of a high-temperature tube furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to create a stable, repeatable, and contaminant-free environment. This control is the critical factor that enables advanced material synthesis, analysis, and treatment.

The Foundation: A Controlled Processing Environment
The defining advantage of a tube furnace is its ability to isolate a sample from external variables. This is achieved through a combination of its physical design and sophisticated control systems.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical geometry of a tube furnace is fundamental to its performance. By arranging heating elements around the process tube, it ensures that heat radiates evenly toward the center from all directions.
This design minimizes temperature gradients across the sample, a critical factor for achieving consistent material properties. Horizontal models, in particular, often feature extended uniform heating zones ideal for processing larger or multiple samples simultaneously.
Precision Temperature Control
Modern tube furnaces utilize advanced PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers and high-quality thermocouples to regulate temperature with exceptional accuracy, often within ±1°C of the setpoint.
This level of precision is non-negotiable for scientific research and high-tech manufacturing, where even minor temperature deviations can compromise experimental results or product quality. It ensures that processes are not just accurate, but also highly repeatable.
Absolute Atmosphere Management
Many advanced material processes are highly sensitive to oxygen or other atmospheric contaminants. Tube furnaces excel at creating a controlled atmosphere.
They can be sealed and equipped with vacuum pumps to evacuate ambient air. Subsequently, a specific, inert gas like nitrogen or argon can be introduced, creating a pure, oxygen-free environment essential for preventing oxidation and unwanted chemical reactions.
Translating Control into Application Versatility
The precise environmental control offered by tube furnaces makes them indispensable tools across a wide range of scientific and industrial fields.
Synthesis of Advanced Materials
The creation of novel materials like advanced ceramics, high-purity crystals, or specialized metal alloys often requires strict adherence to a specific temperature and atmosphere profile. The tube furnace provides the ideal environment for these synthesis and crystal growth processes.
Heat Treatment and Material Modification
Applications like annealing, tempering, and hardening are used to alter the microstructure and physical properties of materials. The uniform heating of a tube furnace ensures that the entire component receives the same treatment, preventing weak spots or inconsistent performance.
Research and Development
In R&D settings, tube furnaces serve as a versatile platform for exploring new material behaviors under extreme conditions. Researchers can systematically test how materials respond to different temperatures, atmospheres, and thermal cycles, accelerating the discovery process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Considerations
While powerful, a tube furnace is a specialized tool with specific considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Sample Volume and Geometry
By design, the processing volume of a tube furnace is limited by the diameter of the tube. This makes them ideal for smaller components, powders, or wafers but less suitable for bulk processing of large, irregularly shaped objects, where a box furnace might be a better fit.
The Critical Choice of Process Tube
The tube itself is a consumable component whose material dictates the furnace's capabilities.
- Quartz tubes are common for temperatures up to approximately 1200°C and allow for visual observation of the sample.
- Alumina tubes are required for higher temperatures (up to 1700-1800°C) but are opaque.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
High-quality tube furnaces are built with multi-layer, high-purity fiber insulation to minimize heat loss and improve energy efficiency. Some industrial designs are also engineered to recover and reuse waste heat or flue gas, reducing both operational costs and environmental impact.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your specific application should guide your priorities when evaluating a high-temperature tube furnace.
- If your primary focus is novel material synthesis: You must prioritize a system with excellent vacuum capabilities and precise gas flow control for atmosphere management.
- If your primary focus is batch heat treatment: Look for a horizontal furnace with a documented, long, and uniform heating zone to ensure process consistency across larger samples.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: A versatile model with interchangeable tube options and a wide temperature range will provide the greatest experimental flexibility.
Ultimately, selecting a high-temperature tube furnace is an investment in process control, experimental repeatability, and the certainty of your results.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Feature | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | Cylindrical heating for even distribution | Heat treatment, material modification |
| Precision Control | PID controllers, ±1°C accuracy | Scientific research, high-tech manufacturing |
| Atmosphere Management | Vacuum and inert gas capabilities | Synthesis of advanced materials, oxidation prevention |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precise, customizable options like Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















