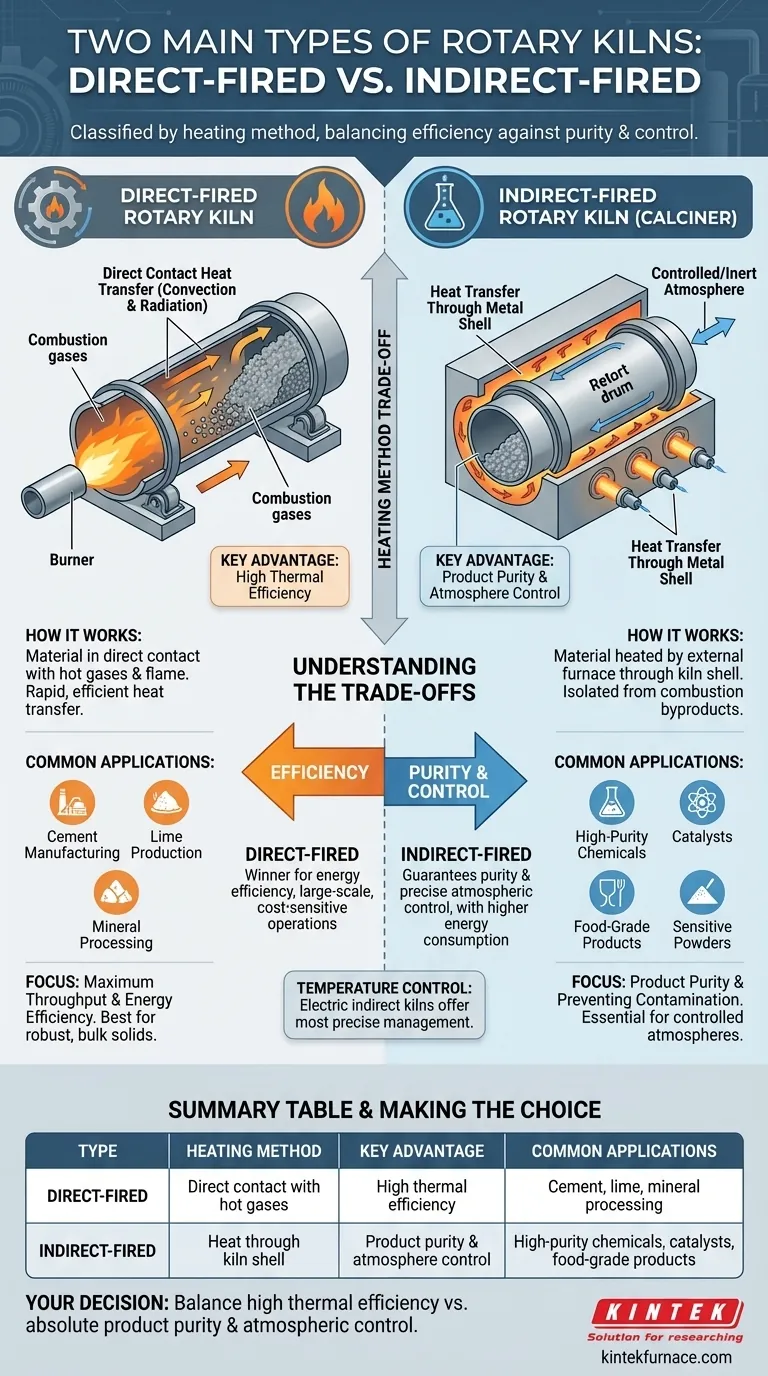
The two primary types of rotary kilns, classified by their heating method, are direct-fired and indirect-fired. In a direct-fired kiln, the material being processed is in direct contact with the hot gases and flame from the heat source. Conversely, an indirect-fired kiln heats the material by applying heat to the exterior of the rotating shell, with no contact between the material and the combustion byproducts.
The choice between a direct and indirect kiln is not about which is inherently better, but about a fundamental trade-off. Your decision must balance the need for high thermal efficiency against the requirement for absolute product purity and atmospheric control.

The Mechanics of Direct-Fired Kilns
A direct-fired kiln is designed for maximum heat transfer and energy efficiency. It is the workhorse for high-volume industrial processes where the material is robust.
How It Works
A burner firing fuel like natural gas or oil is positioned at one end of the rotating drum. The resulting hot combustion gases flow through the kiln, making direct contact with the cascading material inside, transferring heat through both convection and radiation.
Key Advantage: Thermal Efficiency
Because the heat source is in direct contact with the material, heat transfer is rapid and highly efficient. This design allows for very high processing temperatures and large throughputs, making it the most energy-efficient option for bulk solids.
Common Applications
Direct-fired kilns are standard in industries like cement manufacturing, lime production, and mineral processing. In these applications, the final product's quality is not compromised by exposure to the combustion gases.
The Mechanics of Indirect-Fired Kilns
An indirect-fired kiln, sometimes called a rotary calciner, prioritizes product purity and a controlled processing environment over raw thermal efficiency.
How It Works
The rotating drum (or "retort") containing the material is enclosed within a stationary furnace or surrounded by high-power electric heating elements. Heat is transferred through the metal shell of the retort to the material inside. The material never touches the flame or combustion byproducts.
Key Advantage: Atmosphere Control
This design perfectly isolates the processing material. It allows for a highly controlled or inert atmosphere inside the retort, which is critical for preventing unwanted reactions or contamination. This is impossible to achieve in a direct-fired system.
Common Applications
Indirect kilns are essential for processing high-purity chemicals, catalysts, food-grade products, and sensitive powders. They are also used for processes that require a specific reducing or oxidizing atmosphere that would be incompatible with combustion gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Efficiency vs. Purity
Choosing the correct kiln requires a clear understanding of your process goals and material sensitivities. The wrong choice can lead to an inefficient process or a contaminated product.
The Efficiency of Direct Firing
Direct-fired kilns are the clear winner for energy efficiency. The direct heat transfer minimizes energy loss, making them ideal for large-scale, cost-sensitive operations where product contamination from flue gas is not a concern.
The Purity of Indirect Firing
Indirect-fired kilns introduce a thermal barrier—the kiln shell—which makes heat transfer less efficient. This results in higher energy consumption per ton of product, which is the necessary price for guaranteeing product purity and precise atmospheric control.
Other Key Considerations
Temperature control is another factor. While both types can be controlled, electrically heated indirect kilns offer the most precise and responsive temperature management, which can be critical for materials with narrow processing windows.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your material's characteristics and your final product requirements are the only factors that matter when selecting a heating method.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput and energy efficiency: A direct-fired kiln is the superior choice, provided your material is not sensitive to combustion gases.
- If your primary focus is product purity and preventing contamination: An indirect-fired kiln is essential, as it isolates your material from the heat source.
- If your primary focus is running a specific chemical reaction in a controlled atmosphere: An indirect-fired kiln is your only viable option to manage the internal gas environment.
Ultimately, understanding this core distinction empowers you to select the right tool for your specific thermal processing goal.
Summary Table:
| Type | Heating Method | Key Advantage | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-Fired | Direct contact with hot gases | High thermal efficiency | Cement, lime, mineral processing |
| Indirect-Fired | Heat through kiln shell | Product purity and atmosphere control | High-purity chemicals, catalysts, food-grade products |
Struggling to choose the right rotary kiln for your lab's thermal processing needs? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, tailored for diverse laboratory requirements. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to ensure precise performance for your unique experiments—whether you prioritize efficiency, purity, or controlled atmospheres. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your process and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency



















