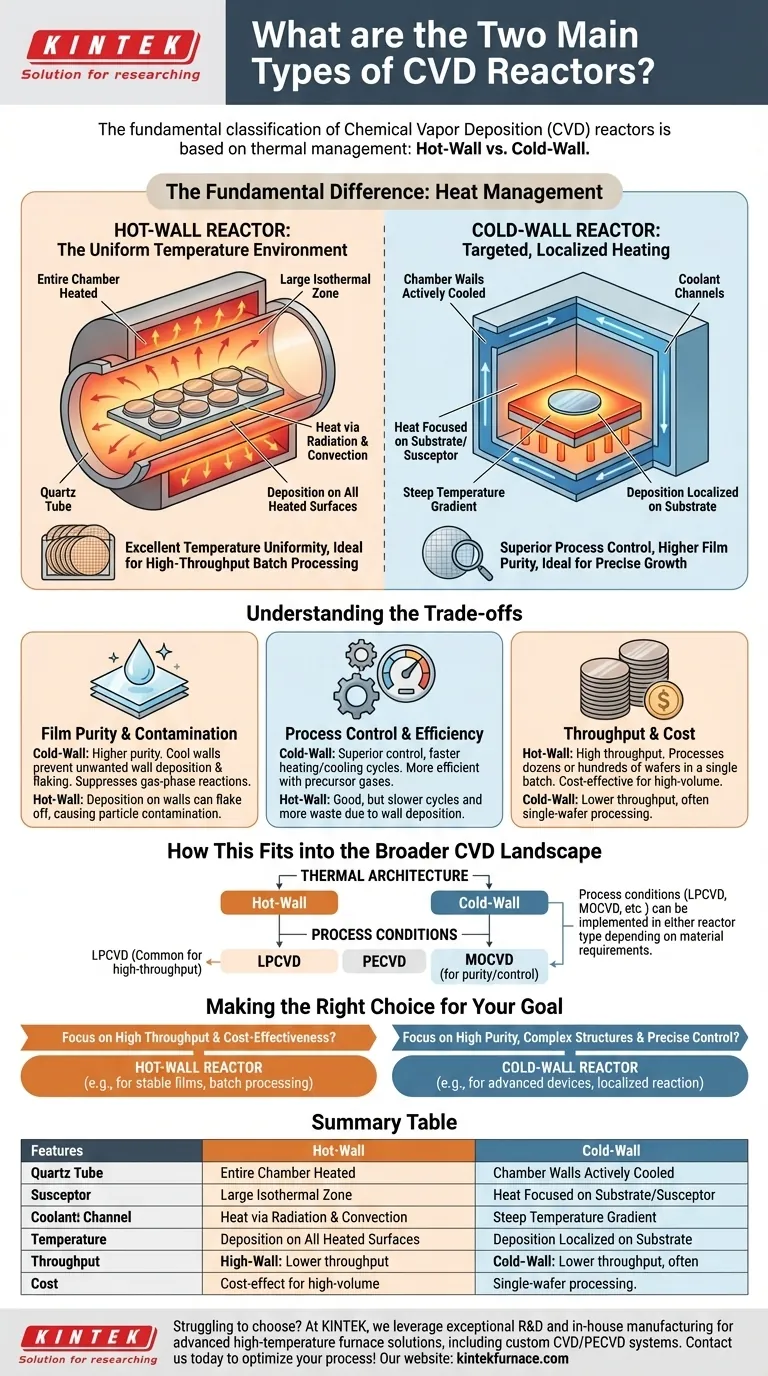
At their core, the two principal types of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) reactors are hot-wall reactors and cold-wall reactors. This fundamental classification is based on thermal management. A hot-wall reactor heats the entire chamber, including the substrates and the reactor walls, to a uniform temperature. In contrast, a cold-wall reactor selectively heats only the substrate while keeping the chamber walls actively cooled.
The choice between a hot-wall and cold-wall design is not merely a technical detail; it is a foundational decision that dictates process control, film purity, throughput, and operational cost, defining the reactor's entire purpose and application.
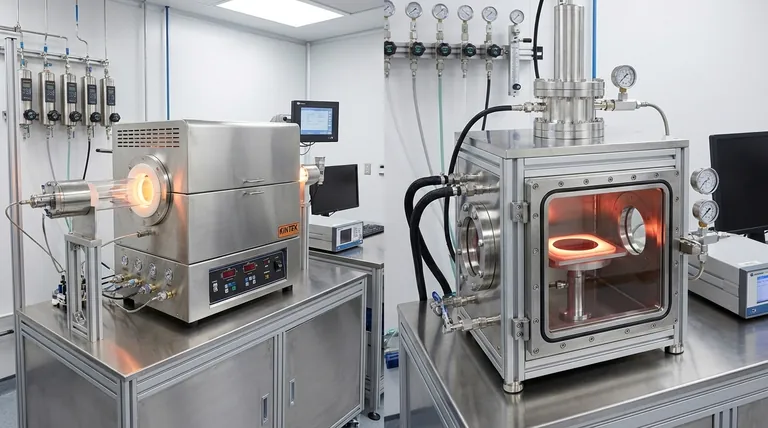

The Fundamental Difference: Heat Management
The way a CVD reactor manages heat is its most defining characteristic. This choice directly influences where and how the chemical reactions occur, which is the essence of the deposition process.
Hot-Wall Reactors: The Uniform Temperature Environment
In a hot-wall design, the entire reaction chamber, often a quartz tube inside a resistive furnace, is brought to the desired process temperature.
This creates a large, isothermal zone. Substrates placed within this zone are heated primarily by radiation and convection from the surrounding hot walls.
The primary advantage is excellent temperature uniformity across a large number of substrates, making it ideal for high-throughput batch processing.
Cold-Wall Reactors: Targeted, Localized Heating
A cold-wall reactor focuses heat energy exclusively on the substrate holder (the susceptor) and the substrates themselves.
The chamber walls are kept cool, often with circulating water. This creates a steep temperature gradient between the hot substrate and the cool surroundings.
This design localizes the chemical reaction directly on the substrate surface, which provides significant advantages in process control and film purity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is universally superior. The selection depends entirely on the goals of the deposition process, balancing throughput against precision.
Film Purity and Particle Contamination
Cold-wall reactors generally produce films with higher purity. By keeping the walls cool, they prevent unwanted deposition on the chamber interior.
In hot-wall systems, deposition occurs on all heated surfaces. This film can flake off over time, creating particles that contaminate the substrates.
Furthermore, the steep temperature gradient in a cold-wall system suppresses unwanted chemical reactions in the gas phase, leading to a cleaner deposition environment.
Process Control and Efficiency
Cold-wall systems offer superior process control. Since the reaction is confined to the hot substrate, chemists and engineers can more precisely manage film growth.
Heating and cooling cycles are also much faster because only the small thermal mass of the substrate and susceptor needs to change temperature.
This targeted heating also makes cold-wall reactors more efficient with precursor gases, as less material is wasted depositing on the chamber walls.
Throughput and Cost
Hot-wall reactors are the champions of high throughput. Their ability to process dozens or even hundreds of wafers in a single batch run makes them extremely cost-effective for established, high-volume manufacturing.
Classic examples include Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) furnaces for depositing polysilicon and silicon nitride films in the semiconductor industry.
While cold-wall systems typically process only one substrate at a time, their precision is non-negotiable for cutting-edge applications like fabricating high-efficiency LEDs or advanced transistors.
How This Fits into the Broader CVD Landscape
The hot-wall versus cold-wall distinction is a classification of thermal architecture. It is separate from, but related to, classifications based on process conditions like pressure or energy source.
Thermal Design vs. Process Type
Terms like LPCVD (Low-Pressure), PECVD (Plasma-Enhanced), and MOCVD (Metal-Organic) describe the conditions under which deposition occurs.
These process types can be implemented in either a hot-wall or cold-wall reactor, depending on the specific requirements of the material being deposited.
Common Configurations
A classic LPCVD system for depositing silicon nitride is almost always a hot-wall furnace to maximize throughput.
Conversely, an MOCVD reactor used to grow complex compound semiconductor layers for LEDs is typically a cold-wall design to achieve the necessary purity and layer-by-layer control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's priorities will dictate which reactor architecture is appropriate. The trade-off is almost always between processing volume and ultimate precision.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and cost-effectiveness for stable films: A hot-wall reactor design is the industry standard for batch processing applications.
- If your primary focus is high purity, complex material structures, and precise film control: A cold-wall reactor offers superior performance by localizing the chemical reaction to the substrate surface.
Understanding this core thermal design principle is the first step to mastering the link between CVD equipment and the quality of the final material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot-Wall Reactors | Cold-Wall Reactors |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Entire chamber heated uniformly | Only substrate heated, walls cooled |
| Temperature Uniformity | Excellent for batch processing | Localized, with steep gradients |
| Film Purity | Lower due to wall deposition | Higher, minimizes contamination |
| Process Control | Good for high throughput | Superior for precise growth |
| Throughput | High, ideal for batch runs | Lower, often single-wafer |
| Common Applications | LPCVD for semiconductors | MOCVD for LEDs, advanced devices |
Struggling to choose the right CVD reactor for your lab's needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you need high throughput with hot-wall designs or superior purity with cold-wall setups. Don't let equipment limitations hold back your research—contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your chemical vapor deposition processes and drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What methods are used to analyze and characterize graphene samples? Unlock Key Techniques for Accurate Material Analysis
- How does a CVD system ensure the quality of carbon layers? Achieving Nanometer Precision with KINTEK
- What environments does a PECVD system provide for silicon nanowires? Optimize Growth with Precise Thermal Control
- Why Use PECVD for Monolithic Integrated Chip Isolation Layers? Protect Your Thermal Budget with High-Quality SiO2
- How does a PECVD system contribute to (n)poly-Si layers? High-Throughput In-Situ Doping Explained



















