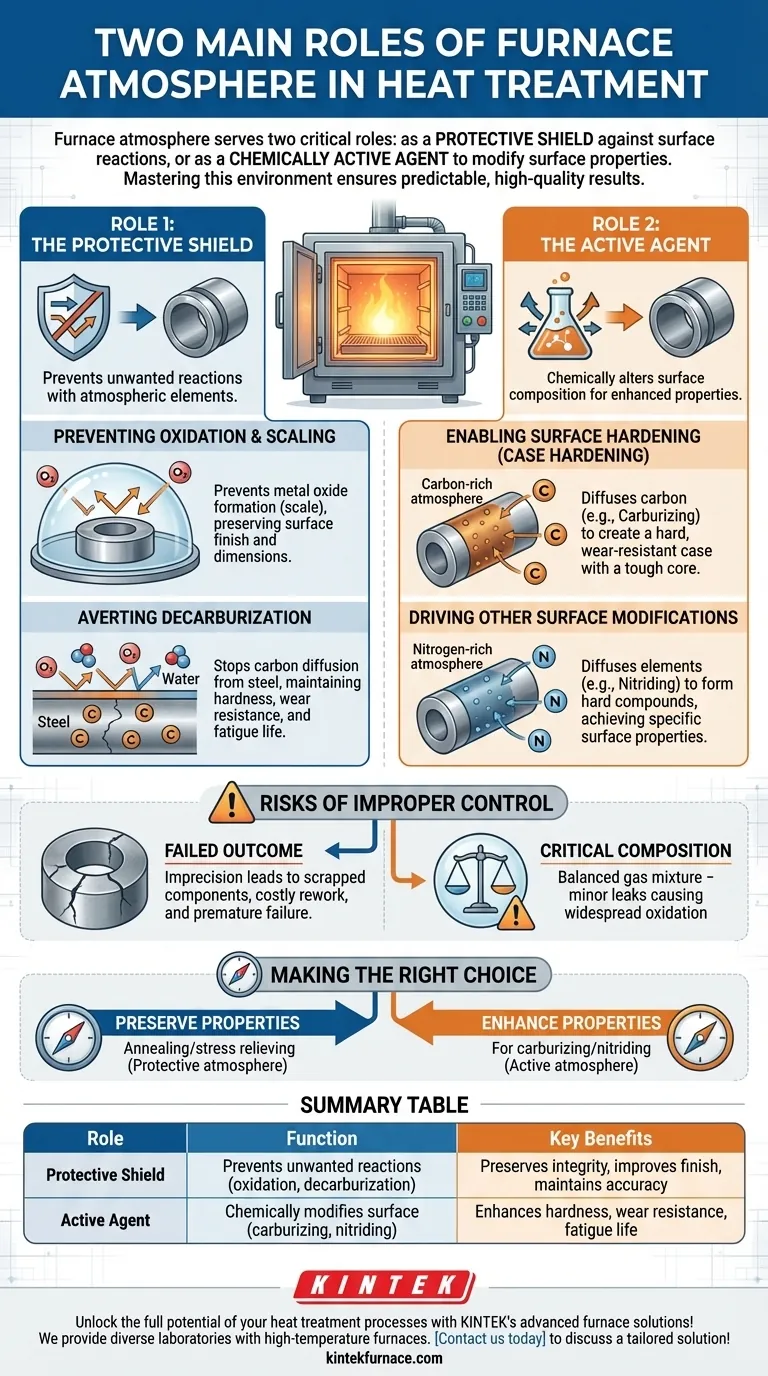
In heat treatment, the furnace atmosphere serves two distinct and critical roles. It acts either as a protective shield to prevent unwanted surface reactions like oxidation, or as a chemically active agent to intentionally modify the composition and properties of the part's surface through controlled reactions.
At its core, controlling the furnace atmosphere is about mastering the chemical environment at high temperatures. Whether protecting the material's integrity or actively enhancing it, the goal is to achieve predictable, high-quality results by preventing harmful reactions and enabling beneficial ones.
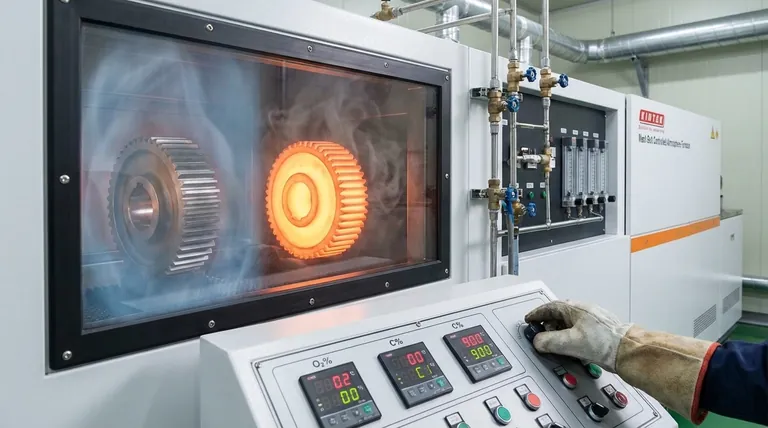

Role 1: The Protective Shield
The most fundamental role of a furnace atmosphere is to act as a barrier between the hot metal part and the surrounding air. At elevated temperatures, metals become highly reactive with atmospheric elements, especially oxygen.
Preventing Oxidation and Scaling
When heated, most metals will readily react with oxygen in the air. This reaction, oxidation, forms a layer of metallic oxide on the surface known as scale.
This scale is detrimental, causing discoloration, poor surface finish, and a loss of material that can compromise the part's dimensional accuracy. A protective atmosphere displaces the oxygen, preventing these reactions from occurring.
Averting Decarburization
For steel components, another significant risk is decarburization. This is the process where carbon atoms diffuse out of the steel's surface, typically reacting with oxygen or water vapor.
Losing surface carbon severely degrades the material's properties, reducing its hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue life. A properly controlled protective atmosphere prevents this carbon loss, ensuring the part maintains its engineered strength.
Role 2: The Active Agent
Beyond mere protection, the furnace atmosphere can be engineered to be chemically reactive. In this role, the atmosphere becomes a key ingredient in the heat treatment process itself, intentionally altering the chemistry of the part's surface.
Enabling Surface Hardening (Case Hardening)
The most common example of an active atmosphere is in carburizing. Here, a carbon-rich atmosphere (using gases like natural gas or propane) is introduced into the furnace.
At high temperatures, carbon from the atmosphere diffuses into the surface of a low-carbon steel part. This creates a "case"—a hard, wear-resistant outer layer—while the part's interior, or "core," remains softer and tougher.
Driving Other Surface Modifications
This same principle applies to other processes. In nitriding, a nitrogen-rich atmosphere (typically from ammonia) is used to diffuse nitrogen into the steel's surface, forming extremely hard nitride compounds.
The atmosphere acts as a carrier, delivering the specific elements needed to achieve a desired surface property that the base material does not possess on its own.
Understanding the Risks of Improper Control
The choice and control of the furnace atmosphere are not trivial details; they are central to the success of the entire heat treatment operation.
The Cost of Imprecision
An improperly controlled atmosphere leads directly to failed outcomes. Parts may emerge from the furnace with a soft surface when they should be hard, or become brittle when they should be tough.
This results in scrapped components, costly rework, and a fundamental failure to meet the engineering specifications, potentially leading to premature failure of the final product in service.
Atmosphere Composition is Critical
It is not enough to simply fill a furnace with "an atmosphere." The precise composition is crucial.
An atmosphere intended to be protective can become damaging if its chemistry is slightly off. For example, a supposedly inert atmosphere with a minor oxygen or moisture leak can cause widespread oxidation and ruin an entire batch of parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your process objective dictates the role the atmosphere must play.
- If your primary focus is preserving the existing properties of a part: You need a protective (inert or reducing) atmosphere to prevent oxidation and decarburization during processes like annealing or stress relieving.
- If your primary focus is enhancing surface properties like hardness and wear resistance: You need an active (chemically reactive) atmosphere for case hardening processes like carburizing or nitriding.
Ultimately, mastering the furnace atmosphere transforms heat treatment from a simple heating process into a precise engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Role | Function | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Protective Shield | Prevents unwanted surface reactions like oxidation and decarburization | Preserves material integrity, improves surface finish, maintains dimensional accuracy |
| Active Agent | Chemically modifies surface composition through processes like carburizing and nitriding | Enhances hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue life for superior performance |
Unlock the full potential of your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering reliable performance and enhanced efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for you!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab



















