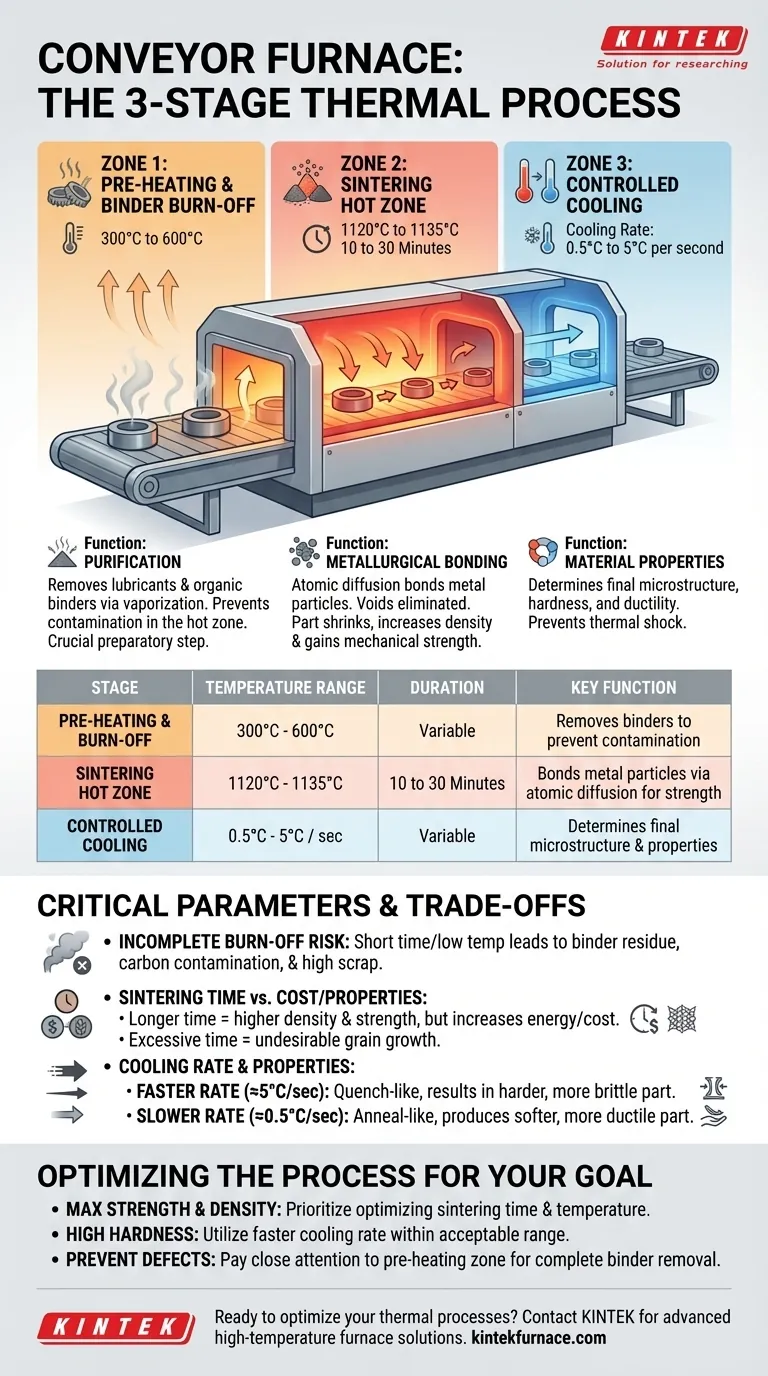
In a conveyor furnace, parts undergo a three-stage thermal process designed for sintering or brazing. The stages are a low-temperature pre-heating zone for purification, a high-temperature zone for metallurgical bonding, and a final zone for controlled cooling to achieve the desired material properties.
The journey through a conveyor furnace is not merely about heating and cooling. It is a precise, multi-zone thermal transformation that methodically turns compacted powder or assembled components into a single, robust, and functional part.
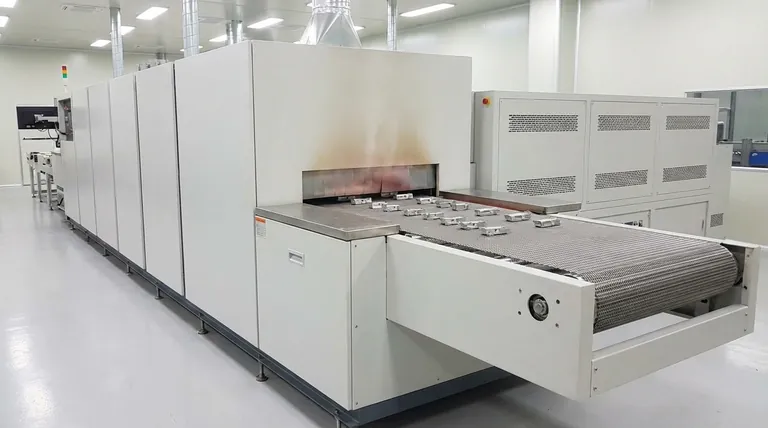

The Three-Zone Thermal Process Explained
A conveyor furnace operates by moving parts at a constant speed through distinct temperature zones. Each zone performs a critical function in the overall manufacturing process, most commonly for sintering powder metal parts.
Zone 1: Pre-heating and Binder Burn-Off (300°C to 600°C)
The first stage is a crucial preparatory step. Before parts can be sintered at high temperatures, any lubricants or organic binders used during the powder compaction phase must be carefully removed.
Heating the parts in this lower temperature range vaporizes these compounds. This prevents them from contaminating the high-temperature sintering zone, which could otherwise cause defects like soot, porosity, or poor metallurgical bonds in the final product.
Zone 2: The Sintering Hot Zone (1120°C to 1135°C)
This is the core of the process where the actual part consolidation occurs. At these high temperatures, which are just below the material's melting point, a process called atomic diffusion takes place.
The individual metal powder particles bond together, forming strong metallurgical necks between them. This process, known as sintering, eliminates the voids between particles, causing the part to shrink, increase in density, and gain significant mechanical strength. The part remains in this zone for 10 to 30 minutes to ensure the bonding is complete.
Zone 3: Controlled Cooling (0.5°C to 5°C per second)
The final stage is not simply about cooling the part down. The rate of cooling is a critical variable that determines the final microstructure and, consequently, the mechanical properties of the part, such as hardness and ductility.
This controlled cooling rate, ranging from 0.5°C to 5°C per second, is carefully managed to prevent thermal shock (which can cause cracking) and to lock in the desired metallurgical phase.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Parameters
Achieving a successful outcome depends on balancing the parameters of each zone. An error in one stage will compromise the entire process.
The Risk of Incomplete Burn-Off
If the pre-heating stage is too short or the temperature too low, binder may not be fully removed. This residue will burn off in the hot zone, leading to carbon contamination on the part surface and inside the furnace, creating a high-scrap, high-maintenance scenario.
Sintering Time vs. Cost and Properties
Longer time in the hot zone can increase part density and strength. However, it also consumes more energy and reduces throughput, increasing costs. Excessive time or temperature can also lead to undesirable grain growth, which can sometimes reduce the material's toughness.
Cooling Rate and Mechanical Properties
The choice of cooling rate is a direct trade-off between hardness and ductility.
- A faster cooling rate (closer to 5°C/sec) acts like a quench, resulting in a harder but potentially more brittle part.
- A slower cooling rate (closer to 0.5°C/sec) is akin to annealing, producing a softer, more ductile part that is easier to machine.
Optimizing the Process for Your Goal
To properly configure a conveyor furnace process, you must begin with the desired properties of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum part strength and density: Prioritize optimizing the sintering time and temperature, ensuring complete atomic diffusion without causing excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is achieving high hardness: Utilize a faster cooling rate within the acceptable range for your material to lock in a hard, martensitic-like microstructure.
- If your primary focus is preventing defects and ensuring consistency: Pay closest attention to the pre-heating zone, guaranteeing sufficient time for complete binder removal before parts enter the high-heat section.
Ultimately, mastering this process means viewing the conveyor furnace not as an oven, but as a tool for precise material science engineering.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature Range | Duration | Key Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-heating and Binder Burn-Off | 300°C to 600°C | Variable | Removes lubricants and binders to prevent contamination |
| Sintering Hot Zone | 1120°C to 1135°C | 10 to 30 minutes | Bonds metal particles via atomic diffusion for strength and density |
| Controlled Cooling | 0.5°C to 5°C per second | Variable | Determines final microstructure and mechanical properties like hardness and ductility |
Ready to optimize your thermal processes with precision? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for your lab. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're sintering, brazing, or developing new materials, we can help you achieve superior results with reliable, efficient equipment. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your manufacturing efficiency and part quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab



















