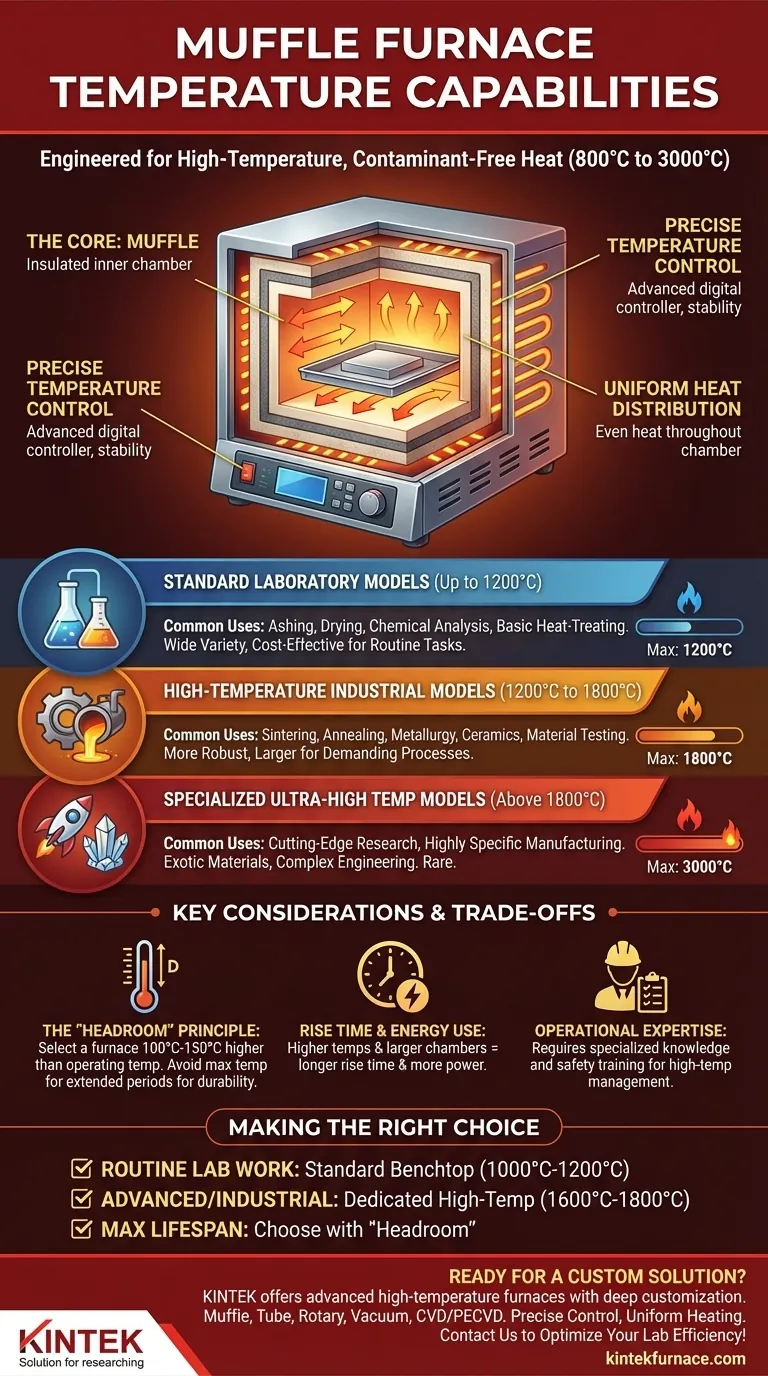
At its core, a muffle furnace is engineered for high-temperature applications, with most models operating in a range of 800°C to 1800°C (1472°F to 3272°F). Standard laboratory furnaces typically reach up to 1200°C, while industrial and high-temperature models are required for processes demanding 1600°C to 1800°C. A few highly specialized units can even exceed these temperatures, reaching up to 3000°C for unique research applications.
A furnace's maximum temperature is only part of the story. The true value lies in its ability to deliver precise, uniform, and contaminant-free heat, making the choice of furnace less about the highest possible number and more about the specific requirements of your process.

Understanding Muffle Furnace Temperature Tiers
Not all muffle furnaces are created equal. Their temperature capabilities are directly tied to their intended application, which dictates their construction, materials, and cost.
Standard Laboratory Models (Up to 1200°C)
These are the workhorses for most general-purpose laboratory tasks. They are commonly used for processes like ashing, chemical analysis, drying, and basic heat-treating.
Their temperature range is sufficient for a wide variety of materials and chemical reactions without the expense and complexity of higher-temperature units.
High-Temperature Industrial Models (1200°C to 1800°C)
These furnaces are built for more demanding applications found in metallurgy, ceramics, and advanced materials science.
Processes like sintering ceramic powders, annealing metals to relieve internal stresses, or testing material properties at extreme temperatures require this higher operational range. They are typically more robust and larger than standard lab models.
Specialized Ultra-High Temperature Models (Above 1800°C)
These units are rare and designed for cutting-edge research or highly specific industrial manufacturing. Reaching temperatures of 3000°C requires exotic materials and complex engineering, placing them in a category of their own.
Key Factors That Define a Furnace's Capability
The maximum temperature rating is a headline feature, but a furnace's true performance is determined by a combination of critical engineering elements.
The Central Role of the Muffle
The term "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber that separates the material being heated from the heating elements. This design is crucial as it prevents contamination from combustion byproducts (in fuel-fired furnaces) and protects the heating elements from the sample.
The material of the muffle, often a high-purity ceramic or refractory alloy, is a primary factor in determining the furnace's maximum safe operating temperature.
Precision Temperature Control
A high temperature is useless if it cannot be controlled. Modern muffle furnaces use advanced digital controllers (often PID controllers) to precisely set and maintain a target temperature with minimal fluctuation. This temperature stability is critical for achieving repeatable and reliable results.
Uniform Heat Distribution
A quality furnace heats the entire chamber evenly. This thermal uniformity ensures that a sample, regardless of its position inside the muffle, experiences the same temperature conditions. This prevents inconsistent results, where one part of a sample is properly treated while another is not.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Choosing a muffle furnace involves balancing performance with practical limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
The "Headroom" Principle
Never operate a furnace at its absolute maximum temperature for extended periods. Doing so puts extreme stress on the heating elements and insulation, significantly shortening the equipment's lifespan.
As a rule, select a furnace with a maximum temperature at least 100°C to 150°C higher than your highest required operating temperature. This "headroom" ensures durability and more stable performance.
Rise Time and Energy Use
The time it takes for a furnace to reach its setpoint is known as the rise time. Higher maximum temperatures and larger chambers naturally require more power and a longer rise time, impacting both workflow efficiency and operational cost.
Operational Expertise
While modern furnaces have user-friendly controls, operating them safely—especially high-temperature models—requires specialized knowledge. Users must be trained to manage heating and cooling rates to prevent thermal shock to the furnace or the material inside.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your work.
- If your primary focus is routine laboratory work (e.g., ashing, drying): A standard benchtop furnace with a 1000°C to 1200°C maximum temperature is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials or industrial processes (e.g., sintering, annealing): You will need a dedicated high-temperature model capable of reaching 1600°C to 1800°C to meet your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment lifespan and process stability: Always select a furnace with a maximum temperature well above your typical operating point to create a safe operational buffer.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about matching its engineered capabilities to your specific thermal processing goal.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1200°C | Ashing, drying, basic heat-treating | Cost-effective for routine lab tasks |
| 1200°C to 1800°C | Sintering, annealing, material testing | Robust design for industrial demands |
| Above 1800°C | Specialized research, ultra-high temp processes | Requires exotic materials and expertise |
Ready to elevate your thermal processing with a custom muffle furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering precise temperature control, uniform heating, and enhanced durability. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















