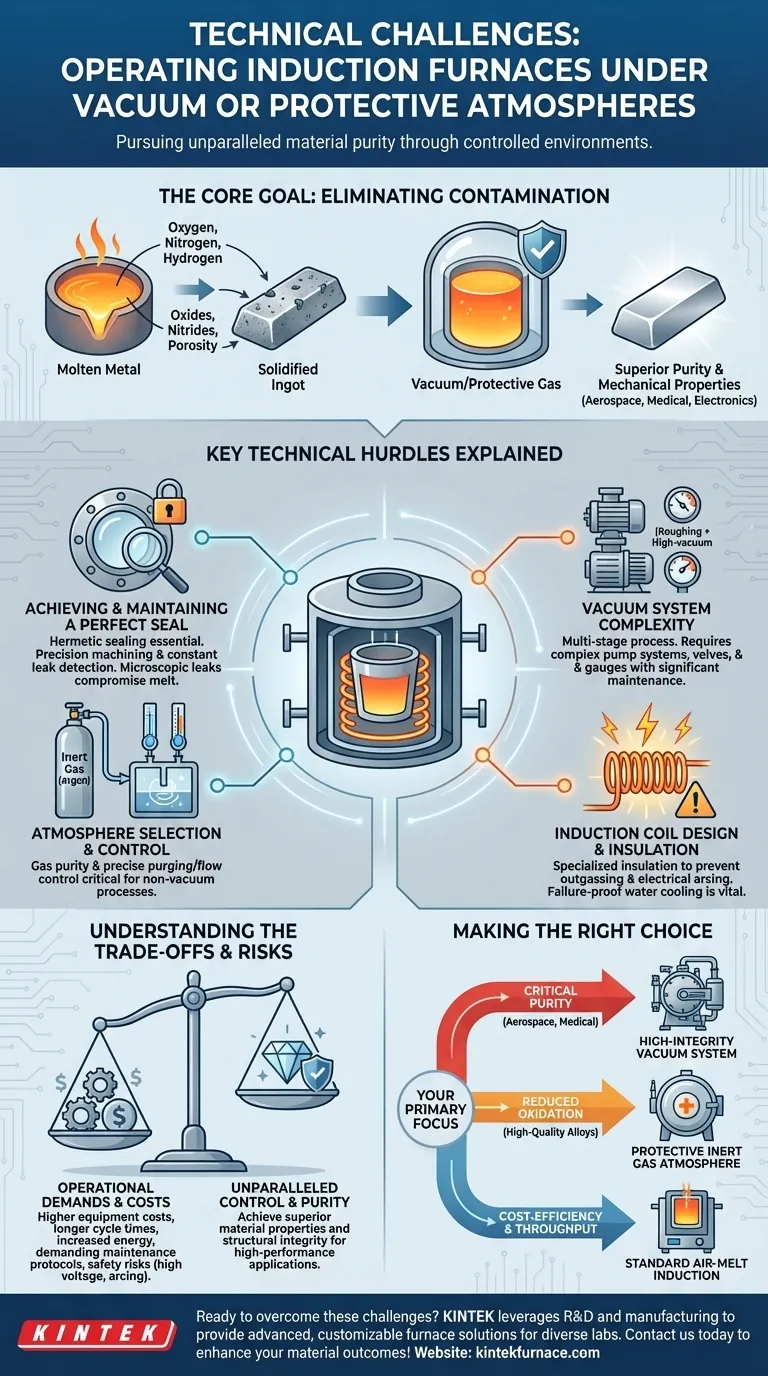
Operating an induction furnace in a controlled atmosphere presents significant technical challenges centered on system integrity, operational complexity, and cost. The core difficulties include achieving and maintaining high-integrity seals, managing complex vacuum systems, controlling the protective atmosphere, designing specialized induction coils for the environment, and ensuring operator safety. These factors collectively lead to higher equipment and operational costs compared to standard air-melt furnaces.
The technical hurdles of vacuum and controlled-atmosphere induction melting are not arbitrary burdens. They are the direct and necessary consequence of pursuing the highest possible material purity by completely isolating the molten metal from atmospheric contamination.
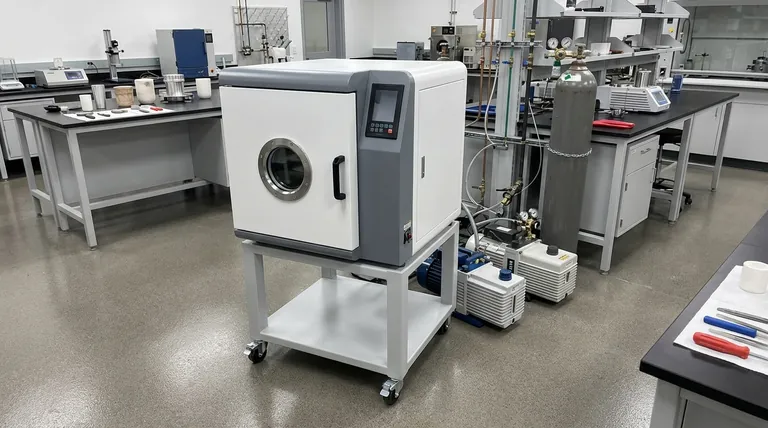

The Core Goal: Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
Before dissecting the challenges, it is crucial to understand why we accept this complexity. The entire purpose is to prevent molten metal from reacting with gases in the air.
Why Contamination Matters
Oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen present in the atmosphere readily react with hot, molten metal. These reactions form unwanted oxides and nitrides, which become trapped as solid inclusions in the final material. Dissolved gases can also come out of solution during solidification, creating porosity and voids.
The Promise of Purity
By removing these reactive gases, we create materials with unparalleled cleanliness and structural integrity. This results in superior mechanical properties, such as improved strength, ductility, and fatigue life, which are non-negotiable for high-performance applications in aerospace, medical implants, and electronics.
Key Technical Hurdles Explained
Each challenge stems from the fundamental need to create a perfectly controlled environment around the molten metal.
Achieving and Maintaining a Perfect Seal
The furnace chamber must be hermetically sealed to prevent any leaks from the outside atmosphere. This requires precision-machined flanges, high-quality seals, and robust chamber construction. Even a microscopic leak can compromise an entire melt by introducing contaminants. Constant leak detection is a critical operational task.
The Complexity of Vacuum Systems
Achieving a vacuum is not a simple one-step process. It requires a multi-stage system, typically involving a "roughing" pump to remove the bulk of the air and a "high-vacuum" pump (like a diffusion or turbomolecular pump) to reach the required low pressures. This system of pumps, valves, and gauges adds significant complexity and maintenance overhead.
Atmosphere Selection and Control
For processes not requiring a deep vacuum, a protective atmosphere of inert gas (like argon) is used. The challenge here is twofold: ensuring the purity of the gas itself and purging the chamber of all air before introducing the inert gas. Precise control over gas flow and pressure is essential throughout the melt cycle.
Induction Coil Design and Insulation
The induction coil itself operates within this controlled environment. This presents unique design problems. The insulation materials must not "outgas" (release trapped vapors) under vacuum, as this would contaminate the melt. Furthermore, the risk of electrical arcing between the coil turns is much higher in a partial vacuum, requiring specific insulation design and careful control over voltage and pressure. The coil's water cooling system is absolutely critical and must be failure-proof.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Adopting this technology involves a clear understanding of its inherent costs and operational demands.
Increased Equipment and Operating Costs
Vacuum chambers, pumping systems, and sophisticated power supplies are significantly more expensive than their air-melt counterparts. Operating costs are also higher due to longer cycle times (for pump-down and purging) and increased energy consumption.
Operational Complexity and Safety
These are not "set and forget" systems. They demand highly trained operators who understand the vacuum process and can respond to issues. Safety is paramount, with risks including high voltage, the potential for powerful electrical arcing, and managing the integrity of water cooling systems that are adjacent to molten metal.
Demanding Maintenance Protocols
Consistent results depend on rigorous maintenance. As recommended practice, this includes regularly checking the water cooling system, inspecting for vacuum leaks, cleaning the furnace chamber to remove any residue, and verifying that all sensors like thermocouples and power supplies are functioning correctly. Neglecting this discipline leads to failed melts and safety hazards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use a vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace must be driven by the end goal for the material.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material purity for critical applications: Investing in a high-integrity vacuum system and rigorous operational discipline is the only path to producing materials for aerospace or medical use.
- If your primary focus is reducing general oxidation for high-quality alloys: A simpler, positive-pressure furnace using a protective inert gas (like argon) can be a more cost-effective solution than a deep vacuum.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency and high throughput: For applications where some level of oxidation is acceptable, a standard air-melt induction furnace remains the superior and more economical choice.
Ultimately, mastering controlled-atmosphere induction melting is a strategic decision to trade operational simplicity for unparalleled control over final material properties.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Issues | Impact on Operation |
|---|---|---|
| Achieving and Maintaining Seals | Precision machining, leak detection | Risk of contamination, requires constant monitoring |
| Vacuum System Complexity | Multi-stage pumps, valves, gauges | Higher maintenance, longer cycle times |
| Atmosphere Control | Gas purity, purging, flow management | Essential for inert environments, adds operational steps |
| Induction Coil Design | Outgassing, electrical arcing, insulation | Needs specialized materials, critical for safety |
| Operational Safety | High voltage, arcing, cooling system failures | Demands trained operators, rigorous protocols |
Ready to overcome the technical challenges of induction furnaces and achieve unparalleled material purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical implants, or electronics, our expertise ensures superior performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and material outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors



















