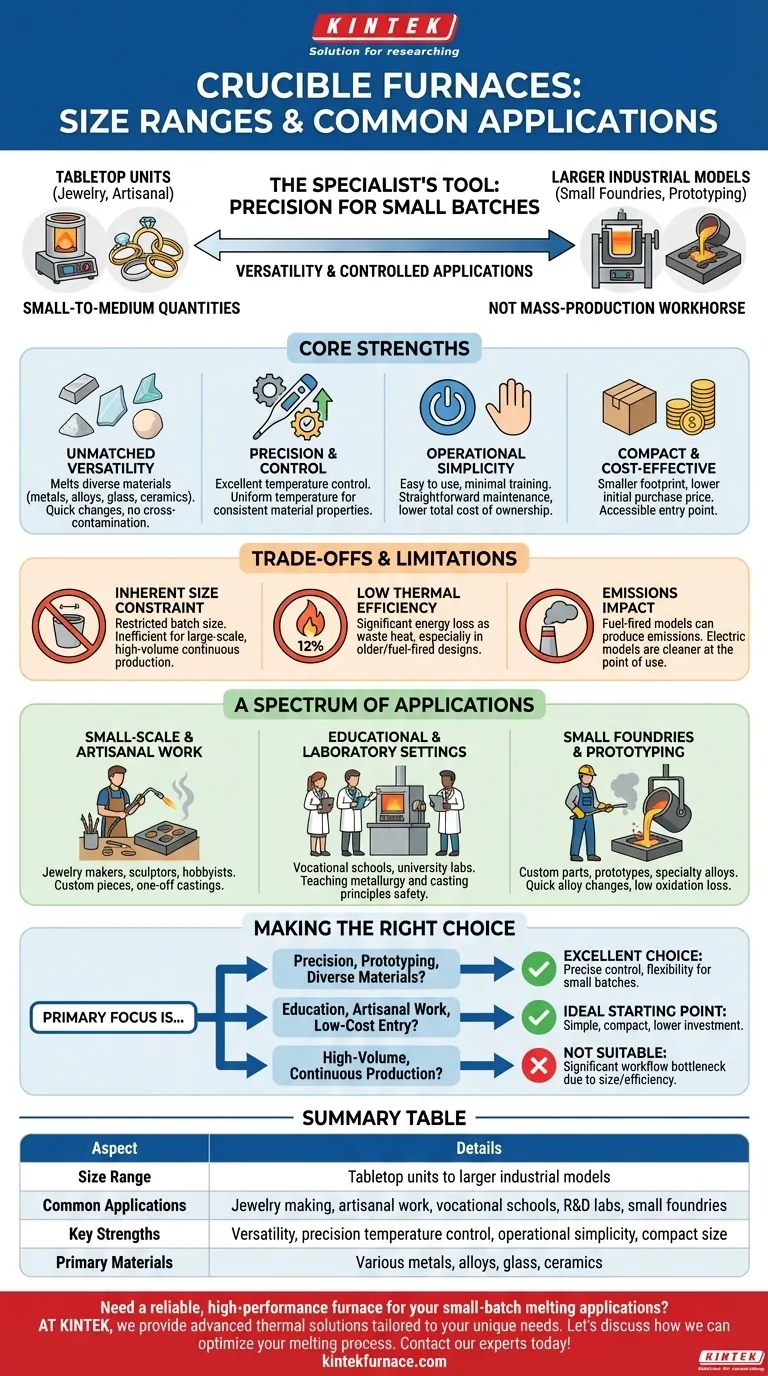
In short, crucible furnaces range from small, tabletop units used for jewelry to larger industrial models for small foundries. They are primarily applied in settings that require melting small-to-medium quantities of metal with precision, such as laboratories, artisanal workshops, vocational schools, and small-scale manufacturing operations.
A crucible furnace is a specialist's tool, not a mass-production workhorse. Its value lies in its versatility and precision for smaller batches, making it ideal for specific, controlled applications rather than high-volume output.
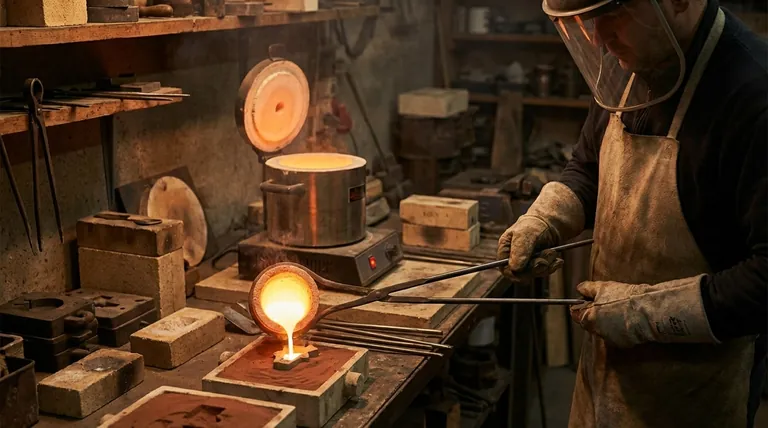

The Core Strengths of Crucible Furnaces
To understand where crucible furnaces fit, we must first examine their fundamental advantages. These attributes define their ideal use cases.
Unmatched Versatility
Crucible furnaces are exceptionally versatile. They are capable of melting a wide variety of materials, including different metals, alloys, glass, and even some ceramics.
This flexibility allows for quick changes between different materials without significant cross-contamination, as the material is contained entirely within the crucible.
Precision and Control
Modern crucible furnaces, particularly electric and graphite models, offer excellent temperature control. This precision is critical for working with alloys that have stringent temperature requirements.
The ability to maintain a uniform temperature ensures consistent material properties, which is vital for quality control in prototyping and small-scale production.
Operational Simplicity
These furnaces are designed for ease of use and typically require minimal specialized training to operate.
Maintenance is also straightforward, which reduces operational downtime and lowers the total cost of ownership, a key factor for small businesses and educational institutions.
Compact and Cost-Effective
Compared to larger industrial furnaces, crucible furnaces have a much smaller physical footprint. This makes them perfect for workshops or labs where space is limited.
Their initial purchase price is also significantly lower, making them an accessible and cost-effective entry point into metal casting and material science.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No tool is perfect. The strengths of a crucible furnace are balanced by inherent limitations that make it unsuitable for certain tasks.
The Inherent Size Constraint
The most significant limitation is batch size. By their nature, crucible furnaces are restricted in the volume of material they can process at one time.
This makes them inefficient and impractical for large-scale industrial applications that demand continuous or high-volume metal casting.
The Efficiency Question
Crucible furnaces, especially older or fuel-fired designs, can have very low thermal efficiency, sometimes as low as 12%. This means a large portion of the energy is lost as waste heat.
While electric models are more efficient at the point of use, they can lead to higher utility costs, a crucial factor to consider in your operational budget.
Emissions and Environmental Impact
Traditional fuel-fired crucible furnaces can produce significant emissions, which may not comply with modern environmental regulations.
Electric crucible furnaces almost entirely eliminate direct emissions, offering a much cleaner alternative, though the source of the electricity itself still has an environmental footprint.
A Spectrum of Applications: From Art to Industry
The balance of strengths and weaknesses dictates where crucible furnaces excel.
Small-Scale and Artisanal Work
For jewelry makers, sculptors, and hobbyists, the compact size, precision, and relatively low cost of a crucible furnace are ideal. It allows for the creation of custom pieces and one-off castings.
Educational and Laboratory Settings
Vocational schools and university engineering labs rely on crucible furnaces for their safety and ease of use. They provide a practical, hands-on way to teach the principles of metallurgy and casting.
Small Foundries and Prototyping
Small foundries use these furnaces for producing custom parts, prototypes, and specialty alloys. The ability to perform quick alloy changes with low oxidation loss is a major advantage in a research and development or bespoke manufacturing context.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a crucible furnace is the correct solution, align your primary goal with the technology's core capabilities.
- If your primary focus is precision, prototyping, or working with diverse materials: A crucible furnace is an excellent choice due to its precise temperature control and flexibility for small batches.
- If your primary focus is education, artisanal work, or low-cost entry: The operational simplicity, compact size, and lower initial investment make a crucible furnace the ideal starting point.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: A crucible furnace is not suitable; its size and efficiency limitations will create a significant bottleneck in your workflow.
Ultimately, choosing a crucible furnace is about selecting the right tool for a specific, controlled task, not a solution for every metal-melting challenge.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Size Range | Tabletop units to larger industrial models |
| Common Applications | Jewelry making, artisanal work, vocational schools, R&D labs, small foundries |
| Key Strengths | Versatility, precision temperature control, operational simplicity, compact size |
| Primary Materials | Various metals, alloys, glass, ceramics |
Need a reliable, high-performance furnace for your small-batch melting applications?
At KINTEK, we understand that precision and versatility are paramount for jewelers, artisans, researchers, and small foundries. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced thermal solutions tailored to your unique needs.
Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental or production requirements.
Let's discuss how we can optimize your melting process. Contact our experts today for a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















