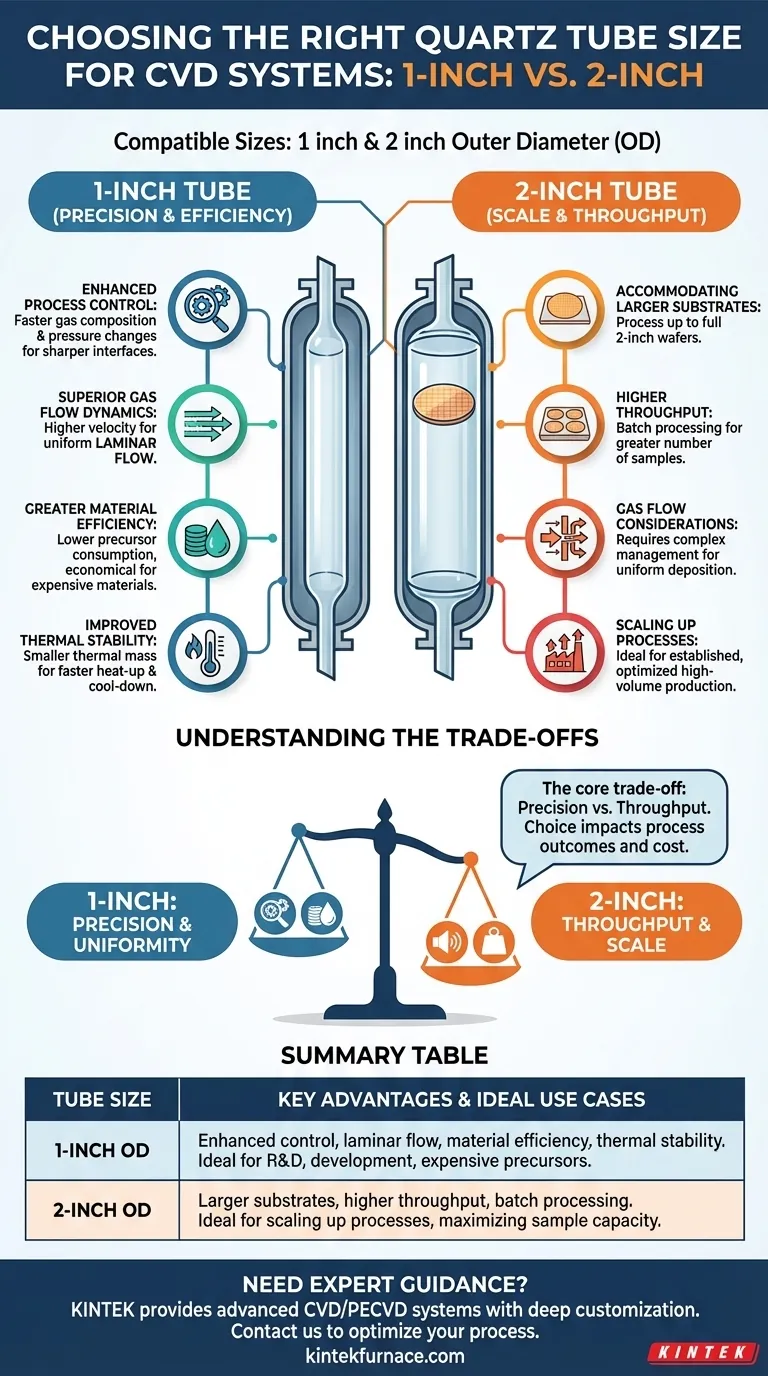
The CVD systems in question are engineered to be compatible with two standard quartz tube sizes: 2 inch and 1 inch outer diameter. While both are supported, the choice between them is a critical process decision that fundamentally impacts experimental outcomes and operational efficiency.
Choosing between a 1-inch and 2-inch tube is not just about physical fit. It's a strategic decision that balances process scale and throughput against process control and material efficiency.

Why Tube Diameter is a Critical Process Parameter
The quartz tube in a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system is more than a simple container. It is the reaction chamber where all critical processes—heating, gas flow, and chemical reaction—take place.
The tube's diameter directly defines the geometry of this reaction environment. This geometry dictates gas flow dynamics, thermal uniformity, and precursor consumption, making the tube size a primary variable in your process design.
The Case for the 2-Inch Tube: Maximizing Scale
The larger 2-inch tube is designed for applications where throughput and substrate size are the dominant concerns.
Accommodating Larger Substrates
The most direct advantage is the ability to process larger substrates, such as full 2-inch wafers. This is essential for creating larger-area films or devices.
Higher Throughput
For smaller samples, the larger diameter allows you to process a greater number of substrates in a single run. This batch processing capability significantly increases throughput for established processes.
Gas Flow Considerations
Achieving perfectly uniform deposition across a wider 2-inch area can require more complex gas flow management and higher total flow rates to avoid precursor depletion along the gas path.
The Case for the 1-Inch Tube: Precision and Efficiency
The smaller 1-inch tube is the standard choice for research, development, and processes that demand the highest degree of control.
Enhanced Process Control
A smaller internal volume means that changes in gas composition or pressure occur more rapidly. This allows for sharper interfaces in multi-layer depositions and more responsive process control.
Superior Gas Flow Dynamics
For a given gas flow rate, the velocity of the gas is higher in a narrower tube. This higher velocity helps ensure a more laminar flow, which is critical for achieving uniform film thickness and preventing unwanted recirculation zones.
Greater Material Efficiency
The smaller volume requires significantly less precursor gas to achieve the desired partial pressure. This makes the 1-inch tube far more economical when working with expensive or rare precursor materials, which is common in R&D settings.
Improved Thermal Stability
A 1-inch tube has a smaller thermal mass, allowing for faster heat-up and cool-down cycles. The temperature profile across the smaller diameter is also typically more uniform and easier to control.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Direct Comparison
Your choice involves a fundamental compromise between scale and precision. Understanding these trade-offs is key to preventing failed experiments and wasted resources.
Throughput vs. Precision
The core trade-off is clear: the 2-inch tube prioritizes throughput, while the 1-inch tube prioritizes process control and uniformity. What you gain in sample capacity with the larger tube, you may sacrifice in fine-tuned control.
Cost of Operation
For developing new processes, the 1-inch tube is more cost-effective due to lower precursor consumption. The 2-inch tube only becomes economical on a per-sample basis if you can consistently utilize its full capacity.
Process Scalability
Be aware that a process perfected in a 1-inch tube will likely require re-optimization when transferred to a 2-inch tube. The changes in thermal properties and gas flow dynamics are significant and cannot be ignored.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your decision on the specific objective of your work.
- If your primary focus is research, process development, or using expensive precursors: The 1-inch tube offers the superior control, uniformity, and material efficiency you need.
- If your primary focus is maximizing sample throughput or processing larger substrates (up to 2 inches): The 2-inch tube is the appropriate choice for scaling up an already optimized process.
- If you are developing a new process for future scale-up: Begin with the 1-inch tube to establish parameters efficiently, but budget time for process re-validation when moving to the 2-inch tube.
Selecting the correct tube diameter is the foundational step in engineering a stable, repeatable, and efficient CVD process.
Summary Table:
| Tube Size | Key Advantages | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| 1-Inch OD | Enhanced process control, superior laminar flow, material efficiency, improved thermal stability | R&D, process development, expensive precursors |
| 2-Inch OD | Accommodates larger substrates, higher throughput, batch processing | Scaling up processes, maximizing sample capacity |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right quartz tube for your CVD system? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, whether you're in research, development, or scaling production. Contact us today to optimize your process and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab



















