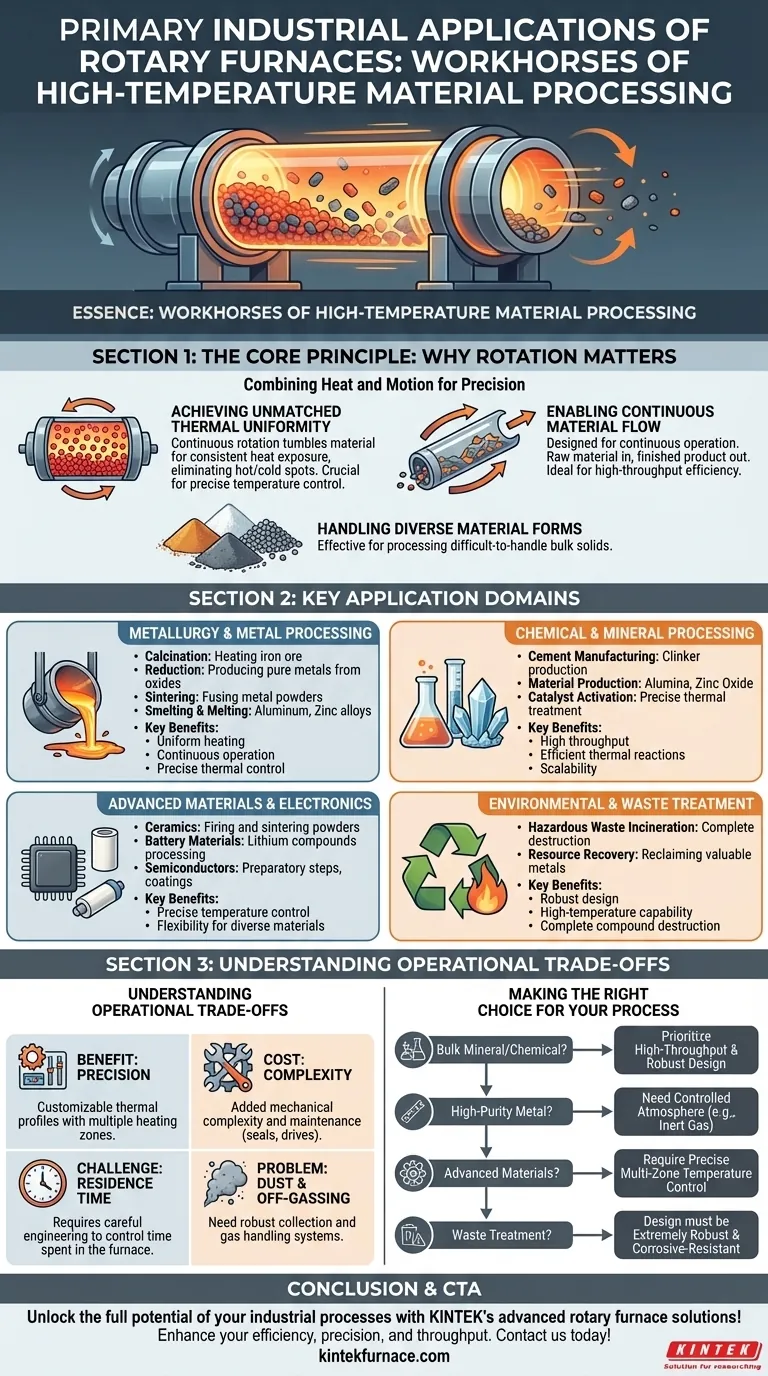
In essence, rotary furnaces are the workhorses of high-temperature material processing. Their primary industrial applications are found in metallurgy for creating metals and alloys, chemical processing for inducing thermal reactions like calcination, and advanced materials manufacturing for producing everything from cement and ceramics to battery components.
The immense versatility of a rotary furnace stems from its fundamental design: a slowly rotating tube that guarantees exceptionally uniform heating. This core principle makes it the definitive choice for any process that demands precise thermal control over powders, granules, or other bulk solids.
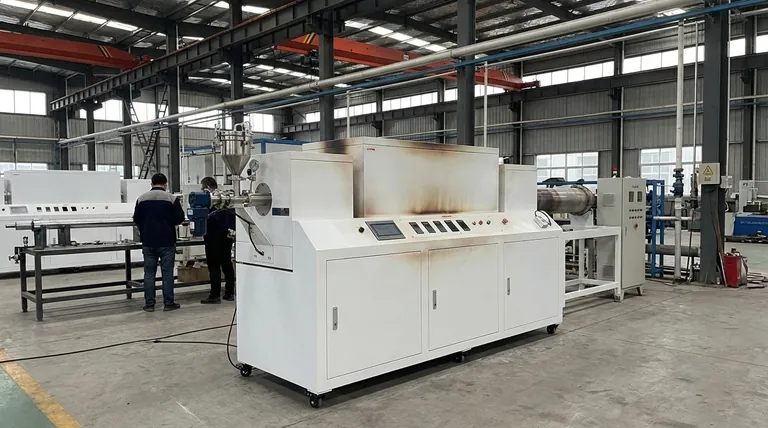

The Core Principle: Why Rotation Matters
The effectiveness of a rotary furnace is not just about heat; it's about the combination of heat and motion. This dynamic approach solves problems that are inherent in static, batch-based furnaces.
Achieving Unmatched Thermal Uniformity
The continuous rotation gently tumbles the material inside the furnace. This action ensures that every particle is consistently and evenly exposed to the heat source, eliminating hot spots and cold spots.
This uniformity is critical for processes where precise temperature control dictates the final material properties, preventing under-processed or over-processed results.
Enabling Continuous Material Flow
Unlike static furnaces that operate in discrete batches, rotary furnaces are designed for continuous operation. Raw material is fed into one end of the tilted tube and slowly travels to the other end as it rotates, emerging as a finished product.
This design is ideal for high-throughput industrial environments that require a constant, predictable output stream, maximizing production efficiency.
Handling Diverse Material Forms
The tumbling action is exceptionally effective at processing a wide range of materials that are difficult to handle in other furnace types. This includes fine powders, granules, pellets, and other bulk solids.
Key Application Domains Explained
The combination of uniform heating and continuous flow makes the rotary furnace indispensable across several major industries. The specific process performed within the furnace defines its application.
Metallurgy and Metal Processing
In metallurgy, these furnaces are crucial for transforming raw ores and powders into refined metals. Key processes include:
- Calcination: Heating iron ore to prepare it for pelletizing and smelting.
- Reduction: Removing oxygen from metal oxides to produce pure metals.
- Sintering: Fusing metal powders together to create dense, solid parts.
- Smelting & Melting: Used for lower-temperature metals like aluminum and zinc alloys.
Chemical and Mineral Processing
The chemical industry relies on rotary furnaces, often called kilns in this context, for large-scale thermal reactions.
- Cement Manufacturing: The production of cement clinker is one of the most common applications globally.
- Material Production: Used to manufacture alumina, vermiculite, and zinc oxide.
- Catalyst Activation: Precisely heating materials to activate their catalytic properties.
Advanced Materials and Electronics
For high-performance materials, the precise control offered by a rotary furnace is paramount.
- Ceramics: Firing and sintering ceramic powders to create dense, uniform components.
- Battery Materials: Roasting and processing powders like lithium compounds for use in modern batteries.
- Semiconductors: Used in preparatory steps for creating semiconductor materials and specialized coatings.
Environmental and Waste Treatment
The robust nature and high temperatures achievable in rotary furnaces make them ideal for waste processing.
- Hazardous Waste Incineration: The high temperatures and long residence time ensure the complete destruction of hazardous organic compounds.
- Resource Recovery: Heating industrial byproducts or waste to reclaim valuable metals or other substances.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, rotary furnaces come with specific design considerations and limitations that must be understood.
The Benefit of Precision vs. The Cost of Complexity
The ability to have multiple, independently controlled heating zones allows for highly customized thermal profiles. However, the rotating seals, drive mechanism, and support structures add a layer of mechanical complexity and maintenance compared to a simple static furnace.
The Challenge of Residence Time
While throughput is high, controlling the exact amount of time a material spends in the furnace (residence time) depends on the tube's rotation speed, angle of inclination, and material flow characteristics. Achieving a very narrow residence time distribution requires careful engineering.
The Problem of Dust and Off-Gassing
The tumbling action, while beneficial for heating, can create significant dust with fine powders. This necessitates robust dust collection and gas handling systems to manage emissions and prevent product loss.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The ideal application for a rotary furnace depends entirely on your material, desired output, and the specific thermal transformation required.
- If your primary focus is bulk mineral or chemical processing: Prioritize a high-throughput, energy-efficient design tailored for continuous operation and robust material handling.
- If your primary focus is high-purity metal or alloy production: You need a furnace capable of maintaining a controlled atmosphere (e.g., inert or reducing gas) to prevent unwanted oxidation.
- If your primary focus is developing advanced materials: You require precise, multi-zone temperature control and the flexibility to adjust rotation speed and residence time.
- If your primary focus is waste treatment or resource recovery: The design must be extremely robust, built with materials that can withstand corrosive compounds and very high temperatures.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace's strength lies in its unique ability to transform bulk materials through controlled, uniform, and continuous motion.
Summary Table:
| Application Domain | Key Processes | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy and Metal Processing | Calcination, Reduction, Sintering, Smelting | Uniform heating, Continuous operation, Precise thermal control |
| Chemical and Mineral Processing | Cement manufacturing, Catalyst activation, Material production | High throughput, Efficient thermal reactions, Scalability |
| Advanced Materials and Electronics | Ceramics firing, Battery materials processing, Semiconductor preparation | Precise temperature control, Flexibility for diverse materials |
| Environmental and Waste Treatment | Hazardous waste incineration, Resource recovery | Robust design, High-temperature capability, Complete destruction of compounds |
Unlock the full potential of your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored for metallurgy, chemical processing, advanced materials, and waste treatment. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your efficiency, precision, and throughput!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits



















