At their core, rotary furnaces are designed for heat treatment processes that demand exceptional uniformity across bulk materials. The primary processes performed are melting, oxidation, calcination, and thermal decomposition, where consistent temperature and atmospheric exposure are critical for achieving the desired chemical and physical transformations.
The defining advantage of a rotary furnace is not just the heat it provides, but how it delivers it. Its continuous rotation ensures every particle of the material is heated evenly, making it the ideal choice for processes where consistency across a large volume is the primary goal.
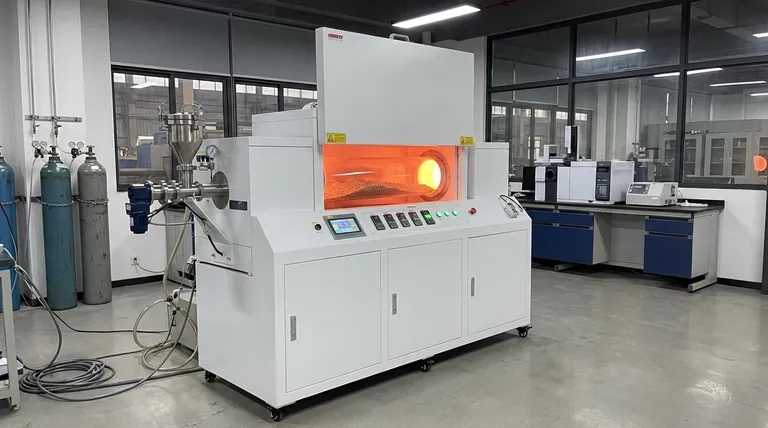

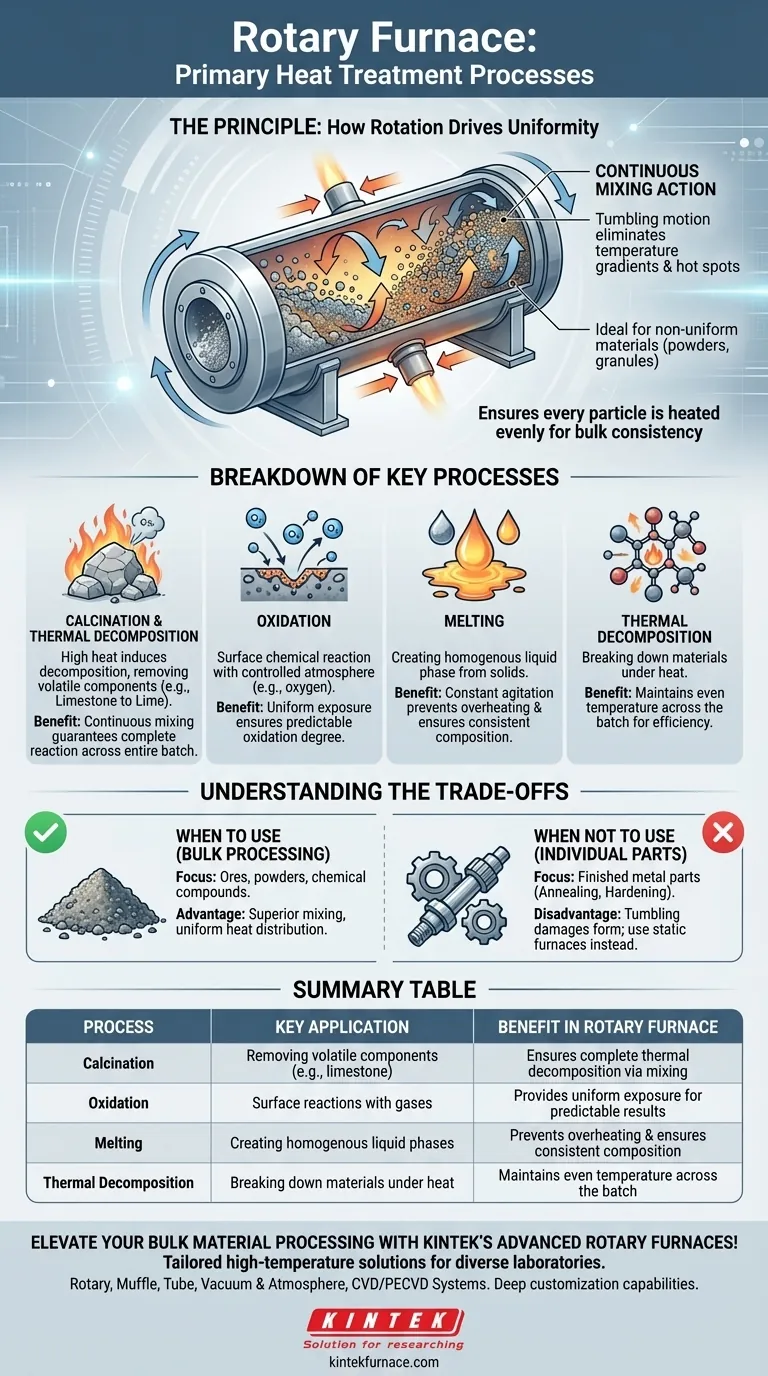
The Principle: How Rotation Drives Uniformity
A rotary furnace's effectiveness stems from its unique mechanical design. It consists of a long, inclined cylindrical barrel that rotates slowly while being heated externally.
Continuous Mixing Action
As the barrel rotates, the material inside is constantly tumbled and mixed. This action continuously exposes new surfaces to the heat source and the internal atmosphere.
This tumbling motion is crucial because it eliminates temperature gradients and hot spots that can occur in static furnaces, ensuring the entire batch is processed under identical conditions.
Ideal for Non-Uniform Materials
This design is exceptionally well-suited for processing powders, granules, and other loose solids. The mixing ensures that even irregularly shaped materials receive uniform heat exposure, which is difficult to achieve in a static environment.
Breakdown of Key Processes
The uniform heating provided by a rotary furnace makes it ideal for several specific thermal treatments that are sensitive to temperature variations.
Calcination and Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is a process that uses high heat to induce thermal decomposition, often to remove a volatile component from a solid. A common example is converting limestone (calcium carbonate) into lime (calcium oxide).
For this reaction to be complete and efficient, the entire mass of material must reach and hold the target temperature. The rotary furnace's mixing action guarantees this, preventing parts of the batch from being under-processed.
Oxidation
Oxidation involves a chemical reaction on the surface of a material, often by introducing a controlled atmosphere (like oxygen) into the heated chamber.
The tumbling motion ensures that the entire surface area of every particle is consistently exposed to the reactive gas. This leads to a uniform and predictable degree of oxidation throughout the material batch.
Melting
When melting materials, the goal is to create a homogenous liquid phase. The constant agitation inside a rotary furnace prevents some parts of the charge from overheating while others remain solid. This results in faster, more efficient melting and a final product with consistent composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful for bulk materials, the design of a rotary furnace makes it unsuitable for all heat treatment applications. Its strengths in one area create limitations in another.
When a Rotary Furnace Isn't the Right Choice
Processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering are typically performed on finished or semi-finished metal parts. These treatments are designed to modify the mechanical properties of a specific object without altering its shape.
The tumbling action of a rotary furnace would damage these parts and is completely unsuitable for applications where the component's form and position must be maintained.
Bulk Processing vs. Individual Parts
The fundamental trade-off is between bulk material processing and discrete part treatment.
Rotary furnaces excel at treating a large volume or mass of material (like ores, powders, or chemical compounds) uniformly. For treating individual, formed objects, a static or batch-style furnace (such as a horizontal or box furnace) is the appropriate choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is processing bulk powders, ores, or granules: A rotary furnace is the ideal choice due to its superior mixing and uniform heat distribution.
- If your primary focus is a chemical reaction like calcination or oxidation: The consistent heat and atmospheric exposure of a rotary furnace will deliver the most reliable results.
- If your primary focus is heat treating finished metal parts like gears or shafts: You must use a static furnace (e.g., box, pit, or horizontal) to preserve the component's shape and integrity.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's core mechanical function to your specific process requirements is the key to a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Application | Benefit in Rotary Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Removing volatile components (e.g., limestone to lime) | Ensures complete thermal decomposition via continuous mixing |
| Oxidation | Surface reactions with gases (e.g., controlled oxidation) | Provides uniform exposure to atmosphere for predictable results |
| Melting | Creating homogenous liquid phases from solids | Prevents overheating and ensures consistent composition |
| Thermal Decomposition | Breaking down materials under heat | Maintains even temperature across the batch for efficiency |
Elevate your bulk material processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're handling powders, granules, or ores, our furnaces ensure uniform heating for processes like calcination and oxidation. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment outcomes and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput



















