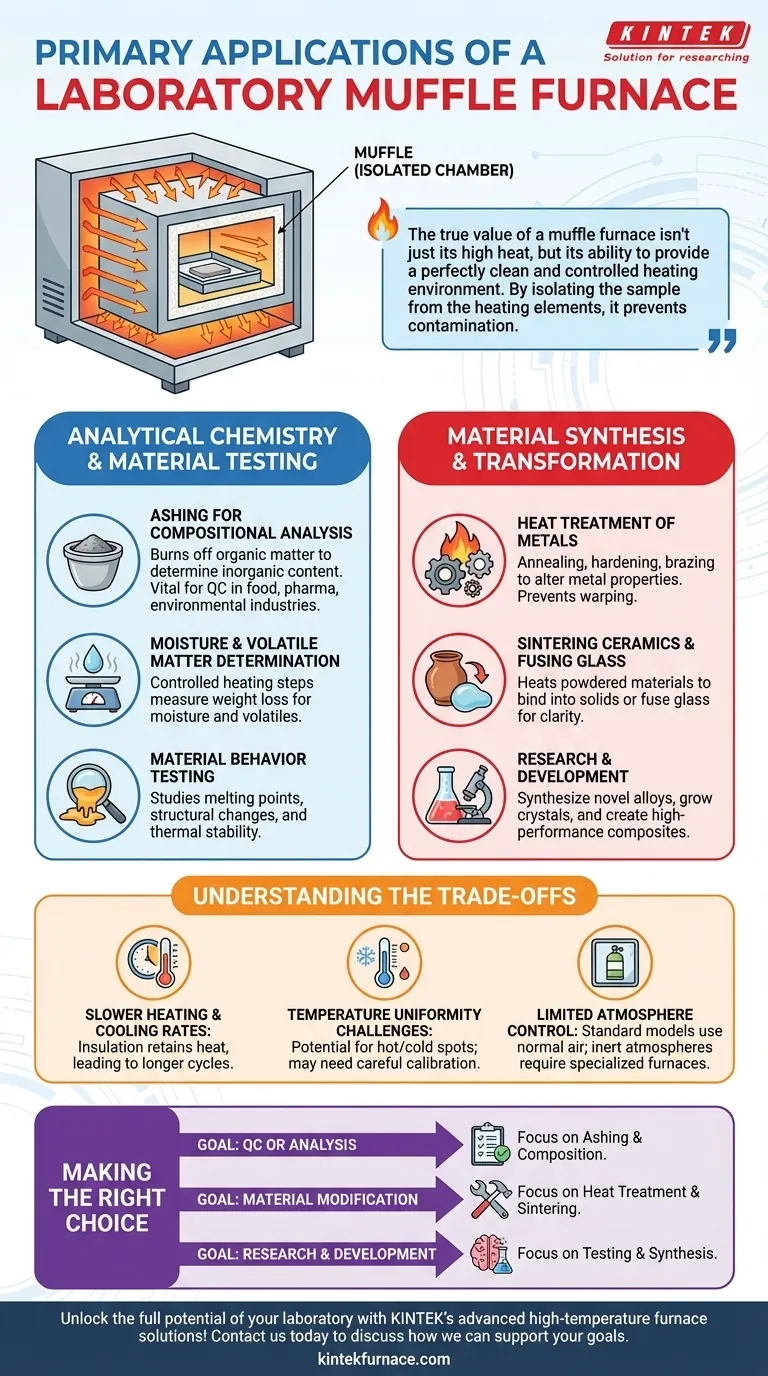
At its core, a laboratory muffle furnace is used for two fundamental types of high-temperature tasks: analytical testing and material transformation. Its primary applications involve processes like ashing, where a sample is burned to determine its non-combustible content, and heat-treating, where materials like metals or ceramics are heated to alter their physical properties. These functions are critical across fields ranging from metallurgy and materials science to pharmaceuticals and environmental analysis.
The true value of a muffle furnace isn't just its high heat, but its ability to provide a perfectly clean and controlled heating environment. By isolating the sample from the heating elements, it prevents contamination, which is the key to achieving accurate analytical results and pure material transformations.

The Core Principle: A Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Environment
A muffle furnace is uniquely designed to deliver pristine heating conditions. This capability is what enables its wide range of applications.
What is a "Muffle"?
The name comes from the furnace's central component: an insulated inner chamber, or "muffle." This chamber holds the sample and separates it entirely from the actual heating elements.
The heating elements heat the outside of the muffle, which then radiates thermal energy evenly into the chamber. This indirect heating is the furnace's defining feature.
Why Isolation Matters
This separation is critical because it prevents any byproducts from the heating source, such as gases from fuel combustion or flaking from electric coils, from contaminating the sample.
For analytical chemistry, this purity ensures test results are accurate. For materials science, it guarantees the integrity and desired properties of the finished material.
Application Category 1: Analytical Chemistry & Material Testing
This group of applications leverages the furnace's clean environment to precisely measure a sample's composition and behavior at high temperatures.
Ashing for Compositional Analysis
Ashing is arguably the most common application. A sample is heated to a high temperature to completely burn off all organic and volatile substances.
What remains is the ash, or the non-combustible, inorganic content. Weighing the sample before and after ashing allows for a precise calculation of its composition. This is vital for quality control in the food, pharmaceutical, and environmental industries.
Moisture and Volatile Matter Determination
By using a series of controlled temperature steps, a muffle furnace can be used to determine a sample's moisture and volatile matter content.
The weight loss after heating to a low temperature (e.g., 105°C) indicates moisture content, while subsequent weight loss at a much higher temperature reveals the amount of other volatile materials.
Material Behavior Testing
Researchers use muffle furnaces to study how materials behave under extreme heat. This includes determining a material's melting point, analyzing its structural changes, and testing its overall thermal stability for quality control and R&D.
Application Category 2: Material Synthesis & Transformation
These applications use high heat to fundamentally change a material's physical structure or chemical properties.
Heat Treatment of Metals
In metallurgy, muffle furnaces are essential for heat treating. This includes processes like annealing (to soften metal and improve ductility), hardening (to increase strength), and brazing or soldering components together.
The precise temperature control and uniform heating prevent warping and ensure the metal achieves its target properties without surface contamination.
Sintering Ceramics and Fusing Glass
Manufacturing advanced ceramics involves sintering, a process where powdered material is heated until its particles bind together to form a solid, dense object.
Similarly, the furnace is used for creating enamel coatings and fusing glass. The clean environment is crucial for achieving clarity and strength in the final product.
Research and Development
In laboratory settings, muffle furnaces are indispensable tools for developing new materials. Scientists can create novel alloys, grow crystals, and synthesize high-performance composites that require precise and contaminant-free high-temperature conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the design of a muffle furnace introduces specific limitations that are important to recognize.
Slower Heating and Cooling Rates
The insulated muffle that ensures thermal uniformity also retains heat effectively. This means muffle furnaces generally heat up and cool down more slowly than direct-heating ovens, which can be a drawback for processes requiring rapid thermal cycling.
Temperature Uniformity Challenges
While designed for uniform heating, some models can still develop hot or cold spots within the chamber. Achieving absolute temperature uniformity often requires careful calibration and may necessitate furnaces with multiple heating zones for critical applications.
Limited Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with a normal air atmosphere. If a process requires an inert (e.g., argon, nitrogen) or reactive atmosphere, a specialized and significantly more expensive furnace with gas-purging capabilities is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right application depends entirely on whether your goal is to analyze a sample or to transform it.
- If your primary focus is quality control or analysis: You will primarily use ashing to determine the non-volatile content of samples in industries like pharmaceuticals, food, or environmental science.
- If your primary focus is material modification: You will use heat treatment processes like annealing, hardening, or sintering to alter the physical properties of metals and ceramics.
- If your primary focus is research and development: You will leverage the furnace's controlled environment to test material properties at high temperatures or to synthesize novel materials.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace empowers you to control heat with precision, free from the variables of contamination.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Chemistry & Material Testing | Ashing, Moisture Determination, Material Behavior Testing | Pharmaceuticals, Food, Environmental Science |
| Material Synthesis & Transformation | Heat Treatment (Annealing, Hardening), Sintering, Fusing Glass | Metallurgy, Ceramics, Materials Science |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in processes like ashing, heat treatment, and material synthesis. Ready to elevate your research? Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















