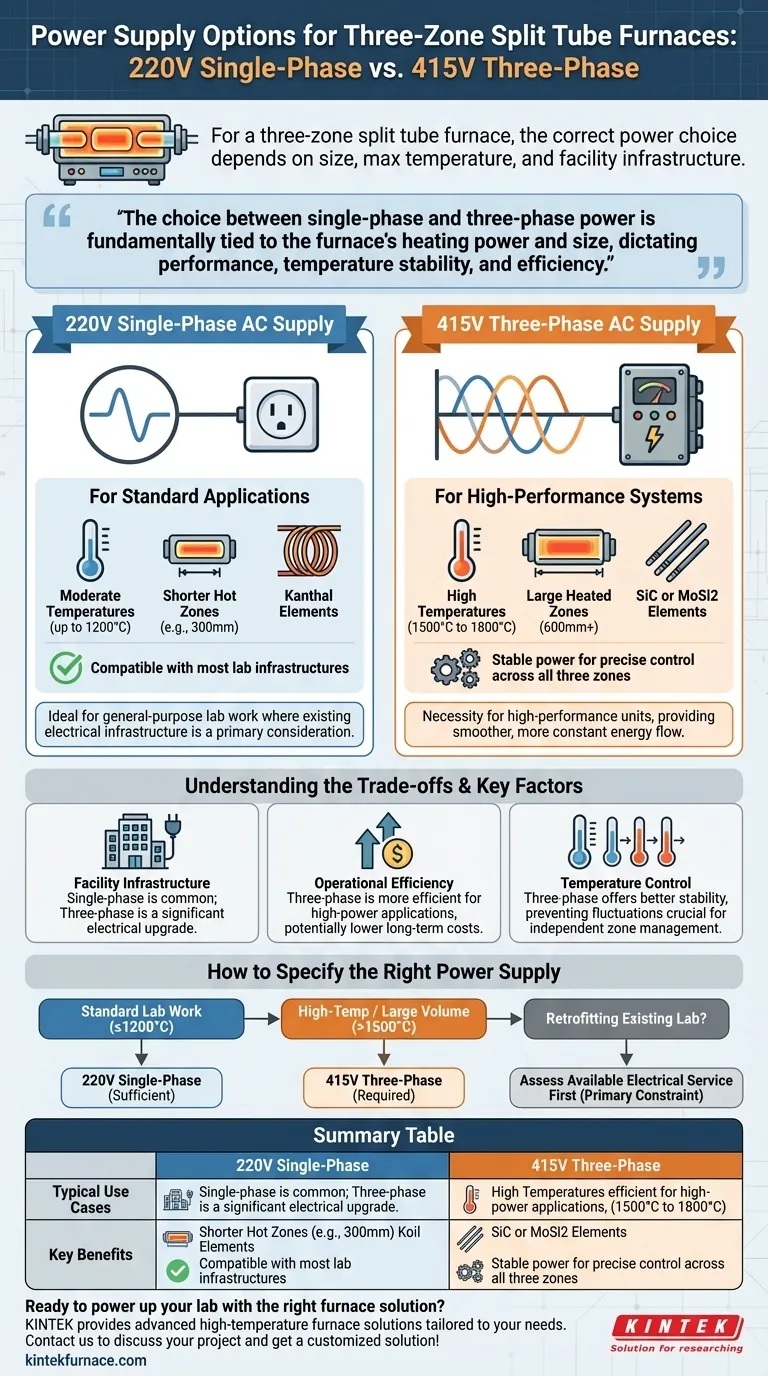
For a three-zone split tube furnace, the two primary power supply options are a 220V, Single Phase AC supply and a 415V, Three Phase AC supply. The correct choice depends directly on the furnace's size, maximum temperature rating, and the electrical infrastructure of your facility.
The choice between single-phase and three-phase power is not merely about facility compatibility. It is fundamentally tied to the furnace's heating power and size, which in turn dictate its performance, temperature stability, and operational efficiency.

The Link Between Power and Furnace Performance
The power supply is the heart of the furnace system. Its capacity determines the speed, stability, and ultimate temperature the furnace can achieve. For a sophisticated three-zone furnace, this choice is critical.
The Role of Heating Power
A furnace's power requirement is dictated by its maximum temperature and the size of its heated zones. Higher temperatures and larger volumes require significantly more power.
The heating elements used are a key factor. Furnaces using Kanthal elements for temperatures up to 1200°C have lower power demands than those using SiC (Silicon Carbide) or MoSi2 (Molybdenum Disilicide) for temperatures approaching 1800°C.
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Delivery
Think of a single-phase supply as a single, pulsing power line. It is common and sufficient for many standard lab appliances and smaller furnaces.
A three-phase supply uses three power lines, delivering power in overlapping waves. This provides a smoother, more constant, and more efficient flow of energy, which is essential for high-demand equipment.
Impact on Temperature Control
Three-zone furnaces are used for applications requiring excellent temperature uniformity and precise control. The stable power delivery of a three-phase system is better suited to independently managing the three heating zones, preventing fluctuations that could impact experimental results.
Matching the Supply to the Furnace Specification
The decision is ultimately driven by the furnace's design specifications. Manufacturers match the power supply to the capabilities of the unit.
220V Single-Phase: For Standard Applications
A 220V single-phase configuration is typically reserved for smaller furnaces. This includes models with shorter hot zones (e.g., 300mm) and more moderate maximum temperatures (e.g., 1200°C).
These units are ideal for general-purpose lab work where existing electrical infrastructure is a primary consideration.
415V Three-Phase: For High-Performance Systems
A 415V three-phase supply is the standard for high-performance furnaces. This is a necessity for units with high maximum temperatures (1500°C to 1800°C) or large heated zones (600mm or more).
The high, stable power is required to drive powerful SiC or MoSi2 heating elements and maintain precise control across all three zones under heavy thermal load.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace means balancing performance needs with practical constraints. The power supply is often the most significant constraint.
Facility Infrastructure is a Hard Limit
Your choice may be dictated by what your building can provide. Most standard labs are wired for single-phase power. Installing a three-phase circuit is a significant electrical upgrade that requires planning and investment.
Operational Efficiency
For high-power applications, three-phase power is more efficient. While the initial installation cost may be higher, the long-term operational cost of running a large, power-hungry furnace can be lower due to this improved efficiency.
Customization and Specification
As noted in furnace specifications, power and controls are often customizable. When ordering a furnace, the power supply is a key part of the discussion with the manufacturer to ensure the final product meets your research needs and facility capabilities.
How to Specify the Right Power Supply
Base your decision on the intended application of the furnace and a realistic assessment of your facility.
- If your primary focus is standard lab work with moderate temperatures (up to ~1200°C): A 220V single-phase furnace is likely sufficient and will be compatible with most lab infrastructures.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature materials processing (>1500°C) or large sample volumes: A 415V three-phase supply is almost certainly required to provide the necessary power and stability.
- If you are retrofitting an existing lab with limited power: You must first assess your available electrical service, as this will be the primary constraint on the performance of the furnace you can install without major upgrades.
Ultimately, selecting the correct power supply is the first step in ensuring your furnace operates safely, efficiently, and to its full performance specification.
Summary Table:
| Power Supply Option | Typical Use Cases | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| 220V Single-Phase | Standard lab work, temperatures up to 1200°C, smaller hot zones (e.g., 300mm) | Compatible with most lab infrastructures, cost-effective for moderate applications |
| 415V Three-Phase | High-temperature processing (1500°C to 1800°C), large heated zones (600mm+), precise control | Stable power delivery, better efficiency, supports high-power elements like SiC/MoSi2 |
Ready to power up your lab with the right furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're handling standard applications or high-performance materials processing, we'll help you select the ideal power supply and furnace for optimal efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss your project and get a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes



















