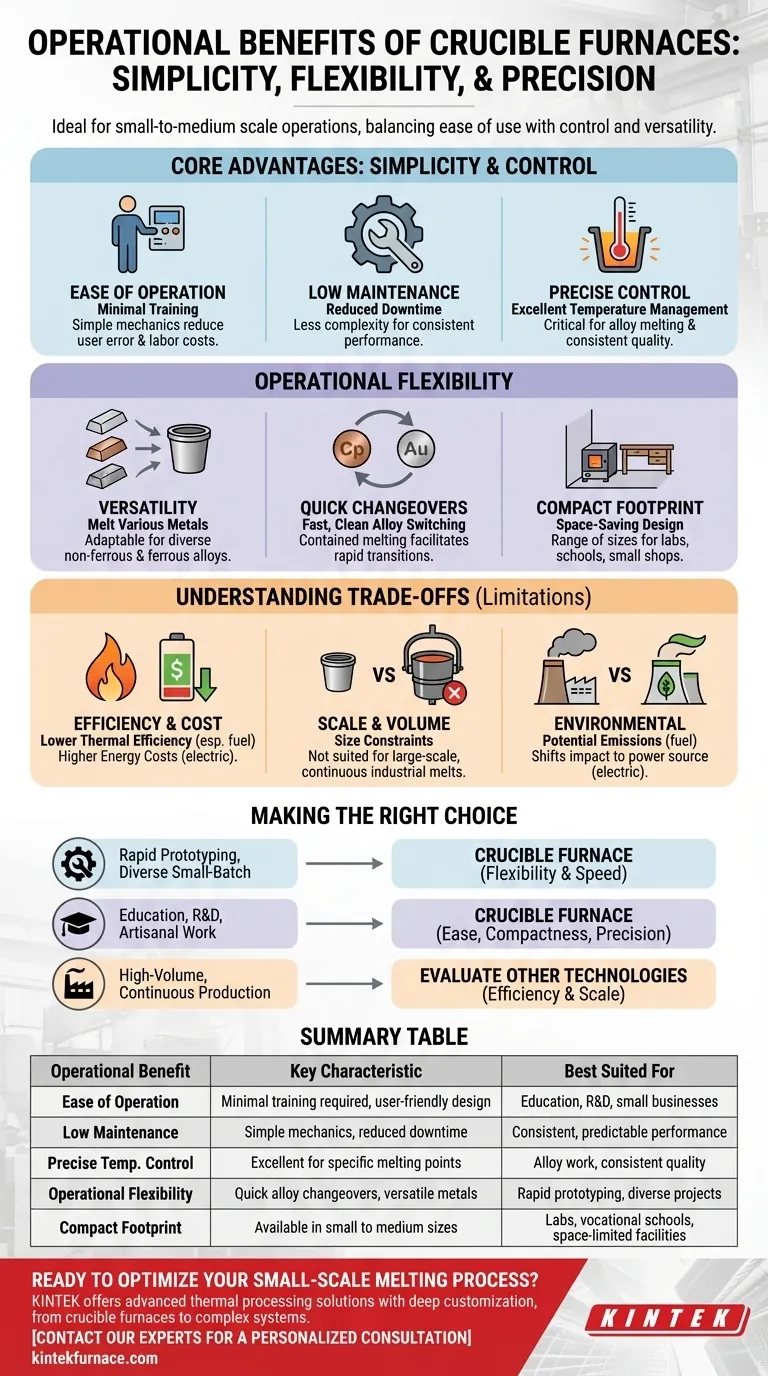
At their core, the operational benefits of crucible furnaces are centered on their simplicity, low maintenance needs, and precise control. These furnaces are exceptionally easy to operate, require minimal specialized training, and their straightforward maintenance reduces downtime, making them a reliable choice for many applications.
While often chosen for their ease of use, the true value of a crucible furnace lies in its flexibility and precision for small-to-medium scale operations. The key is understanding that these benefits are balanced against significant trade-offs in energy efficiency and production volume.
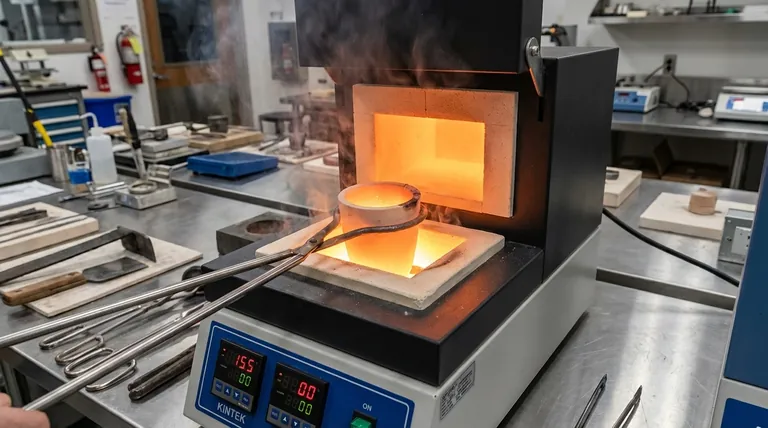

The Core Advantages: Simplicity and Control
The primary appeal of crucible furnaces comes from their user-friendly design and the high degree of control they offer over the melting process.
Ease of Operation
Crucible furnaces are designed to be straightforward. Their simple mechanics mean operators require minimal training to manage melting processes effectively, reducing labor costs and the potential for user error.
Low Maintenance Requirements
The design of these furnaces minimizes complexity, which translates directly to reduced maintenance. This means less operational downtime and more consistent, predictable performance over the furnace's lifespan.
Precise Temperature Management
Crucible furnaces provide excellent temperature control. This precision is critical for working with alloys that have specific melting points and for achieving desired material properties, ensuring consistent quality from batch to batch.
Unlocking Operational Flexibility
Beyond basic operation, crucible furnaces provide a level of flexibility that is essential for certain types of work, from laboratories to small-scale foundries.
Versatility Across Materials
A single crucible furnace can be used to melt a wide variety of non-ferrous and ferrous metals. This adaptability makes it a valuable asset for shops that handle diverse projects and materials.
Rapid Alloy Changeovers
Because the metal is contained entirely within the crucible, switching from one alloy to another is fast and clean. This quick-change capability is ideal for operations that do not dedicate a furnace to a single metal.
Compact Footprint
Crucible furnaces are available in a range of sizes, from small tabletop units to larger industrial models. Their generally compact size makes them perfect for facilities with limited space, such as research labs, vocational schools, and small businesses.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To make an informed decision, you must weigh the benefits against the inherent limitations of the technology. These furnaces are not a universal solution.
Energy Efficiency and Cost
Crucible furnaces are known for having low thermal efficiency, with some fuel-fired models operating as low as 12%. While electric models eliminate direct emissions, they can lead to significantly higher energy costs, which must be factored into any operational budget.
Scale and Volume Limitations
The very nature of a crucible-based system imposes size constraints. These furnaces are not suited for large-scale, high-volume industrial applications where continuous pouring and massive melts are required. They excel in small to medium-batch processing.
Environmental Considerations
Traditional fuel-fired crucible furnaces can produce high emissions. While modern electric versions solve this problem, they shift the cost and environmental impact to the source of electricity generation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a crucible furnace depends entirely on aligning its strengths with your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or diverse, small-batch alloys: A crucible furnace's flexibility and quick changeover capability are its greatest assets.
- If your primary focus is education, R&D, or artisanal metalworking: The ease of use, compact size, and precise temperature control make it an ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous industrial production: You should evaluate other furnace technologies, as a crucible's efficiency and scale will become limiting factors.
Understanding these distinct operational trade-offs empowers you to select the right tool for your specific metalworking goals.
Summary Table:
| Operational Benefit | Key Characteristic | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Operation | Minimal training required, user-friendly design | Education, R&D, small businesses |
| Low Maintenance | Simple mechanics, reduced downtime | Consistent, predictable performance |
| Precise Temperature Control | Excellent for specific melting points | Alloy work, consistent quality |
| Operational Flexibility | Quick alloy changeovers, versatile for various metals | Rapid prototyping, diverse projects |
| Compact Footprint | Available in small to medium sizes | Labs, vocational schools, space-limited facilities |
Ready to Optimize Your Small-Scale Melting Process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and workshops with advanced thermal processing solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements—whether you need the simplicity of a crucible furnace or a more advanced system.
Let us help you achieve superior results with the right equipment for your specific needs.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















