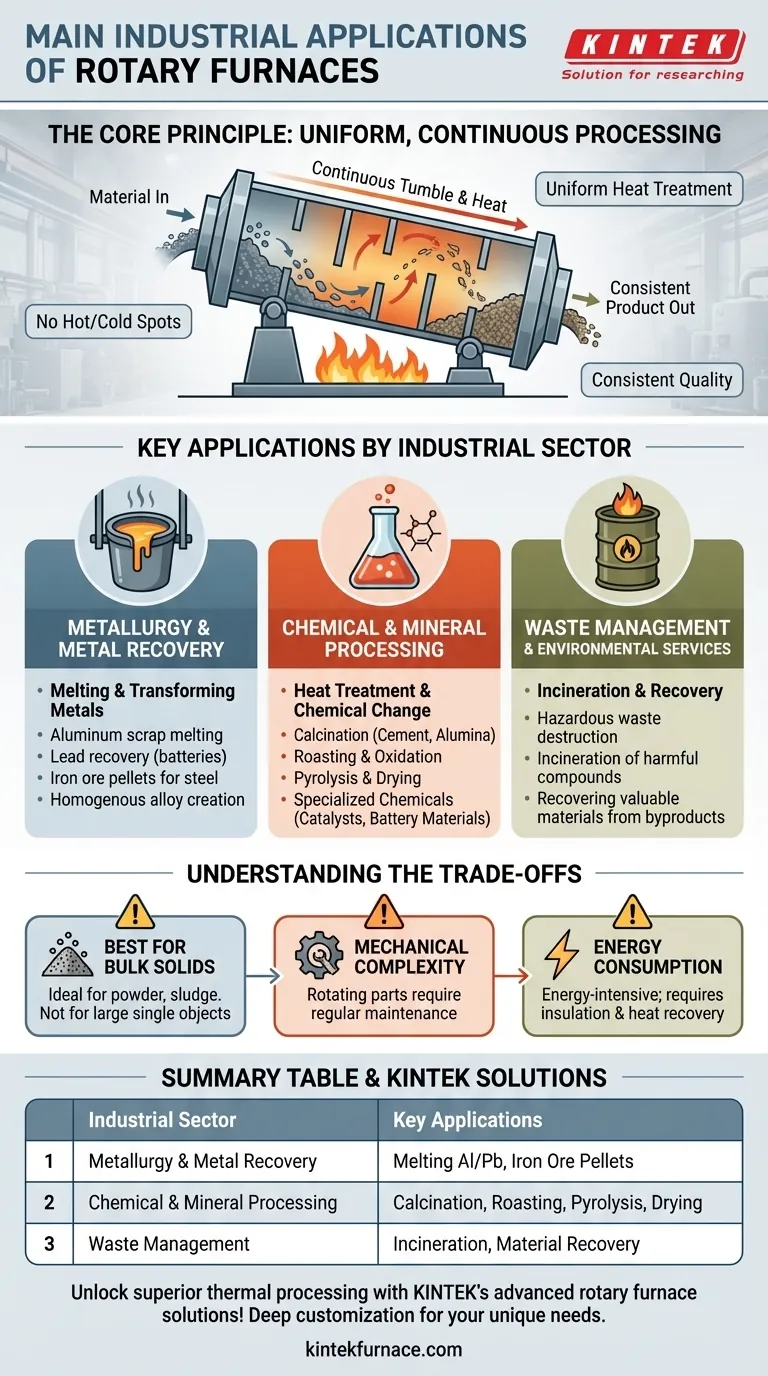
At their core, rotary furnaces serve three primary industrial functions: transforming the chemical or physical properties of materials, melting metals for recycling and production, and processing waste streams. Their versatility allows them to be used in sectors ranging from metallurgy and chemical manufacturing to building materials and environmental services.
The true value of a rotary furnace is not just its high temperature, but its ability to tumble and mix bulk materials continuously. This ensures every particle receives uniform heat treatment, which is critical for consistent product quality in large-scale industrial processes.
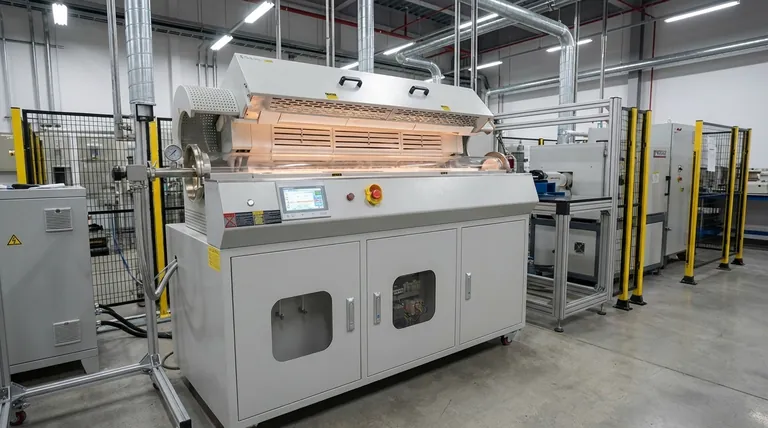

The Core Principle: Uniform, Continuous Processing
A rotary furnace is essentially a large, rotating cylinder (a kiln or retort) that is heated externally or internally. Material is fed into one end, and the gentle tumbling motion caused by the rotation ensures it is evenly exposed to heat as it travels to the other end.
This design is fundamentally different from a static or "batch" furnace. The continuous movement guarantees that there are no hot or cold spots within the material, leading to a highly consistent and predictable final product.
Key Applications by Industrial Sector
The ability to provide uniform, high-temperature treatment to granular or powdered materials makes rotary furnaces indispensable across several major industries.
Metallurgy and Metal Recovery
This is a primary application, focusing on melting and transforming metals. Rotary furnaces are used for smelting ores to extract metals and for melting down scrap for recycling.
Key processes include the melting of aluminum scrap, the recovery of lead from used battery paste, and the creation of iron ore pellets for steel production. The mixing action is excellent for creating homogenous metal alloys.
Chemical and Mineral Processing
This is the broadest field of application, where the goal is to induce a chemical or physical change in a material. This process is often called heat treatment.
Specific applications include:
- Calcination: Heating a material to drive off volatile substances, such as producing cement clinker or alumina.
- Roasting and Oxidation: Heating in the presence of air to cause a chemical reaction, a common step in mineral processing.
- Pyrolysis: Decomposing materials at high temperatures in the absence of oxygen.
- Drying: Removing moisture from powders, crystals, or filter cakes.
These furnaces are also critical for producing specialized chemicals like catalysts, zinc oxide, and materials for lithium batteries, where precise temperature control is paramount.
Waste Management and Environmental Services
Rotary furnaces, often called rotary kilns in this context, are a preferred technology for treating hazardous and non-hazardous waste.
Their high operating temperatures and long residence times ensure the complete incineration and destruction of harmful organic compounds. They are also used to recover valuable materials from industrial byproducts, turning a waste stream into a revenue source.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, rotary furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to proper application.
Best for Bulk Solids
The design excels with granular, powdered, or sludgy materials. It is generally unsuitable for processing single, large, solid objects, which would be better handled in a batch or hearth furnace.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, including the drive system, support rollers, and seals at either end of the kiln, introduces mechanical complexity. These components require regular maintenance to prevent failures and ensure efficient operation.
Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining high temperatures in a large, continuous process is energy-intensive. Proper insulation and heat recovery systems are critical to managing operational costs, but the fundamental energy demand remains significant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing technology depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is transforming bulk minerals or chemicals: A rotary kiln is ideal for ensuring the uniform chemical and physical changes required for processes like calcination or roasting.
- If your primary focus is melting and recycling metals: A tilting rotary furnace provides efficient melting, mixing, and pouring for materials like aluminum scrap or lead paste.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material production: A specialized, indirectly heated rotary tube furnace offers precise temperature control and atmosphere separation for sensitive products like catalysts or battery components.
Understanding these core functions and trade-offs allows you to recognize the precise role and value a rotary furnace brings to any industrial flowsheet.
Summary Table:
| Industrial Sector | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Metallurgy and Metal Recovery | Melting aluminum scrap, lead recovery from batteries, iron ore pellet production |
| Chemical and Mineral Processing | Calcination (e.g., cement clinker), roasting, pyrolysis, drying, catalyst production |
| Waste Management and Environmental Services | Incineration of hazardous waste, material recovery from byproducts |
Unlock superior thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories and industries with high-performance furnaces, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs in metallurgy, chemical processing, or waste management. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















