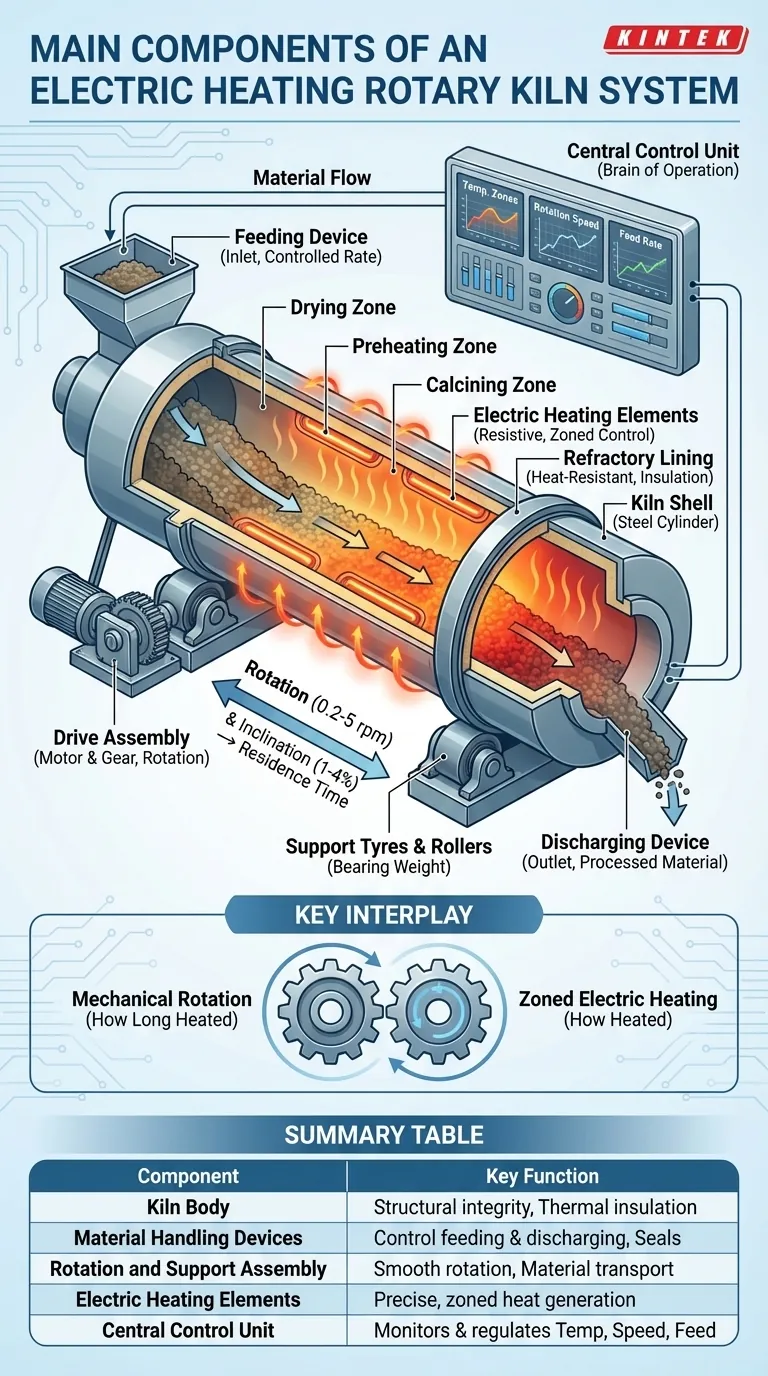
At its core, an electric rotary kiln is an integrated system of five primary components working in unison. These are the kiln body, the material handling devices for feeding and discharging, the rotation and support assembly, the electric heating elements, and the central control unit. Together, they create a precisely controlled, high-temperature environment for processing materials as they move through a rotating cylinder.
While appearing to be a simple rotating furnace, the true function of an electric rotary kiln is defined by the interplay between its mechanical rotation, which dictates how long the material is heated, and its zoned electric heating, which dictates how the material is heated.

The Core Structure: Containment and Insulation
The kiln body is the central vessel where the entire thermal process takes place. Its design is a critical balance between structural integrity and thermal insulation.
The Kiln Shell
The kiln shell is the external steel cylinder or drum. It provides the structural backbone for the entire assembly.
This outer structure supports all other components, including the internal lining, the support tyres, and the drive gear.
The Refractory Lining
Inside the steel shell is a refractory lining, a layer made of high-temperature-resistant bricks or castable material.
This lining has two essential functions: it protects the steel shell from the extreme internal process heat (often up to 1100°C) and it minimizes heat loss to the outside, improving thermal efficiency.
The Engine of Motion: Rotation and Material Transport
The kiln's rotation is not just for mixing; it is the primary mechanism for transporting material from the inlet to the outlet. The speed of this transport is meticulously controlled.
The Drive Assembly
The drive assembly, typically consisting of an electric motor and a large gear, provides the power to rotate the kiln body.
This mechanism ensures the slow, consistent rotation required for uniform material heating.
Support Tyres and Rollers
Large steel rings, known as riding rings or support tyres, are attached to the outside of the kiln shell.
These tyres rest on a series of heavy-duty rollers (or trunnion wheels), which bear the entire weight of the kiln and allow it to rotate smoothly. Thrust rollers are also used to prevent the kiln from sliding downhill due to its inclination.
The Role of Inclination and Speed
The entire kiln is mounted at a slight downward slope, typically between 1% and 4%. This inclination, combined with the rotation speed (usually 0.2 to 5 rpm), determines the rate at which material travels through the kiln.
Controlling these two parameters is how operators manage the material's residence time—the total duration it spends inside the heated zone.
The Heart of the Process: Zoned Electric Heating
Unlike fuel-fired kilns, electric kilns use resistive heating elements for a cleaner and more precisely controlled heat source.
Electric Heating Elements
The heat is generated by electric heating elements, such as alloy wires or silicon carbide rods, strategically placed within the kiln.
These elements are arranged to radiate heat directly onto the material bed, ensuring efficient energy transfer. For example, they are often located at the bottom of the kiln, directly under the material.
The Power of Zoned Temperature Control
Crucially, the heating elements are often grouped into multiple temperature control zones along the length of the kiln.
This allows for the creation of a precise temperature profile. Each zone—such as drying, preheating, and calcining—can be set to a different temperature, allowing the material to be heated gradually and accurately as it progresses.
The Complete System: Material Handling and Control
To function as a continuous process, the kiln relies on systems to introduce raw material, remove the finished product, and manage all operating parameters.
Feeding and Discharging Devices
The feeding device introduces raw material into the upper (inlet) end of the kiln at a controlled rate.
At the lower end, a discharging device collects the processed material as it exits. Both ends typically use specialized seals to contain heat and control the internal atmosphere, which is critical for oxidation or reduction reactions.
The Central Control Unit
The control unit is the brain of the entire operation. This system monitors and regulates all key parameters.
It manages the temperature of each heating zone, the kiln's rotation speed, and the material feed rate to ensure the process is stable, repeatable, and meets the exact specifications required for the final product.
Understanding the Key Operational Trade-offs
While precise, electric rotary kilns come with specific considerations that are critical for efficient and reliable operation.
Energy Cost vs. Precision
Electric heating offers superior temperature control and a clean atmosphere, free from combustion byproducts. However, electricity is often a more expensive energy source than natural gas or other fuels, making operational cost a key factor.
Mechanical Wear and Maintenance
The rotation assembly, particularly the support rollers, tyres, and drive gear, is under constant mechanical stress. Regular inspection and maintenance are mandatory to prevent costly downtime and ensure the kiln's structural integrity.
Refractory Service Life
The internal refractory lining degrades over time due to thermal cycling and chemical interaction with the processed material. The lifespan of the lining is a significant operational constraint, and its eventual replacement represents a major maintenance event.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these components allows you to focus your attention on the parts most critical to your operational success.
- If your primary focus is process control and product quality: The zoned heating elements and the central control unit are your most critical components for achieving a precise thermal profile.
- If your primary focus is operational uptime and reliability: Pay close attention to the drive assembly, support rollers, and the integrity of the refractory lining through regular maintenance.
- If your primary focus is thermal efficiency and cost: Proper insulation from the refractory lining and effective sealing at the material inlet and outlet are paramount to minimizing energy loss.
Recognizing how these components function as an integrated system is the first step toward mastering your high-temperature material processing.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Kiln Body | Provides structural integrity and thermal insulation for the process chamber |
| Material Handling Devices | Control feeding and discharging of materials with specialized seals |
| Rotation and Support Assembly | Enables smooth rotation and material transport via drive, tyres, and rollers |
| Electric Heating Elements | Generate precise, zoned heat for controlled temperature profiles |
| Central Control Unit | Monitors and regulates temperature, rotation speed, and feed rate for stability |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's high-temperature processing with a custom electric rotary kiln? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, boosting efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems



















