At its core, a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace is an integrated system designed to melt metals and alloys in a highly controlled, oxygen-free environment. The main components are the furnace body, a vacuum system, a medium-frequency power supply paired with an induction coil, a material handling mechanism, and a central control system. Each part works objetivos to achieve the precise conditions needed for producing high-purity, homogenous metals.
A VIM furnace is not just a heater. It is a sophisticated metallurgical tool where the vacuum system creates a pristine environment, and electromagnetic induction simultaneously heats, melts, and stirs the metal, ensuring superior purity and uniformity.
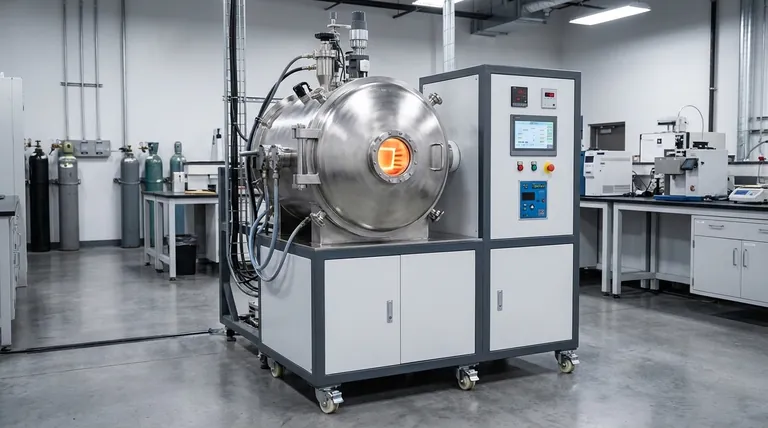

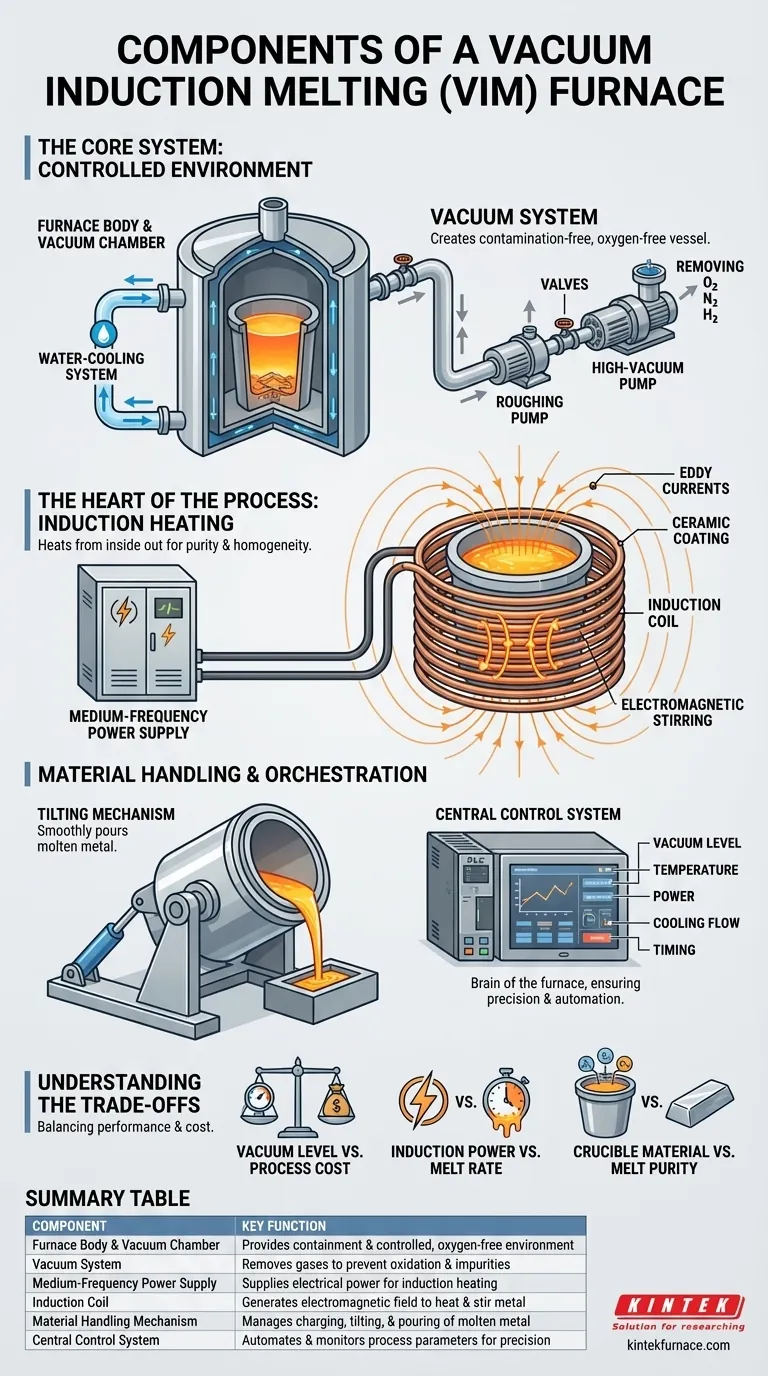
The Core System: Creating a Controlled Environment
To produce high-quality alloys, you must first have absolute control over the melting environment. The furnace body and vacuum system work together to create a contamination-free reaction vessel.
The Furnace Body & Vacuum Chamber
The furnace body is the primary containment vessel. It is typically a double-walled, high-strength steel chamber.
This double-wall design creates a "water jacket." A water-cooling system constantly circulates water through this jacket to manage the intense heat, protecting the structural integrity of the furnace and its critical seals.
The Vacuum System
The vacuum system is what puts the "vacuum" in VIM. Its purpose is to remove air—and specifically oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen—from the chamber before and during melting.
This system consists of a series of pumps and valves. A roughing pump first removes the bulk of the air, and then a high-vacuum pump (like a diffusion or turbo-molecular pump) takes the chamber压力 to the required low level. Removing these atmospheric and dissolved gases is essential to prevent oxidation and the formation of impurities.
The Heart of the Process: Induction Heating
Unlike a traditional furnace that uses external burners or electric resistance, a VIM furnace heats the metal from the inside out using electromagnetic forces.
The Medium-Frequency Power Supply
This is the high-amperage electrical source. The power supply converts standard plant power into the specific medium-frequency current required to drive the induction process. The power level AgNOSTICS determines the melt rate and maximum temperature.
The Induction Coil (Inductor)
The induction coil is a precision-wound spiral of hollow copper tubing, often coated in a ceramic refractory for insulation. The power supply energizes this coil, creating a powerful, rapidly alternating electromagnetic field.
When a conductive metal charge is placed inside the coil, this field induces strong electrical eddy currents within the metal itself. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense, rapid heat. This process also creates a natural electromagnetic stirring action, ensuring отличный temperature and compositional homogeneity in the molten bath.
Material Handling and Orchestration
Once the environment is set and the heating mechanism is active, other components manage the physical process and ensure everything works in harmony.
The Tilting Mechanism
To pour the molten metal into a mold, the entire furnace assembly must be tilted. A hydraulic or electromechanical tilting mechanism provides the force and control to do this smoothly and safely.
The Central Control System
This is the brain of the furnace. Modern VIM systems use a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC), sensors, and a human-machine interface (like a touch screen).
The control system monitors and regulates every critical parameter in real time, including vacuum level, temperature, power padrões, cooling water flow, and process timing. This automation ensures repeatability and precision.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting or operating a VIM furnace involves balancing competing priorities. Each component choice has direct implications for performance and cost.
Vacuum Level vs. Process Cost
Achieving a deeper vacuum results in higher-purity metal by removing more dissolved gases. However, this requires more advanced, expensive, and slower pumping systems, which increases both capital investment and cycle time.
Induction Power vs. Melt Rate
A more powerful medium-frequency supply will melt metal faster, increasing throughput. This requires a more robust power infrastructure and a more capable cooling system, significantly raising operating costs.
Crucible Material vs. Melt Purity
The crucible, or refractory lining, that holds the molten metal is not inert. It can slowly react with the alloy, introducing trace impurities. The choice of crucible material is a critical trade-off between its cost, lifespan, and chemical compatibility with the specific metal being produced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal VIM furnace configuration depends entirely on your primary metallurgical objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity for superalloys: Invest in a high-performance vacuum system with multiple pumping stages and carefully select your crucible materials.
- If your primary focus is high throughput for specialty steels: Prioritize a powerful medium-frequency power supply, an efficient cooling system, and a robust tilting mechanism.
- If your primary focus is alloy development and flexibility: Emphasize a sophisticated PLC control system with advanced data logging and a furnace design that allows for easy crucible changes.
Understanding how these components function as an integrated system is the first step toward mastering the production of high-performance alloys.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Furnace Body & Vacuum Chamber | Provides containment and controlled, oxygen-free environment |
| Vacuum System | Removes gases to prevent oxidation and impurities |
| Medium-Frequency Power Supply | Supplies electrical power for induction heating |
| Induction Coil | Generates electromagnetic field to heat and stir metal |
| Material Handling Mechanism | Manages charging, tilting, and pouring of molten metal |
| Central Control System | Automates and monitors process parameters for precision |
Ready to elevate your metal production with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, is enhanced by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on superalloys, specialty steels, or alloy development, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our VIM furnaces can optimize your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















