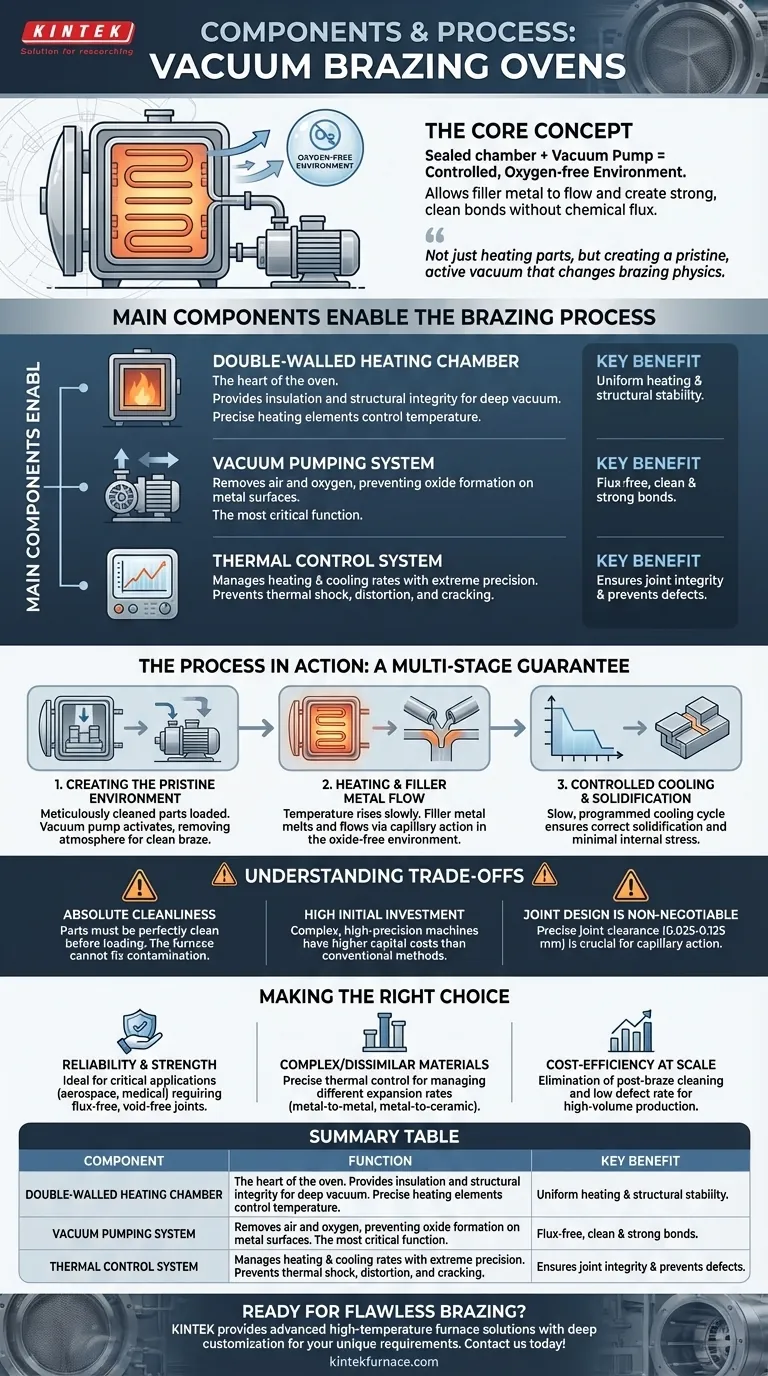
At its core, a vacuum brazing oven consists of two primary components: a sealed, double-walled heating chamber and a powerful vacuum pump system. These parts work in concert to create a highly controlled, oxygen-free environment. This allows a filler metal to melt and flow into the joints of an assembly, creating exceptionally clean and strong bonds without the need for chemical flux.
The simplicity of a vacuum oven's core components belies its true function. Its purpose is not merely to heat parts, but to create a pristine, active vacuum that fundamentally changes the physics of the brazing process, enabling metallurgical bonds that are impossible to achieve in open air.

How the Components Enable the Brazing Process
A vacuum furnace is an integrated system where each component plays a critical role in achieving a perfect braze. Understanding how they interact reveals why this process is chosen for high-stakes applications.
The Double-Walled Heating Chamber
This is the heart of the oven, where the entire thermal process takes place. Its double-walled construction provides insulation and ensures structural integrity when a deep vacuum is pulled. Inside, sophisticated heating elements precisely control the temperature of the parts being brazed.
The Vacuum Pumping System
This system is responsible for removing air—and most importantly, oxygen—from the heating chamber. By eliminating oxygen, the furnace prevents the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces as they are heated. This is the single most important function that separates vacuum brazing from other methods.
The Thermal Control System
An integrated but distinct system, the thermal controller manages the heating and cooling rates with extreme precision. It gradually ramps the temperature up to the filler metal's melting point (e.g., 580-620°C for aluminum), holds it there to allow flow, and then controls the cooling rate to prevent thermal shock, distortion, or cracking in the final assembly.
The Process in Action
These components facilitate a multi-stage process that guarantees joint integrity.
Step 1: Creating the Pristine Environment
After meticulously cleaned parts are loaded and the chamber is sealed, the vacuum pump system activates. It removes the atmosphere, creating the clean environment necessary for the braze to succeed.
Step 2: Heating and Filler Metal Flow
The thermal control system and heating elements work together to slowly raise the temperature. Once the brazing temperature is reached, the filler metal melts. Because the vacuum has prevented any oxides from forming on the base metals, the molten filler flows cleanly and evenly into the joint through capillary action.
Step 3: Controlled Cooling and Solidification
Once the filler has fully penetrated the joint, the thermal control system initiates a slow, programmed cooling cycle. This ensures the filler metal solidifies correctly and that the finished assembly is free from internal stresses, which is critical when joining dissimilar materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the vacuum brazing process is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is dependent on controlling variables both inside and outside the furnace.
The Absolute Need for Cleanliness
A vacuum furnace cannot fix contaminated parts. The process relies on the parts being perfectly clean before they are loaded. Any residual oils, dirt, or heavy oxides will inhibit the braze, and the furnace environment cannot remove them.
High Initial Investment
Vacuum brazing furnaces are complex, high-precision machines. The initial capital cost is significantly higher than for conventional ovens or torch brazing setups.
Joint Design is Non-Negotiable
The process is precise, not forgiving. For capillary action to work effectively, the clearance between the parts to be joined must be tightly controlled, typically between 0.025 mm and 0.125 mm. An incorrect gap will result in a failed joint, regardless of the furnace's quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting vacuum brazing depends entirely on the required outcome for your components.
- If your primary focus is reliability and strength: The flux-free, void-free joints created in a vacuum are ideal for critical applications like aerospace, medical, and high-performance automotive parts.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or dissimilar materials: The precise thermal control of a vacuum furnace is essential for managing different expansion rates and preventing stress when joining metals to other metals or to ceramics.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency at scale: Despite the high initial cost, the elimination of post-braze cleaning and the extremely low defect rate make vacuum brazing highly efficient for high-volume production.
Ultimately, a vacuum brazing oven is a tool for achieving metallurgical perfection in a controlled environment.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Double-Walled Heating Chamber | Provides insulation and houses heating elements for precise temperature control | Ensures structural integrity and uniform heating in a vacuum environment |
| Vacuum Pumping System | Removes air and oxygen to prevent oxide formation | Enables flux-free brazing for exceptionally clean and strong bonds |
| Thermal Control System | Manages heating and cooling rates with precision | Prevents thermal shock and distortion, ensuring joint integrity |
Ready to achieve flawless brazing results? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum brazing ovens can enhance your process with reliable, high-strength joints for aerospace, medical, and other critical applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do the radiant heating and controlled cooling functions of a vacuum brazing furnace benefit Kovar-to-SS joints?
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- Why is precise temperature and time control in a vacuum brazing furnace necessary for joint performance? Get Expert Tips
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?



















