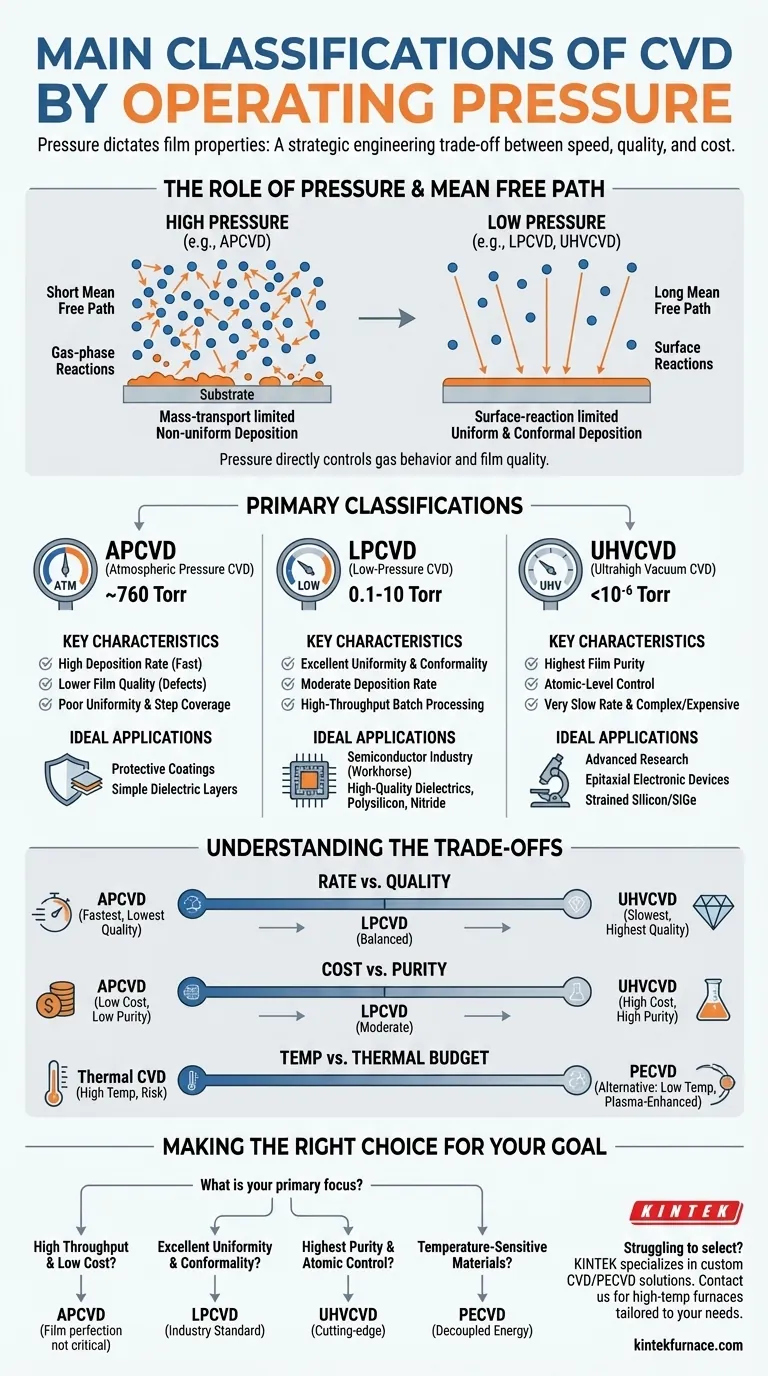
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is classified based on the pressure inside the reaction chamber, as this fundamentally dictates the film's properties. The main classifications are Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD), Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD), and Ultrahigh Vacuum CVD (UHVCVD). Most modern, high-precision applications rely on LPCVD or UHVCVD to achieve superior film quality.
The choice between different CVD processes is a strategic engineering decision. It involves a critical trade-off between deposition speed, the quality of the resulting film (its uniformity and purity), and the overall cost and complexity of the operation.
The Role of Pressure in Film Deposition
The operating pressure is the single most important parameter in a CVD process because it directly controls the behavior of gas molecules. This, in turn, determines the quality and characteristics of the deposited film.
Understanding Mean Free Path
Pressure determines the mean free path—the average distance a gas molecule travels before colliding with another.
At high pressure (like in APCVD), the mean free path is very short. This leads to frequent collisions in the gas phase, often causing reactions to occur before the precursor molecules even reach the substrate surface.
At low pressure (like in LPCVD and UHVCVD), the mean free path is much longer. Molecules are more likely to travel directly to the substrate surface without interruption, making the deposition process more controlled.
The Impact on Deposition Mechanism
This difference in mean free path creates two distinct deposition regimes.
Mass-transport limited processes, common in APCVD, are dominated by the rate at which reactant gases can diffuse through the dense gas layer to the substrate. This often results in non-uniform deposition.
Surface-reaction limited processes, characteristic of LPCVD, are governed by the rate at which chemical reactions occur on the substrate surface itself. This is slower but results in highly uniform and conformal films.
Primary Classifications by Operating Pressure
Each pressure regime offers a distinct set of advantages and is suited for different applications.
Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD)
APCVD operates at standard atmospheric pressure. Because of the high pressure and short mean free path, it is characterized by very high deposition rates.
However, this speed comes at the cost of film quality. The process is prone to gas-phase reactions that can form particles, leading to defects. The resulting films often have poor uniformity and step coverage (the ability to evenly coat complex, non-flat surfaces).
Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD)
LPCVD operates at pressures significantly below atmosphere (e.g., 0.1-10 Torr). This increases the mean free path, allowing the process to become surface-reaction limited.
The result is films with excellent uniformity and conformality, making LPCVD the workhorse of the semiconductor industry for depositing layers over intricate device structures. It allows for high-density vertical stacking of wafers, enabling high-throughput batch processing.
Ultrahigh Vacuum CVD (UHVCVD)
UHVCVD operates at extremely low pressures (typically below 10⁻⁶ Torr), creating a near-perfect vacuum. This environment minimizes gas-phase contaminants to an extreme degree.
This process offers the highest possible film purity and precise, atomic-level control over growth. It is used for creating highly advanced materials, such as strained silicon or SiGe heterostructures, but it is very slow and requires expensive, complex equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a CVD method requires balancing competing priorities. No single process is best for every application.
Rate vs. Quality
There is a direct trade-off between deposition speed and film quality.
APCVD offers the fastest deposition but produces the lowest quality films in terms of uniformity and purity. UHVCVD provides the highest quality and purity but is exceptionally slow. LPCVD strikes a balance, offering excellent quality at a moderate rate.
Cost vs. Purity
The equipment required for vacuum operation dictates the cost. APCVD systems are relatively simple and inexpensive.
LPCVD systems require robust vacuum pumps and controls, increasing their cost. UHVCVD systems are orders of magnitude more expensive due to the need for ultra-clean materials and sophisticated pumping systems to achieve and maintain extreme vacuums.
Temperature vs. Thermal Budget
Thermal CVD processes (APCVD, LPCVD) typically require high temperatures to drive the chemical reactions. This can damage temperature-sensitive substrates or underlying device layers.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is a critical alternative. By using a plasma to generate reactive chemical species, PECVD can achieve high-quality film deposition at much lower temperatures, making it essential for modern device fabrication.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements will determine the optimal CVD process.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and low cost: APCVD is often the best choice for applications where film perfection is not critical, such as protective coatings or simple dielectric layers.
- If your primary focus is excellent film uniformity and conformality: LPCVD is the industry standard for depositing high-quality dielectrics, polysilicon, and nitride films in microelectronics.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible film purity and atomic-level control: UHVCVD is necessary for cutting-edge research and the fabrication of advanced epitaxial electronic devices.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive materials: PECVD is the essential solution, as it decouples the reaction energy from thermal input.
Understanding these foundational operating conditions empowers you to select the process that aligns precisely with your technical goals and economic constraints.

Summary Table:
| Classification | Operating Pressure | Key Characteristics | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| APCVD | Atmospheric (~760 Torr) | High deposition rate, lower film quality, poor uniformity | Protective coatings, simple dielectric layers |
| LPCVD | Low (0.1-10 Torr) | Excellent uniformity and conformality, moderate rate | Semiconductor industry, high-quality dielectrics |
| UHVCVD | Ultrahigh Vacuum (<10⁻⁶ Torr) | Highest purity, atomic-level control, very slow | Advanced research, epitaxial electronic devices |
| PECVD | Variable (with plasma) | Low-temperature deposition, good quality | Temperature-sensitive materials, modern device fabrication |
Struggling to select the right CVD process for your lab's unique needs? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to diverse laboratory requirements. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely match your experimental goals—whether you need superior film quality, high throughput, or low-temperature capabilities. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your CVD operations and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication



















