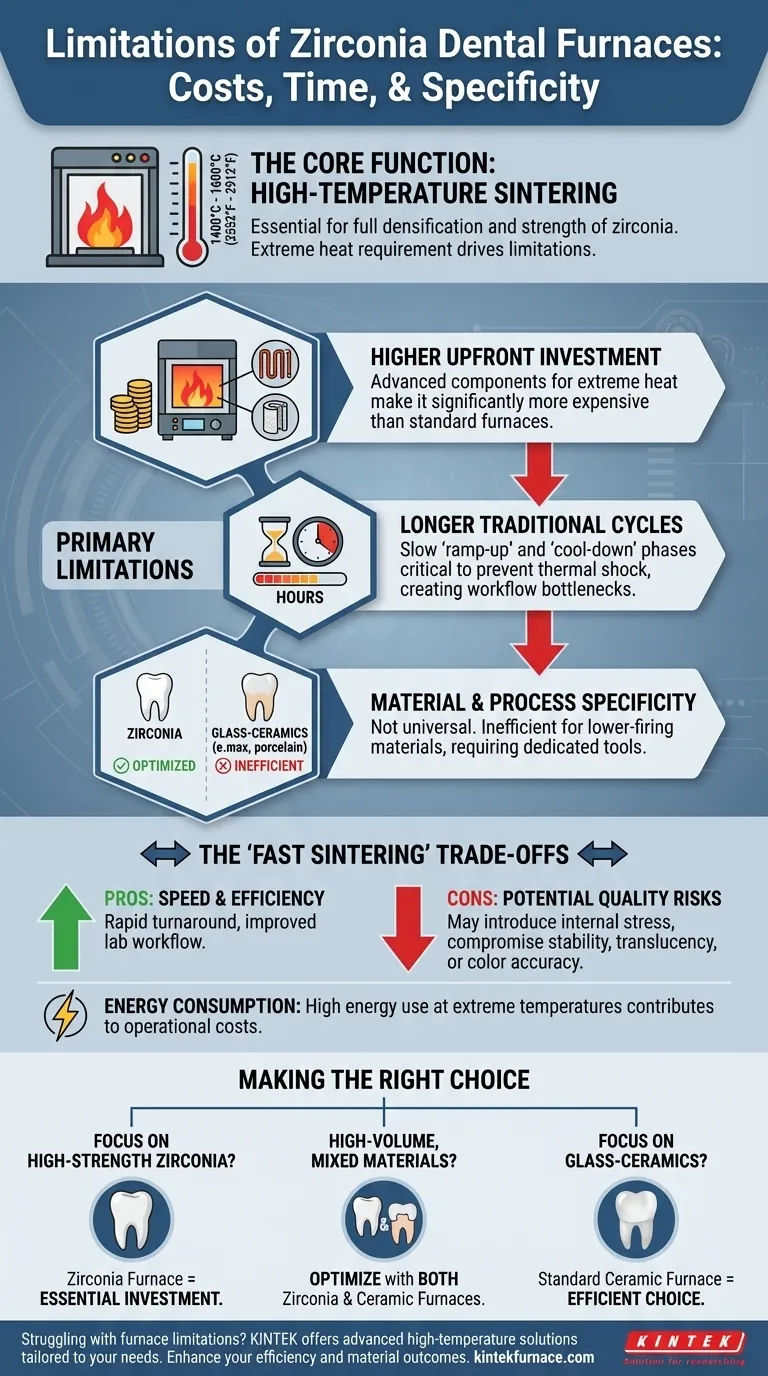
At their core, the primary limitations of a zirconia dental furnace are its higher upfront cost, longer traditional cycle times, and its specialized nature. While essential for processing high-strength zirconia, it is not a universal solution for all dental ceramics, making it an inefficient choice for labs or practices that do not regularly work with this material.
A zirconia furnace is a highly specialized instrument designed for a single, demanding task: sintering zirconia at extremely high temperatures. Its limitations are not flaws in design but are direct consequences of this specialization, revolving around cost, operational time, and a lack of versatility for lower-temperature materials.

The Core Function: High-Temperature Sintering
To understand the limitations of a zirconia furnace, you must first understand its fundamental purpose. Its entire design is built around achieving the extreme temperatures necessary to process zirconia.
The High Heat Requirement
Zirconia restorations require a process called sintering to achieve their final density, strength, and aesthetic properties. This process requires extremely high temperatures, typically ranging from 1400°C to 1600°C (2552°F to 2912°F).
Why This Temperature is Necessary
Only at these temperatures can the pre-sintered zirconia particles fuse together and fully densify. Inadequate heat results in a porous, weak, and aesthetically poor final restoration. This high-temperature capability is what separates zirconia furnaces from standard ceramic or porcelain furnaces.
Analyzing the Primary Limitations
The demanding technical requirements of a zirconia furnace lead directly to its main operational and financial drawbacks.
Higher Upfront Investment
To safely and consistently reach 1600°C, a furnace requires advanced components. This includes high-purity heating elements (like silicon molybdenum rods) and robust, multi-layered insulation. These specialized parts make zirconia furnaces significantly more expensive than standard porcelain furnaces.
Traditionally Longer Sintering Cycles
A complete, conventional sintering cycle can take several hours. This is not just about the time spent at the peak temperature but also includes the slow, controlled "ramp-up" and "cool-down" phases, which are critical for preventing thermal shock and cracking in the restorations. This can create a significant bottleneck in a high-volume lab's workflow.
Material and Process Specificity
A zirconia furnace is optimized for high-temperature sintering. Using it for low-firing materials like glass-ceramics (e.g., e.max) or feldspathic porcelain is inefficient. These materials require different, lower-temperature profiles, making a dedicated zirconia furnace an unsuitable and expensive tool for that work.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Nuance of "Fast Sintering"
Many modern furnaces advertise "fast sintering" cycles, some as short as 65 minutes. While this feature addresses the limitation of long cycle times, it introduces a critical set of trade-offs that every technician must consider.
The Promise of Speed
Fast cycles dramatically improve single-day turnaround times and overall lab efficiency. They achieve this with extremely rapid heating rates and abbreviated holding times.
The Potential Cost of Speed
This speed can come at a cost. Rapid heating and cooling may introduce internal stresses into the zirconia framework. This can potentially compromise the material's long-term stability or have a negative impact on its final translucency and color accuracy. The manufacturer's instructions for both the furnace and the zirconia material must be followed precisely.
The Energy Consumption Factor
Reaching temperatures of 1500°C or more requires a substantial amount of energy. While modern furnaces use efficient insulation, they are still energy-intensive devices, especially compared to lower-temperature porcelain furnaces. This contributes to higher long-term operational costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the primary materials used in your lab or practice.
- If your primary focus is high-strength zirconia restorations: A dedicated zirconia furnace is a non-negotiable and essential investment for achieving proper clinical results.
- If you run a high-volume lab with mixed materials: Optimizing workflow may require owning both a zirconia furnace for high-temp work and a separate, more versatile ceramic furnace for lower-firing materials.
- If your practice primarily uses glass-ceramics or porcelain: A zirconia furnace is an unnecessary expense and operational burden; a standard, lower-temperature ceramic furnace is the more appropriate and efficient choice.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is a strategic decision that aligns your equipment capabilities with your clinical and business objectives.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Higher Upfront Cost | More expensive due to advanced components for high temperatures (1400-1600°C). |
| Longer Cycle Times | Traditional sintering cycles take hours, potentially slowing workflow. |
| Material Specificity | Optimized for zirconia; inefficient for low-temperature ceramics like e.max or porcelain. |
| Energy Consumption | High energy use at extreme temperatures increases operational costs. |
| Trade-offs with Fast Sintering | Rapid cycles may compromise material stability, translucency, or color accuracy. |
Struggling with furnace limitations in your dental lab? KINTEK offers advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet unique experimental requirements. Enhance your efficiency and material outcomes—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the recommended maintenance practices for dental furnaces? Ensure Precision and Longevity for Your Lab
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision
- What is the importance of dental furnaces in dentistry? Ensure Strong, Precise Dental Restorations
- What role does temperature range and accuracy play in dental furnace performance? Ensure Precision for Superior Dental Restorations
- What are the primary functions of ceramic dental furnaces? Achieve Precision and Durability in Dental Restorations



















