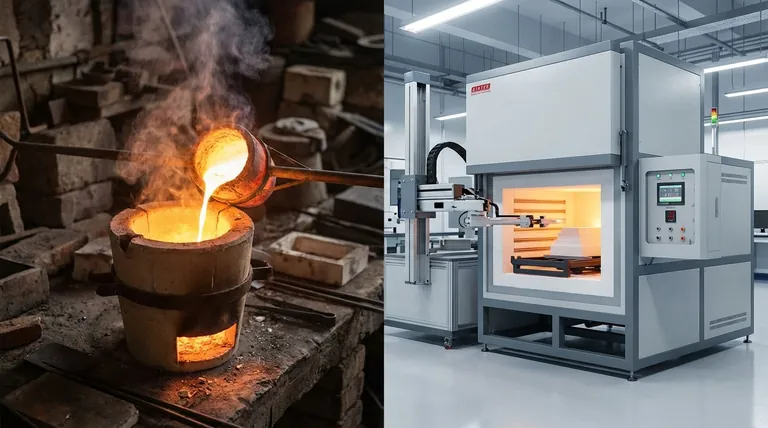
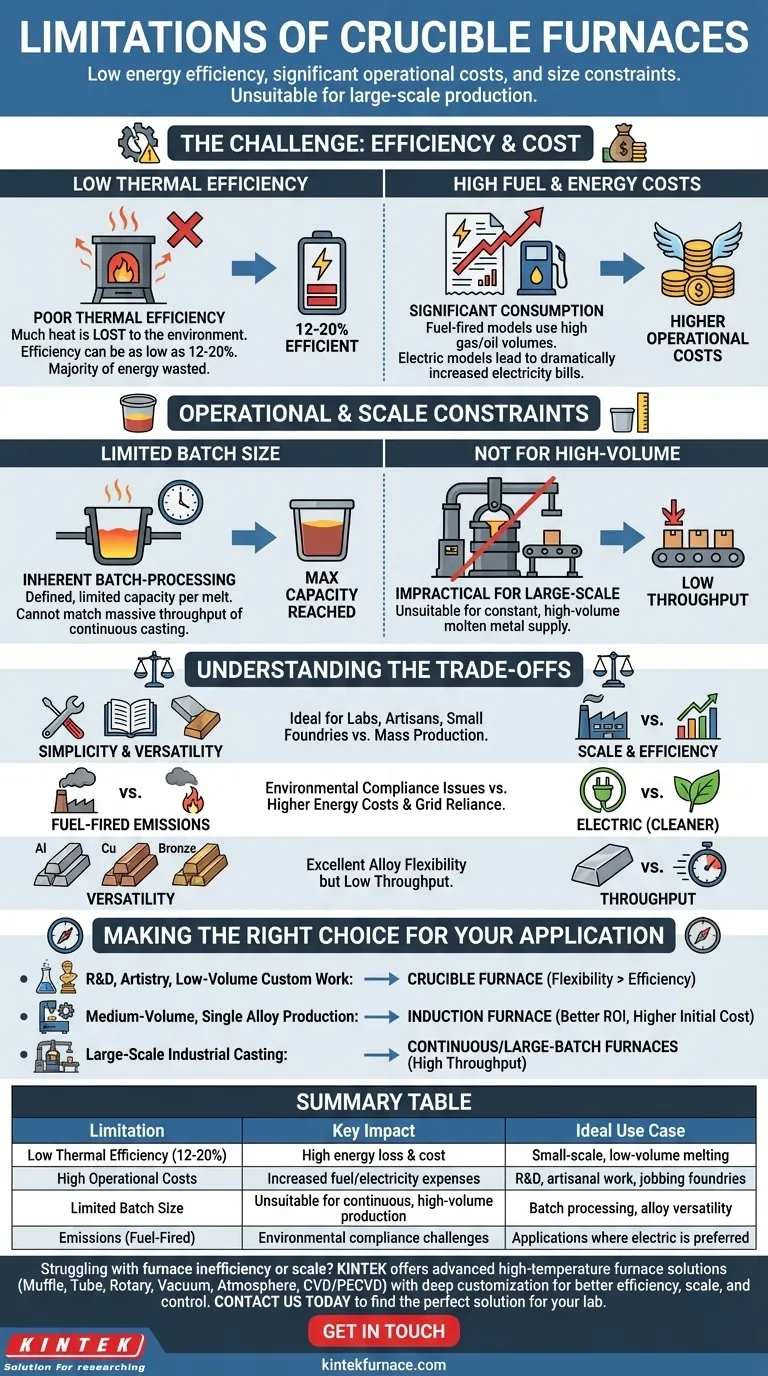
At their core, the primary limitations of crucible furnaces are low energy efficiency, significant operational costs, and inherent size constraints that make them unsuitable for large-scale production. Traditional fuel-fired models also present challenges with high emissions, while their electric counterparts can lead to higher utility expenses.
While crucible furnaces are valued for their simplicity and versatility in handling different metals, their design fundamentally trades large-scale production capacity and energy efficiency for operational flexibility and a smaller footprint.

The Challenge of Efficiency and Cost
The most significant drawbacks of crucible furnaces often relate to their energy consumption and the resulting operational costs. These factors can heavily influence their suitability for commercial applications.
Low Thermal Efficiency
Crucible furnaces are known for their poor thermal efficiency. Much of the heat generated by the fuel or electrical elements is lost to the surrounding environment rather than being absorbed by the metal charge.
In some cases, the efficiency can be as low as 12-20%, meaning the vast majority of energy consumed does not contribute to melting the metal. This is a direct consequence of their simple, indirect heating design.
High Fuel and Energy Costs
This low efficiency translates directly into higher operational costs. Fuel-fired furnaces consume significant amounts of gas or oil, while electric models can dramatically increase electricity bills.
For businesses operating on tight margins, these high energy costs can make crucible furnaces economically unviable for high-volume production compared to more efficient alternatives like induction or channel furnaces.
Operational and Scale Constraints
Beyond cost, the physical design and operating principle of crucible furnaces impose practical limits on their use in industrial settings.
Limited Batch Size
Crucible furnaces are inherently batch-processing systems with a defined, limited capacity. The size of the crucible itself dictates the maximum volume of metal that can be melted at one time.
While sizes range from small tabletop units to larger industrial models, they cannot match the massive throughput of furnaces designed for continuous casting or large-scale foundries. This makes them impractical for applications requiring a constant, high-volume supply of molten metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To make an informed decision, you must weigh these limitations against the furnace's distinct advantages. The choice often comes down to balancing operational needs with physical and financial constraints.
Simplicity vs. Scale
The key trade-off is simplicity for scale. Crucible furnaces are famously easy to operate and maintain, requiring minimal specialized training.
This simplicity, however, is a direct result of a design that is not optimized for large volumes. They are ideal for labs, artisans, or small foundries where ease of use is more critical than mass production.
Emissions: Fuel-Fired vs. Electric
Traditional, fuel-fired crucible furnaces can produce significant emissions and combustion byproducts, which can be a major issue for environmental compliance.
Modern electric crucible furnaces nearly eliminate this problem, offering a clean melting process. However, this advantage is traded for potentially higher energy costs and a greater reliance on the electrical infrastructure.
Versatility vs. Throughput
Crucible furnaces offer excellent versatility. Since the metal is contained within a chemically inert crucible, you can switch between different alloys (e.g., from aluminum to bronze) with minimal contamination risk.
This flexibility is invaluable for jobbing foundries or R&D labs but comes at the cost of low throughput. Furnaces designed for high throughput, like channel furnaces, are typically dedicated to a single alloy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your specific goals, production volume, and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is R&D, artistry, or low-volume custom work: The versatility and simplicity of a crucible furnace often outweigh its efficiency limitations.
- If your primary focus is medium-volume production of a single alloy: A more efficient furnace type, such as an induction furnace, may provide a better return on investment despite a higher initial cost.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial casting: Crucible furnaces are not a practical choice; continuous or large-batch furnaces are necessary to meet production demands.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs empowers you to select the right tool for your specific operational needs.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Low Thermal Efficiency (12-20%) | High energy loss & cost | Small-scale, low-volume melting |
| High Operational Costs | Increased fuel/electricity expenses | R&D, artisanal work, jobbing foundries |
| Limited Batch Size | Unsuitable for continuous, high-volume production | Batch processing, alloy versatility |
| Emissions (Fuel-Fired) | Environmental compliance challenges | Applications where electric is preferred |
Struggling with furnace inefficiency or scale limitations? KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions are engineered to overcome these challenges. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with superior alternatives like our Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, as well as Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, offering better efficiency, scale, and control. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace solution for your specific needs and maximize your lab's performance → Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















