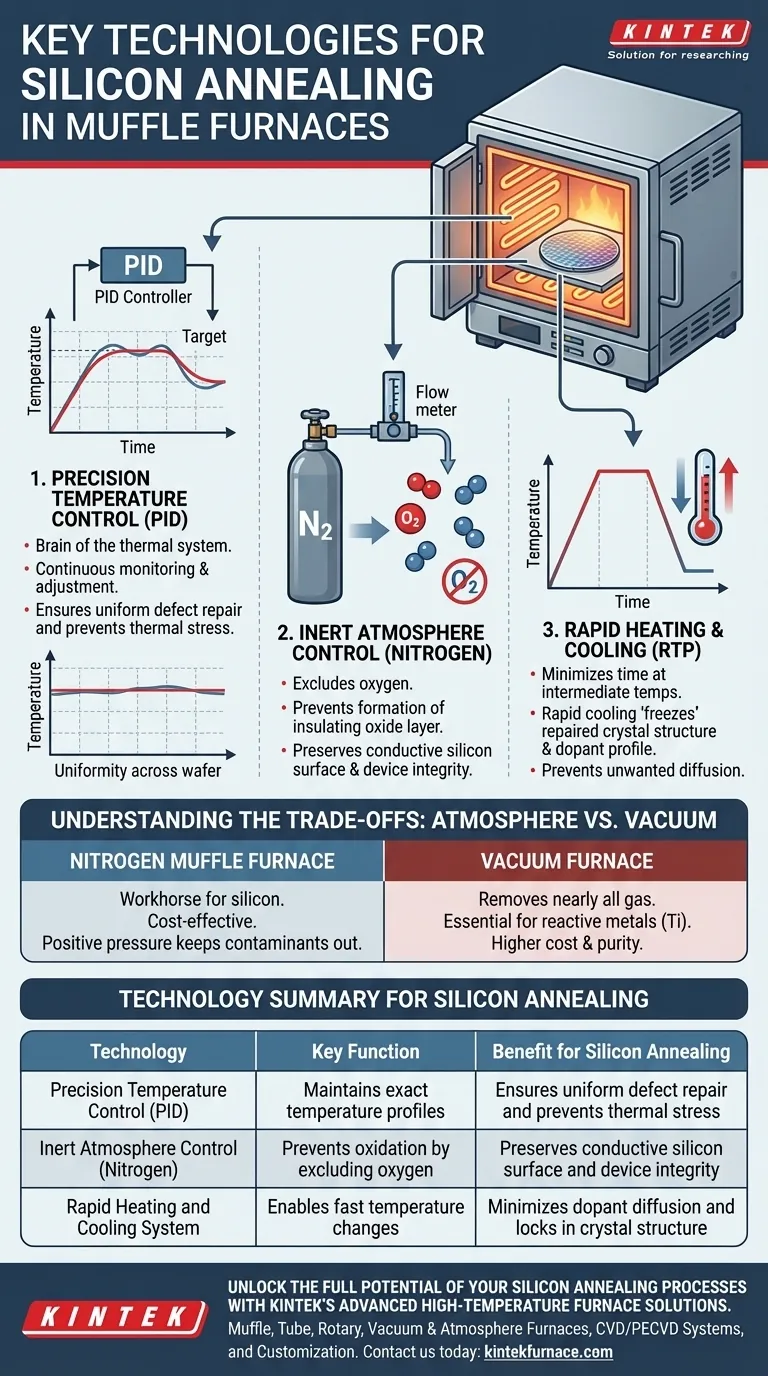
At its core, the effective annealing of silicon-based materials in a muffle furnace relies on three synergistic technologies. These are a precision temperature control system (typically PID), an inert nitrogen atmosphere control system, and a rapid heating and cooling system. Together, they repair crystal lattice damage and electrically activate dopants without introducing new defects like surface oxidation.
The challenge of annealing silicon is not simply heating it up; it's about executing a precise thermal recipe to enhance its electrical properties while protecting its delicate surface and structure. The key technologies are designed to manage heat, atmosphere, and time with extreme precision.

The Core Challenge: Preserving Silicon's Integrity
Annealing is a thermal treatment designed to alter a material's microstructure, relieving internal stresses and improving properties like ductility and electrical conductivity. For silicon in semiconductor manufacturing, this process is critical but fraught with risk.
The Goal: Repairing Crystal Damage
During processes like ion implantation, the silicon crystal lattice becomes damaged. Annealing provides the thermal energy needed for atoms to rearrange themselves back into an ordered, crystalline state, which is essential for proper semiconductor function.
The Risk: Unwanted Reactions and Defects
If not controlled perfectly, the high temperatures can cause unwanted side effects. Silicon readily reacts with oxygen to form silicon dioxide (an insulator), and excessive time at temperature can cause implanted dopants to diffuse too far, ruining the precise electronic junctions of a device.
A Breakdown of Key Annealing Technologies
Each technology in a modern muffle furnace addresses a specific risk associated with annealing silicon.
1. Precision Temperature Control (PID)
A Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller is the brain of the furnace's thermal system. It continuously monitors the temperature and adjusts the heating elements to match a programmed profile with exceptional accuracy.
This precision is non-negotiable. It ensures every part of the silicon wafer receives the exact same thermal treatment, guaranteeing uniform defect repair and preventing thermal stress that could crack the material.
2. Inert Atmosphere Control (Nitrogen)
To prevent the formation of an insulating oxide layer, the annealing chamber is purged of oxygen and filled with an inert gas. Nitrogen (N2) is the industry standard for this task.
By creating a nitrogen-rich environment, the process starves the silicon surface of the oxygen it needs to react. This preserves the silicon's pure, conductive surface, which is critical for subsequent manufacturing steps and final device performance.
3. Rapid Heating and Cooling
The system is designed to change temperatures quickly. This is often referred to as Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP), even when performed in a furnace.
Rapidly heating minimizes the total time the silicon spends at intermediate temperatures, while rapid cooling "freezes" the repaired crystal structure and desired dopant profile in place. This prevents unwanted diffusion and preserves the integrity of the microscopic electronic structures built into the silicon.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
While a nitrogen atmosphere is standard for silicon, the references also mention vacuum furnaces. Understanding the difference is key to appreciating why specific choices are made.
The Role of a Nitrogen Muffle Furnace
This is the workhorse for most silicon-based semiconductor annealing. It provides an excellent, cost-effective solution for preventing oxidation. The positive pressure of the nitrogen gas is highly effective at keeping ambient air and contaminants out of the process chamber.
When to Consider a Vacuum Furnace
Vacuum furnaces remove nearly all gas from the chamber, creating an even purer environment. They are essential for annealing highly reactive metals (like titanium) or for applications in medical devices and aerospace where even trace gas interaction is unacceptable. For standard silicon processing, this level of purity is often unnecessary and more costly to achieve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of annealing technology depends directly on your material and your end goal.
- If your primary focus is annealing silicon wafers for standard semiconductors: A muffle furnace with precision PID temperature control and a flowing nitrogen atmosphere is the ideal and most common solution.
- If your primary focus is annealing stainless steel components or highly reactive metals: A vacuum furnace is required to prevent the specific types of contamination and surface interactions relevant to those materials.
- If your primary focus is maximizing process repeatability and yield: Invest in a system with tightly-regulated PID control and mass flow controllers for the nitrogen supply to ensure every run is identical.
Mastering the thermal process is fundamental to unlocking the full potential of your engineered materials.
Summary Table:
| Technology | Key Function | Benefit for Silicon Annealing |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Temperature Control (PID) | Maintains exact temperature profiles | Ensures uniform defect repair and prevents thermal stress |
| Inert Atmosphere Control (Nitrogen) | Prevents oxidation by excluding oxygen | Preserves conductive silicon surface and device integrity |
| Rapid Heating and Cooling System | Enables fast temperature changes | Minimizes dopant diffusion and locks in crystal structure |
Unlock the full potential of your silicon annealing processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our precision technologies can enhance your lab's efficiency and yield!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















