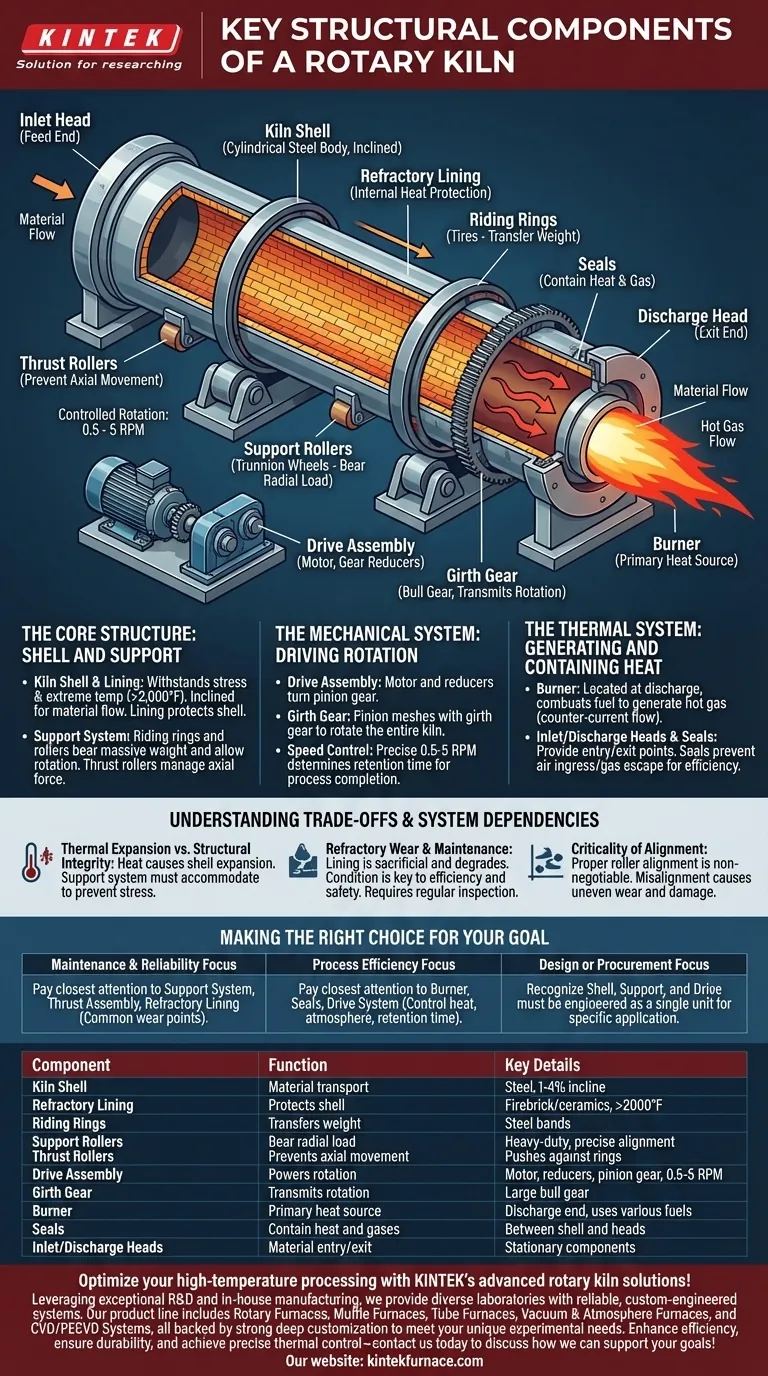
At its core, a rotary kiln is an integrated system designed for high-temperature material processing. Its primary structural components include the cylindrical steel shell, the protective internal refractory lining, the drive assembly that provides rotation, and a robust support system composed of riding rings and rollers that bear the immense load. These elements work in concert to transport, heat, and transform materials in a continuous, controlled process.
A rotary kiln is more than just a furnace; it is a dynamic machine. Its structural integrity depends on a support system (rings and rollers) that manages immense weight and thermal expansion, while its operational success relies on a drive system and seals that ensure controlled rotation and a stable internal atmosphere.
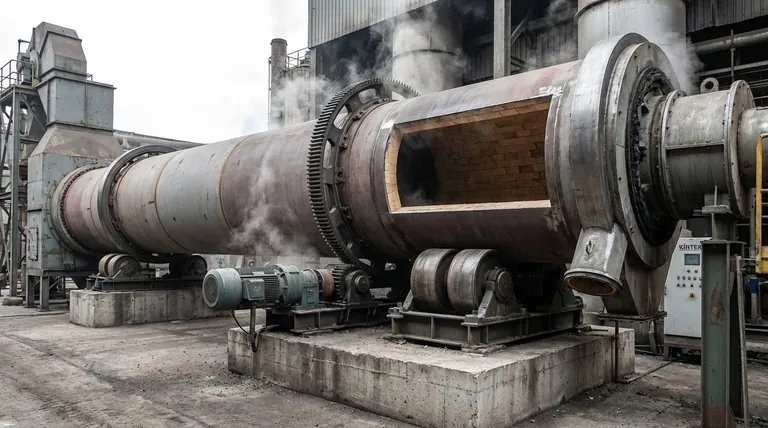

The Core Structure: Shell and Support
The kiln's body and the system that holds it up are fundamental to its operation. These components must withstand enormous mechanical stress and extreme temperatures simultaneously.
The Kiln Shell
The kiln shell is the main cylindrical body, constructed from heavy steel plates. It is slightly inclined from horizontal, typically between 1% and 4%, using gravity to help move material from the feed end to the discharge end as it rotates.
The Refractory Lining
Inside the steel shell is a refractory lining. This layer of heat-resistant material (like firebrick or castable ceramics) protects the steel shell from the extreme internal process temperatures, which can exceed 2,000°F (1,100°C).
Riding Rings (Tires)
Large steel bands, known as riding rings or tires, are fitted around the outside of the kiln shell. Their sole purpose is to transfer the entire weight of the kiln and its contents to the support system below.
Support Rollers (Trunnion Wheels)
The riding rings rest on pairs of support rollers, also called trunnion wheels. These heavy-duty rollers are the bearings that carry the kiln's radial load, allowing the massive structure to rotate with minimal friction.
Thrust Rollers
To prevent the inclined kiln from slowly sliding downhill, one or more thrust rollers are positioned to push against the side of a riding ring. These rollers manage the axial (longitudinal) forces and keep the kiln in its correct position.
The Mechanical System: Driving Rotation
The movement of the kiln is not passive; it is a precisely controlled mechanical action that dictates the efficiency of the entire process.
The Drive Assembly
The drive assembly is the engine of the rotary kiln. It consists of a powerful electric motor connected to a series of gear reducers that turn a small pinion gear.
The Girth Gear
This pinion gear meshes with a massive bull gear, known as the girth gear, which is mounted around the circumference of the kiln shell. The engagement of the pinion and girth gear is what ultimately rotates the entire kiln.
Controlled Rotation Speed
Kilns rotate very slowly, typically between 0.5 and 5 revolutions per minute (RPM). This speed is carefully controlled to manage the material's retention time—how long it spends inside the kiln—which is critical for ensuring the desired chemical reaction or physical change is completed.
The Thermal System: Generating and Containing Heat
The ultimate purpose of the kiln is thermal processing, which requires an efficient system for creating and containing heat.
The Burner
A high-powered burner located at the discharge end of the kiln serves as the primary heat source. It combusts fuel (like natural gas, coal, or oil) to generate the hot gas that flows through the kiln, typically in a direction counter-current to the material flow for maximum thermal efficiency.
Inlet and Discharge Heads
The stationary inlet head (or feed end) and discharge head provide the entry and exit points for the material being processed. The feed system introduces raw material, while the discharge head funnels the finished product out for cooling and further handling.
Kiln Seals
Seals are located where the rotating kiln shell meets the stationary inlet and discharge heads. Their function is critical: they prevent cold air from being drawn into the kiln and stop hot process gases from escaping, which is essential for maintaining temperature control and thermal efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs and System Dependencies
A rotary kiln is a system where every component's performance affects the others. Understanding these interactions is key to reliable operation.
Thermal Expansion vs. Structural Integrity
The intense heat causes the steel shell to expand significantly. The design of the riding rings, which are often mounted to allow for slight movement relative to the shell, and the alignment of the support system must accommodate this expansion. Failure to do so can induce massive stress and lead to structural failure.
Refractory Wear and Maintenance
The refractory lining is a sacrificial component that erodes and degrades over time due to heat, chemical attack, and abrasion. Its condition is a primary factor in the kiln's thermal efficiency and operational safety. Regular inspection and replacement are a major part of any kiln's maintenance budget and downtime schedule.
The Criticality of Alignment
Proper alignment of the support rollers is non-negotiable. Even slight misalignment concentrates the kiln's immense weight onto small areas of the rollers and riding rings, causing accelerated and uneven wear. Severe misalignment can damage the drive gear and even warp the kiln shell itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the function of each component allows you to focus your attention where it matters most for your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and reliability: Pay closest attention to the support system (rollers, rings), thrust assembly, and refractory lining, as these are the most common points of wear and failure.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Your key components are the burner, seals, and drive system, which directly control heat transfer, atmospheric integrity, and material retention time.
- If your primary focus is design or procurement: Recognize that the shell, support system, and drive must be engineered as a unit to handle the specific load, temperature, and material characteristics of your application.
Understanding how these core components function as an integrated system is the first step toward optimizing performance and ensuring long-term operational reliability.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Kiln Shell | Cylindrical body for material transport | Made of steel, inclined 1-4% for gravity flow |
| Refractory Lining | Protects shell from high heat | Uses firebrick or ceramics, withstands >2000°F |
| Riding Rings | Transfers weight to support system | Steel bands on shell exterior |
| Support Rollers | Bear radial load for rotation | Heavy-duty rollers, require precise alignment |
| Thrust Rollers | Prevents axial movement | Pushes against rings to maintain position |
| Drive Assembly | Powers rotation | Motor, reducers, pinion gear, 0.5-5 RPM speed |
| Girth Gear | Transmits rotation from drive | Large bull gear meshing with pinion |
| Burner | Primary heat source | Located at discharge end, uses fuels like gas |
| Seals | Contain heat and gases | Between rotating shell and stationary heads |
| Inlet/Discharge Heads | Material entry and exit points | Stationary components for feed and product handling |
Optimize your high-temperature processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary kiln solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable, custom-engineered systems. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Enhance efficiency, ensure durability, and achieve precise thermal control—contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency



















