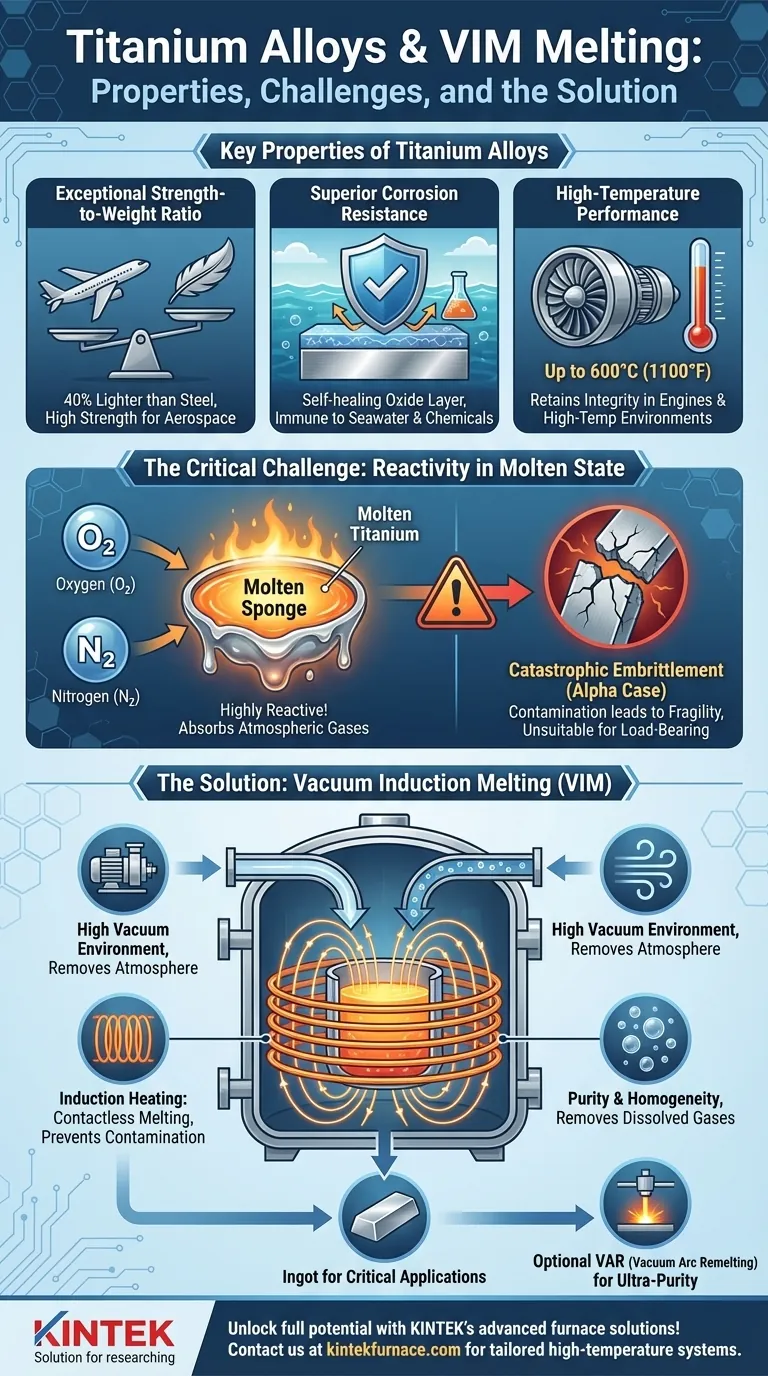
At their core, titanium alloys are prized for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding resistance to corrosion. They are melted in Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnaces not as a matter of preference, but as a critical necessity to protect the molten metal from atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, which would otherwise contaminate the alloy and make it unacceptably brittle for high-performance use.
The decision to use a VIM furnace for titanium is driven by the metal's fundamental chemistry. Because molten titanium is highly reactive, the vacuum environment is the only way to prevent catastrophic contamination and preserve the unique properties that make the alloy valuable in the first place.
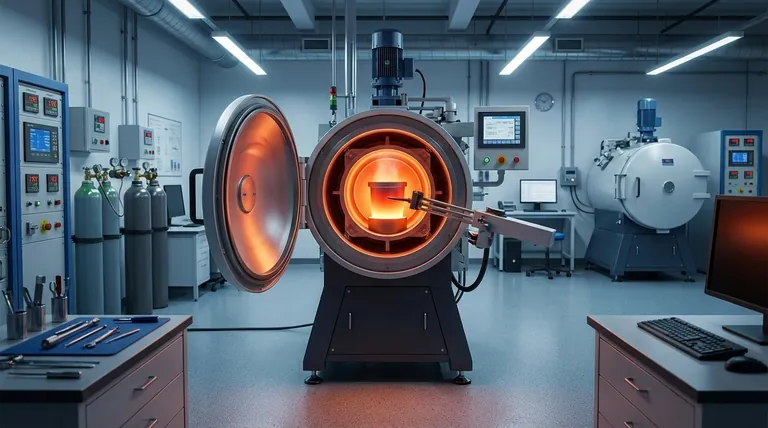

The Defining Properties of Titanium Alloys
To understand the manufacturing constraints, we must first appreciate the material's advantages. Titanium's properties make it an elite material for demanding environments where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
Exceptional Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Titanium alloys possess the strength of many steels but at a significantly lower density (roughly 40% lighter). This makes them indispensable for aerospace applications, where reducing weight directly translates to increased payload capacity and fuel efficiency.
Superior Corrosion Resistance
Titanium naturally forms a stable, self-healing, and highly protective oxide layer (TiO₂) on its surface. This passive film makes it virtually immune to corrosion in seawater, industrial chemicals, and the human body, leading to its widespread use in marine, chemical processing, and biomedical implants.
High-Temperature Performance
Unlike aluminum alloys, which lose strength rapidly at elevated temperatures, many titanium alloys retain their structural integrity up to 600°C (1100°F). This property is crucial for components in aircraft engines and other high-temperature environments.
The Critical Challenge: Titanium's Reactivity
The very properties that make titanium desirable are protected by a thin oxide layer. However, when the metal is melted for casting, this protection is gone, and its underlying reactivity becomes the single most important manufacturing challenge.
The Problem in a Molten State
In its liquid state, titanium is extremely reactive. It has a high affinity for the primary elements in our atmosphere, acting as a "sponge" for oxygen and nitrogen.
The Contamination Effect
When oxygen and nitrogen dissolve into molten titanium, they don't just mix in; they lodge themselves within the metal's crystal lattice. These elements are known as interstitial contaminants.
The Consequence: Catastrophic Embrittlement
Even minute amounts of these dissolved gases can cause a condition known as "alpha case," a brittle, oxygen-enriched layer. This severely reduces the alloy's ductility and fracture toughness, making it fragile and completely unsuitable for any application where it must bear a load.
Why Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) is the Solution
The VIM process is engineered specifically to overcome the challenge of titanium's reactivity. It creates a tightly controlled environment that shields the metal during its most vulnerable phase.
Creating a Sealed Environment
A VIM furnace is a sealed chamber from which nearly all air is pumped out, creating a high vacuum. By removing the atmosphere, the primary sources of oxygen and nitrogen contamination are eliminated before the melting even begins.
The Role of Induction Heating
The process uses electromagnetic induction to heat and melt the titanium. A powerful alternating current is passed through a coil, which generates a magnetic field that induces eddy currents within the metal itself, causing it to heat up and melt without any physical contact from a heating source. This prevents contamination that could come from traditional fuel-fired or arc-based methods.
Achieving Purity and Homogeneity
The vacuum actively pulls out dissolved gases from the melt, further purifying the alloy. Simultaneously, the electromagnetic field creates a natural stirring action, ensuring all alloying elements are distributed evenly for a chemically uniform (homogeneous) final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While VIM is the gold standard for melting reactive metals, it is not without its significant downsides.
High Cost
VIM furnaces are complex, require massive amounts of energy, and are expensive to build and maintain. This cost is a primary reason why titanium components are significantly more expensive than their steel or aluminum counterparts.
Process Complexity
Operating a VIM furnace requires highly skilled personnel and precise control systems to manage vacuum levels, temperature, and pouring rates. The process is far less forgiving than standard air-melting.
Often a Two-Step Process
For the most critical applications, such as rotating parts in a jet engine, VIM is only the first step. The ingot produced by VIM is then used as a consumable electrode and re-melted in a second process, called Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR), to achieve even greater purity and a more refined grain structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice of melting technology is dictated entirely by the material's chemistry and the application's demands.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, non-critical components: Standard atmospheric melting is perfectly suitable for less reactive materials like most carbon steels, cast irons, and many aluminum alloys.
- If your primary focus is high-performance, reactive metals: For materials like titanium alloys, nickel-based superalloys, and specialty medical-grade steels, a vacuum melting process like VIM is an absolute requirement to ensure safety and performance.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between a material's intrinsic properties and its manufacturing process is the key to unlocking its full performance potential.
Summary Table:
| Property / Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High strength, 40% lighter than steel, ideal for aerospace |
| Corrosion Resistance | Self-healing oxide layer, resistant to seawater and chemicals |
| High-Temperature Performance | Maintains integrity up to 600°C, used in engines |
| Reactivity in Molten State | Highly reactive with oxygen and nitrogen, causes embrittlement |
| VIM Furnace Role | Vacuum environment prevents contamination, ensures purity |
| Applications | Aerospace, marine, biomedical implants, chemical processing |
Unlock the full potential of your high-performance materials with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether you're working with reactive metals like titanium alloys or other demanding applications. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your material processing and drive innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















