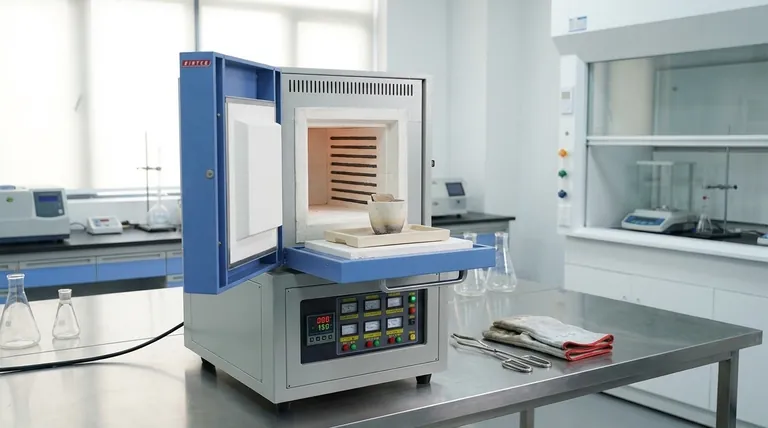
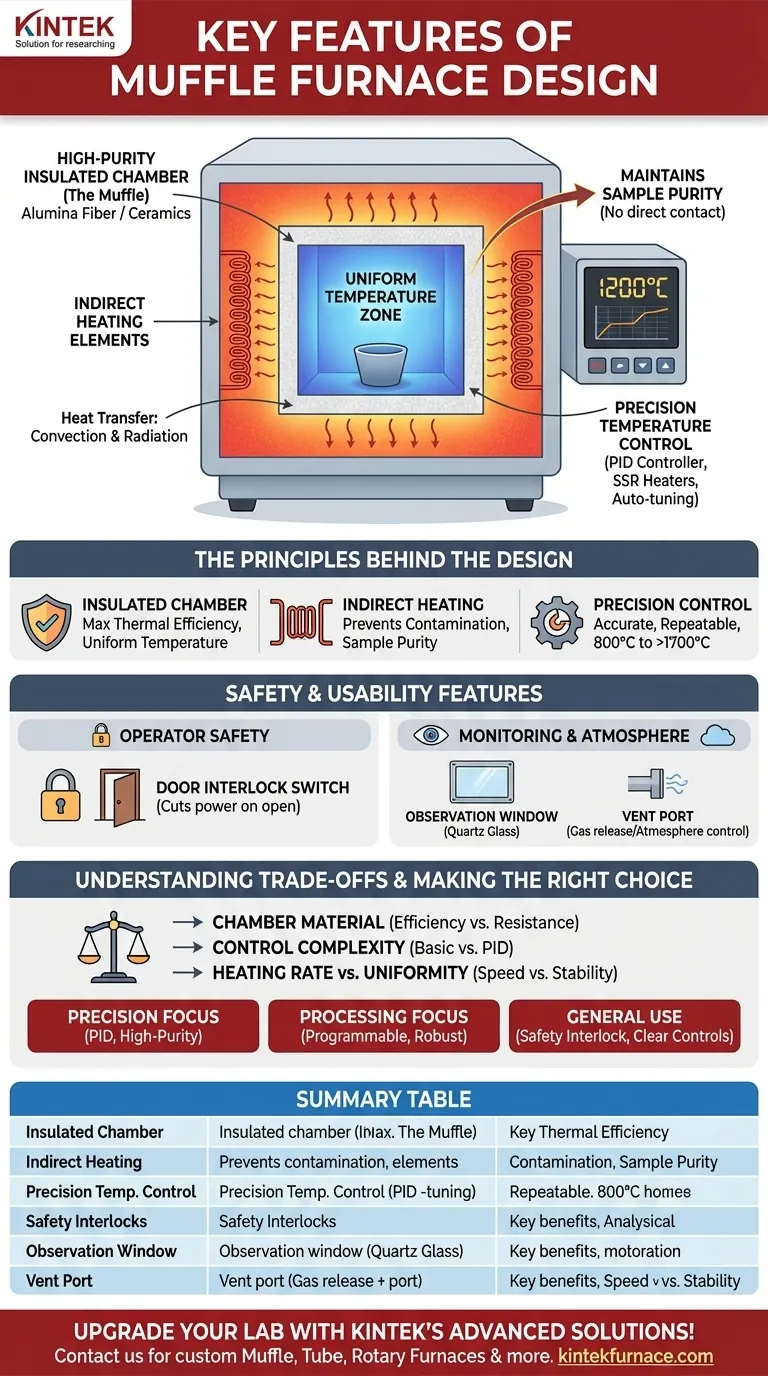
At its core, a muffle furnace is an integrated system designed for high-temperature heating, material isolation, and operational safety. The key design features that enable this are a high-purity insulated chamber, heating elements placed outside this chamber for indirect heat, a precise digital temperature control system, and safety interlocks that cut power when the door is opened. Additional features like observation windows and ventilation ports allow for process monitoring and atmosphere control.
A muffle furnace's design isn't just a collection of parts; it's a purpose-built environment. Its defining characteristic is the separation of the heating elements from the internal chamber, a design choice that prioritizes sample purity and uniform temperature above all else.

The Principles Behind the Design
A muffle furnace is engineered to solve three primary challenges: achieving extremely high and uniform temperatures, preventing contamination of the sample, and ensuring the process is both repeatable and safe for the operator.
The Insulated Chamber (The "Muffle")
The chamber, or "muffle," is the heart of the furnace. It is constructed from highly insulating, heat-resistant materials like high-purity alumina fiber or other ceramics.
This construction serves two purposes. First, it ensures maximum thermal efficiency by retaining heat, which reduces energy consumption. Second, it helps create a highly uniform temperature zone, which is critical for achieving accurate and repeatable test results.
Indirect Heating and Sample Purity
A defining feature of a muffle furnace is its use of indirect heat. The heating elements are positioned outside the sealed inner chamber.
Heat is transferred into the chamber through thermal convection and radiation, rather than by direct contact or exposure to the heating elements. This design is critical for preventing chemical reactions between the sample and the elements, thereby maintaining sample purity.
Precision Temperature Control
Modern muffle furnaces rely on sophisticated control systems to manage the extreme temperatures, which can range from 800°C to over 1700°C.
These systems are typically built around an advanced PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller. This controller continuously receives data from a temperature sensor (such as a J-type sensor) and adjusts the power sent to the SSR-based heaters.
Many controllers feature auto-tuning and are programmable, allowing users to set precise heating rates, hold times, and cooling profiles for complex thermal processes.
Key Features for Safety and Usability
Beyond the core heating system, several features are included to ensure the furnace is practical and safe to operate.
Operator Safety Mechanisms
Given the extreme temperatures, safety is paramount. The most critical feature is a door interlock switch that automatically cuts power to the heating elements the moment the door is opened, protecting the user from direct exposure to the intense heat.
Process Monitoring and Atmosphere Control
Many furnaces include a quartz glass observation window (typically 0.5 inches in diameter). This allows the operator to visually monitor the material inside without opening the door and disrupting the thermal cycle.
A vent port is also a common feature. This allows for the controlled release of gases or fumes produced during heating and can also be used to introduce a specific gas flow, creating a modified atmosphere inside the chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a muffle furnace involves balancing performance, features, and cost. The design choices directly impact its capabilities.
Chamber Material vs. Application
The chamber's material dictates its limits. A furnace with a high-purity alumina fiber chamber is excellent for energy efficiency and purity but may have different chemical resistance or temperature ceilings compared to a dense ceramic chamber.
Control System Complexity
A basic, two-position (on/off) controller is simple and inexpensive. However, for any process requiring accuracy, a PID controller is non-negotiable. It provides far superior temperature stability and prevents significant over- or undershooting of the target temperature.
Heating Rate vs. Uniformity
Some models are designed for very rapid heating and cooling. While excellent for high-throughput work, this can sometimes come at the cost of perfect temperature uniformity across the entire chamber, a trade-off that may not be acceptable for sensitive analytical work.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these design features empowers you to select the right tool for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is analytical precision: Prioritize a furnace with an advanced PID controller, high-purity alumina fiber insulation, and a well-sealed chamber to ensure maximum temperature stability and sample purity.
- If your primary focus is materials processing: Look for programmable controls to automate complex heating cycles and a robust construction with corrosion-resistant materials suitable for your specific process.
- If your primary focus is general use and safety: Ensure the furnace has a reliable door safety interlock, clear controls, and durable insulation like a high-density glass wool blanket for efficiency and longevity.
By recognizing how each feature contributes to the furnace's overall performance, you can confidently choose the instrument that meets your exact needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Insulated Chamber | Made from high-purity alumina fiber or ceramics | Ensures uniform temperature and thermal efficiency |
| Indirect Heating | Heating elements outside the chamber | Maintains sample purity by preventing contamination |
| Precision Temperature Control | Uses PID controllers with auto-tuning | Provides accurate, repeatable thermal processes |
| Safety Interlocks | Door switches that cut power when opened | Protects operators from extreme heat exposure |
| Observation Window | Quartz glass for visual monitoring | Allows process checks without disrupting temperature |
| Vent Port | Enables gas release or atmosphere control | Supports modified atmospheres and fume management |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Achieve superior precision, safety, and efficiency—contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for you!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















