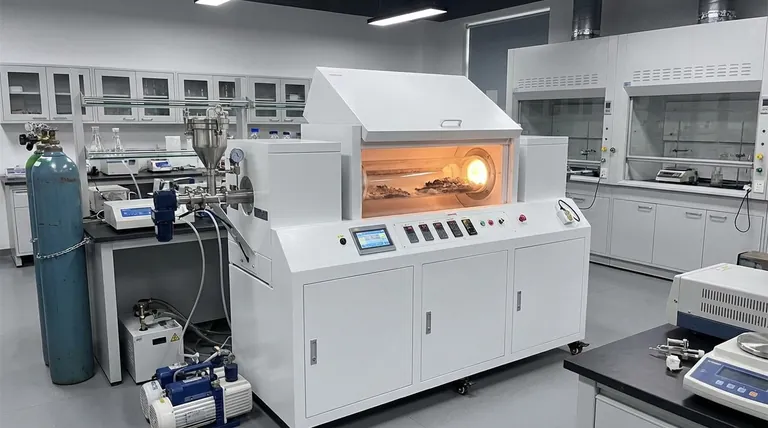
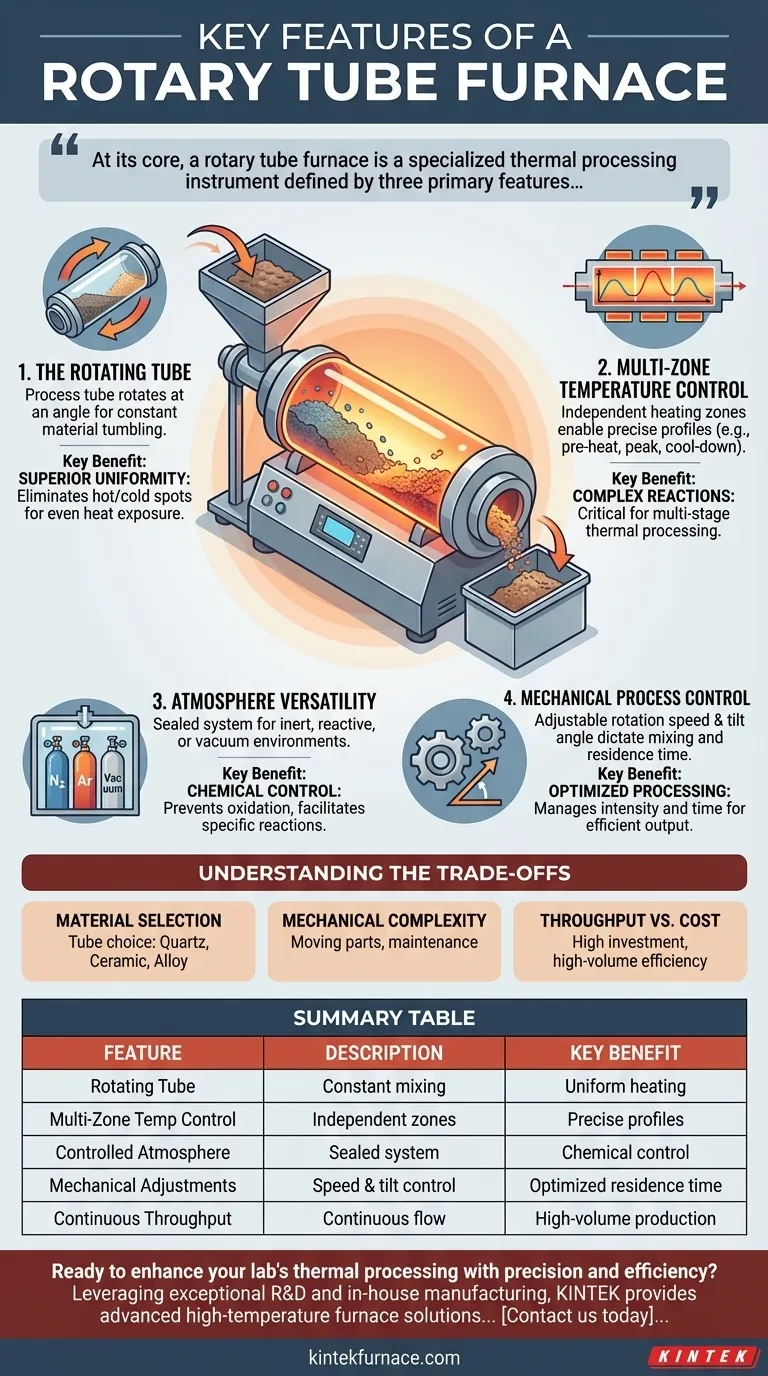
At its core, a rotary tube furnace is a specialized thermal processing instrument defined by three primary features: a constantly rotating process tube, precise multi-zone temperature control, and the ability to maintain a controlled gas atmosphere. This combination enables continuous processing and ensures that the material inside is heated and mixed with exceptional uniformity, a task impossible in a static furnace.
The true value of a rotary tube furnace lies not in its individual components, but in their synergy. It transforms thermal processing from a static, batch-oriented task into a dynamic, controllable, and continuous operation ideal for producing highly consistent materials at scale.

The Core Principle: Dynamic Thermal Processing
Unlike a standard furnace that heats a stationary sample, a rotary tube furnace is built around the concept of dynamic heating and mixing. This fundamental difference unlocks unique processing capabilities.
The Rotating Tube
The central component is the process tube, which is mounted at a slight angle and rotates continuously. This rotation is the key to the furnace's primary benefit: uniformity.
As the tube turns, it constantly tumbles and mixes the material within. This action ensures every particle is exposed to the heat source evenly, eliminating the hot and cold spots that plague static furnaces.
Continuous Throughput
The combination of rotation and a slight downward tilt transforms the furnace into a continuous processing system. Raw material is fed into the higher end of the tube and gradually moves toward the lower end as it rotates, emerging as a finished product.
This design is exceptionally efficient for industrial applications requiring high-volume output, such as calcination, pyrolysis, or drying of powders and granular materials.
Unpacking the Key Control Systems
A rotary tube furnace is more than just a heated, spinning drum. It is a precise instrument where every key parameter can be controlled to optimize a specific chemical or physical transformation.
Multi-Zone Temperature Control
The furnace body is typically divided into multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the length of the tube. This allows you to create a precise temperature profile.
For example, a process might require a pre-heating zone, a central reaction zone at a peak temperature, and a final cool-down zone, all within the same continuous operation. This level of control is critical for complex, multi-stage reactions.
Atmosphere Versatility
Most processes are sensitive to the surrounding atmosphere. Rotary furnaces are designed with sealed systems that allow for precise atmosphere control.
This feature enables operations to be run under an inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation, a reactive gas to facilitate a chemical change, or a vacuum.
Mechanical Process Control
The physical behavior of the material is managed through mechanical adjustments. Controlling rotation speed dictates the intensity of the mixing, while adjusting the tilt angle directly influences how long the material stays in the furnace—a parameter known as residence time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary tube furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Material Selection is Critical
The process tube itself is exposed to extreme thermal and chemical stress. The choice of tube material—typically quartz, ceramic (alumina), or a metal alloy—defines the furnace's maximum operating temperature and its resistance to corrosion from the process material.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The drive gear, rotating seals, and motor that enable the tube's rotation are moving parts. Compared to a simple, static tube furnace, these components introduce additional mechanical complexity and require a more rigorous maintenance schedule to ensure reliability.
Throughput vs. Cost
The sophisticated control systems, robust construction, and mechanical components make rotary tube furnaces a significant capital investment compared to simpler batch ovens. Their value is most apparent in applications where continuous throughput and product uniformity justify the initial cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right thermal equipment depends entirely on your end goal. The features of a rotary tube furnace are tailored for specific outcomes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: A rotary tube furnace is purpose-built for this, offering unmatched efficiency and consistency for processes like roasting, drying, or calcining bulk materials.
- If your primary focus is precise material synthesis: The combination of multi-zone temperature profiling, atmosphere control, and adjustable residence time gives you the granular control needed to optimize chemical reactions and create novel materials.
- If your primary focus is processing non-uniform or thermally sensitive materials: The gentle tumbling action and exceptionally uniform heat exposure prevent localized overheating and ensure every part of your sample is processed identically.
By integrating dynamic movement with precise environmental control, the rotary tube furnace provides a powerful solution for the most demanding thermal processing challenges.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating Tube | Tube rotates at an angle for constant material mixing | Ensures uniform heating and eliminates hot/cold spots |
| Multi-Zone Temperature Control | Independent heating zones along the tube length | Enables precise temperature profiles for complex reactions |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Sealed system for inert, reactive, or vacuum environments | Prevents oxidation and facilitates specific chemical changes |
| Mechanical Adjustments | Control over rotation speed and tilt angle | Manages mixing intensity and residence time for optimization |
| Continuous Throughput | Material moves continuously from feed to discharge | Ideal for high-volume production like calcination and drying |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with precision and efficiency? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our rotary tube furnaces can deliver superior uniformity and continuous throughput for your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries



















