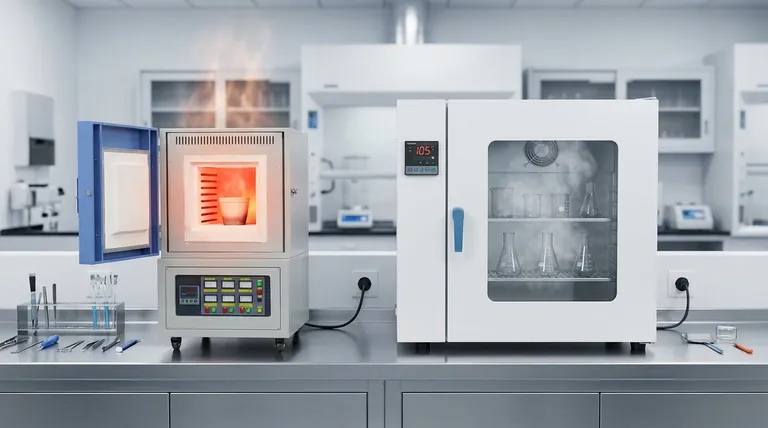
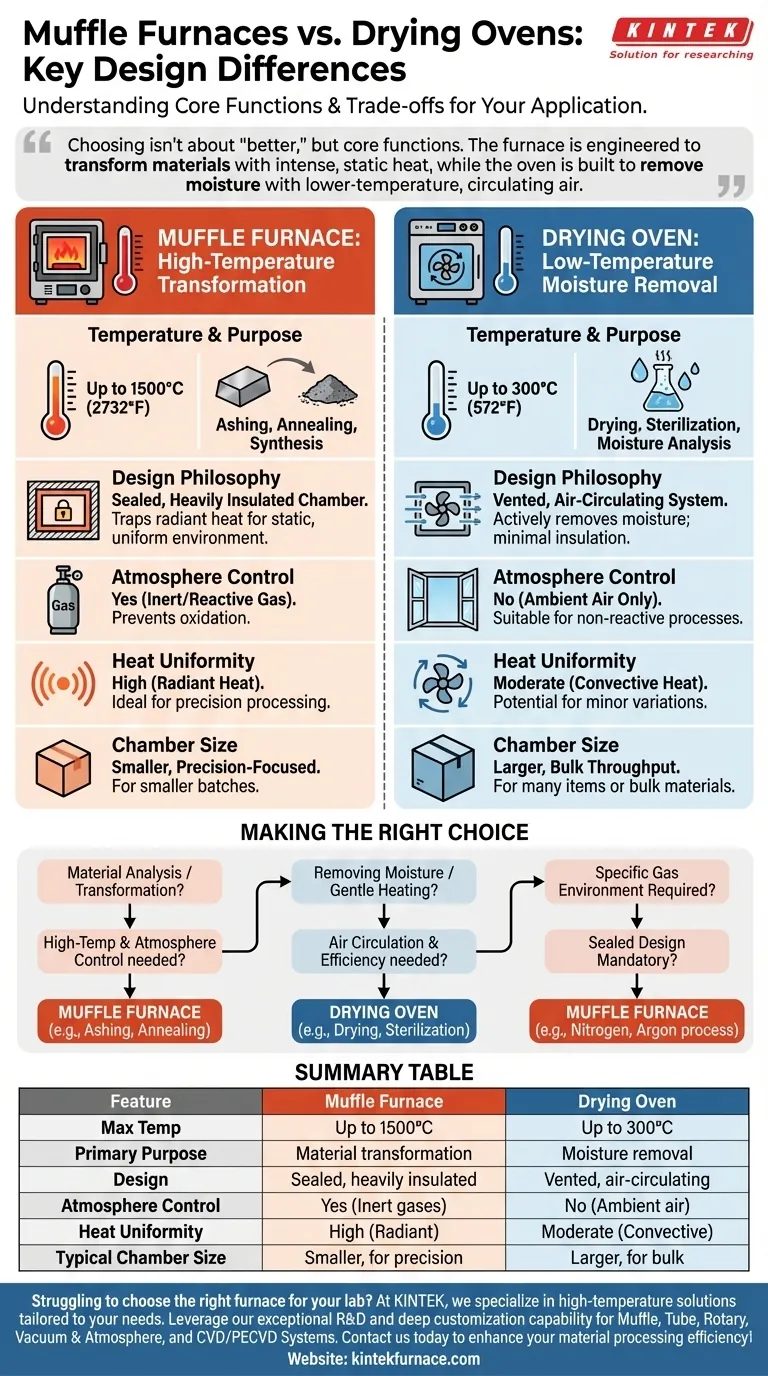
At first glance, a muffle furnace and a drying oven might seem similar, but their designs are driven by fundamentally different purposes. A muffle furnace is a heavily insulated, sealed chamber built for high-temperature material transformations like ashing or annealing, while a drying oven is a minimally insulated, vented chamber designed for low-temperature moisture removal through air circulation. The choice between them is dictated entirely by the process you need to perform.
Choosing between a muffle furnace and a drying oven isn't about which is "better," but about understanding their core functions. The furnace is engineered to transform materials with intense, static heat, while the oven is built to remove moisture with lower-temperature, circulating air.

The Core Difference: Temperature and Purpose
The most significant design distinction is the operational temperature range, which directly reflects the intended application of each device.
Muffle Furnaces: High-Temperature Transformation
A muffle furnace is engineered to reach extremely high temperatures, often up to 1500°C (2732°F) or higher.
This capability is necessary for processes that fundamentally alter a material's chemical or physical properties, such as ashing, heat-treating metals, or advanced materials synthesis.
Drying Ovens: Low-Temperature Moisture Removal
A drying oven, by contrast, operates at much lower temperatures, typically peaking around 300°C (572°F).
Its primary function is not to transform a material, but simply to remove moisture. Common applications include drying laboratory glassware, moisture content analysis, or gentle sterilization of heat-stable equipment.
Design Philosophy: Sealed vs. Vented Environments
The required temperature range dictates how each device manages heat and its internal atmosphere, leading to two opposing design philosophies.
The Muffle Furnace: A Sealed, Insulated Chamber
To achieve and maintain extreme temperatures efficiently, a muffle furnace features a chamber with heavy refractory insulation.
During operation, the chamber is completely sealed. This traps radiant heat from the electric heating elements, ensuring a stable and uniform thermal environment. This sealed design is critical for performance and safety.
The Drying Oven: An Air-Circulating System
A drying oven requires a different approach. Its goal is to carry moisture away from the items inside.
To do this, it actively circulates air, often using fans to pull fresh air across heating elements and then vent the now-moist air out. Because it is not trying to reach extreme temperatures, its insulation is typically minimal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The distinct designs of furnaces and ovens create critical trade-offs in performance and capability.
Atmosphere Control: The Deciding Factor
The sealed nature of a muffle furnace allows for atmosphere control. Air inside the chamber can be purged and replaced with an inert or reactive gas (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation during high-temperature processing.
A drying oven cannot control its atmosphere. Its vented, air-circulating design makes it suitable only for processes that can be performed in ambient air.
Temperature Uniformity: Radiant vs. Convective Heat
A muffle furnace provides highly uniform heat through radiation in a static, sealed environment. This is crucial for applications where every part of a sample must be at the exact same temperature.
A drying oven uses convection (moving hot air), which can sometimes create minor temperature variations or "hot spots" within the chamber. While modern ovens are designed to minimize this, they cannot match the static uniformity of a sealed furnace.
Chamber Size and Throughput
Drying ovens are often designed with larger chambers to accommodate bulk materials or many small items at once, prioritizing throughput for low-temperature tasks.
Muffle furnaces typically have smaller, more controlled chambers. The focus is on precision processing of smaller batches, not bulk capacity, due to the energy and materials required for high-temperature operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct instrument is a matter of matching its core function to your procedural goal.
- If your primary focus is material analysis or transformation (ashing, annealing, melting): A muffle furnace is required for its high-temperature and atmosphere-control capabilities.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture or gentle heating (drying samples, sterilizing glassware): A drying oven is the correct, more efficient tool for its air circulation design.
- If you need to process materials in a specific gas environment (e.g., nitrogen or argon): The sealed design of a muffle furnace is your only option.
Understanding this fundamental distinction between transforming materials and removing moisture ensures you select the right tool for your specific scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Drying Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1500°C (2732°F) | Up to 300°C (572°F) |
| Primary Purpose | Material transformation (e.g., ashing, annealing) | Moisture removal (e.g., drying, sterilization) |
| Design | Sealed, heavily insulated chamber | Vented, air-circulating system |
| Atmosphere Control | Yes (e.g., inert gases) | No (ambient air only) |
| Temperature Uniformity | High (radiant heat) | Moderate (convective heat, potential hot spots) |
| Typical Chamber Size | Smaller, for precision | Larger, for bulk throughput |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental requirements precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our products can enhance your material processing and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















