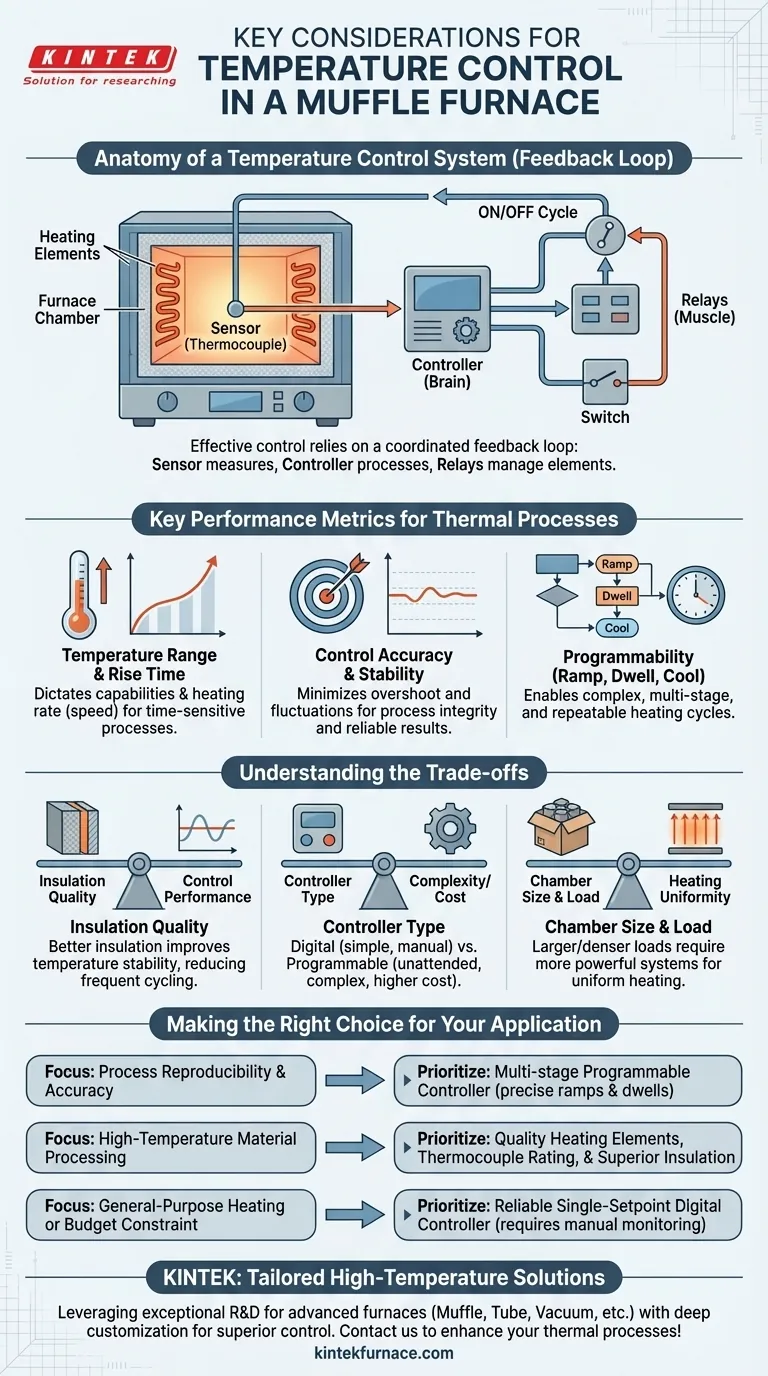
At its core, effective temperature control in a muffle furnace relies on a coordinated system of three parts: a sensor to measure the temperature, a controller to process that information, and a switching mechanism to manage the heating elements. This system's primary goal is to not only reach a desired temperature but to maintain it with stability and accuracy, ensuring the integrity of your process.
The challenge of temperature control is not merely hitting a target number. It is about precisely managing the entire thermal profile—including the rate of heating, the duration at temperature, and the cooling period—to guarantee accurate and reproducible results.

The Anatomy of a Temperature Control System
Understanding how temperature is managed requires looking at the components as an integrated feedback loop. Each part plays a distinct and critical role in achieving thermal precision.
The Sensor: The Thermocouple
A thermocouple is the furnace's nerve ending. It is a temperature sensor placed inside the chamber that provides a real-time measurement of the internal temperature. This measurement is the essential piece of feedback that the entire control system acts upon.
The Brain: The Temperature Controller
The temperature controller is the central processor. It continuously compares the actual temperature reported by the thermocouple to the setpoint temperature you have programmed. Modern furnaces feature programmable controllers that allow you to define complex heating cycles, including ramp rates, dwell times, and cooling stages.
The Muscle: Relays and Heating Elements
Based on the controller's logic, electromagnetic relays act as the switches. If the chamber is too cool, the controller signals the relays to turn the heating elements on. Once the setpoint is reached, it signals them to turn off. This on/off cycle is what maintains the desired temperature.
Key Performance Metrics for Thermal Processes
The effectiveness of a temperature control system is not just about its components, but about its performance. These metrics define how well the furnace can execute a specific thermal task.
Temperature Range and Rise Time
The operating temperature range dictates the furnace's capabilities. For longevity, the furnace's maximum rated temperature should be slightly higher than your typical operating temperature. The rise time, or heating rate, measures how quickly it can reach that maximum temperature, a critical factor for time-sensitive processes.
Control Accuracy and Stability
This is the system's ability to minimize temperature overshoot (exceeding the setpoint) and fluctuations around the setpoint. High accuracy is crucial for processes where even minor temperature deviations can compromise the results, ensuring the chamber remains stable during the entire dwell time (the period spent at the target temperature).
Programmability: Ramp, Dwell, and Cool
Advanced processes require more than a single setpoint. The ability to program ramp rates (the speed of heating/cooling) and dwell times (holding at a specific temperature) is what separates a basic furnace from a precision instrument, enabling complex, multi-stage, and repeatable cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A perfect system is theoretical. In practice, achieving ideal temperature control involves balancing several interconnected factors.
Insulation Quality vs. Control Performance
High-quality insulation does more than save energy; it is fundamental to temperature stability. A poorly insulated furnace loses heat constantly, forcing the heating elements to cycle more frequently. This rapid cycling can lead to wider temperature fluctuations and make precise control more difficult.
Controller Type: Digital vs. Programmable
A basic digital controller allows you to set a single temperature. This is simple and cost-effective but requires manual monitoring and adjustment for any multi-stage process. A programmable controller offers unattended operation and near-perfect reproducibility, but at a higher initial cost and complexity.
Chamber Size and Load
A larger chamber or a denser workload requires more energy and time to heat uniformly. The control system must be powerful enough to manage this thermal mass without significant lag or temperature gradients, where different parts of the chamber are at different temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a furnace requires matching its control capabilities to your specific process goals.
- If your primary focus is process reproducibility and accuracy: You must prioritize a furnace with a multi-stage programmable controller to precisely define ramp rates and dwell times.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material processing: Your main concerns should be the quality of the heating elements, the thermocouple's rating, and superior chamber insulation to ensure stability at extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating or budget is a key constraint: A furnace with a reliable single-setpoint digital controller is sufficient, but you must be prepared for more hands-on monitoring to ensure process consistency.
Ultimately, mastering temperature control is the foundation for achieving reliable and meaningful outcomes with a muffle furnace.
Summary Table:
| Component/Consideration | Key Role/Impact |
|---|---|
| Sensor (Thermocouple) | Measures real-time temperature for feedback |
| Controller (Digital/Programmable) | Compares actual vs. setpoint, manages cycles |
| Relays and Heating Elements | Switches heating on/off based on controller input |
| Temperature Range and Rise Time | Defines furnace capabilities and heating speed |
| Control Accuracy and Stability | Minimizes overshoot and fluctuations for reliable results |
| Programmability (Ramp, Dwell, Cool) | Enables complex, repeatable multi-stage processes |
| Insulation Quality | Affects energy efficiency and temperature stability |
| Chamber Size and Load | Influences heating uniformity and control response |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your lab's unique requirements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental needs for superior temperature control and reproducibility. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















