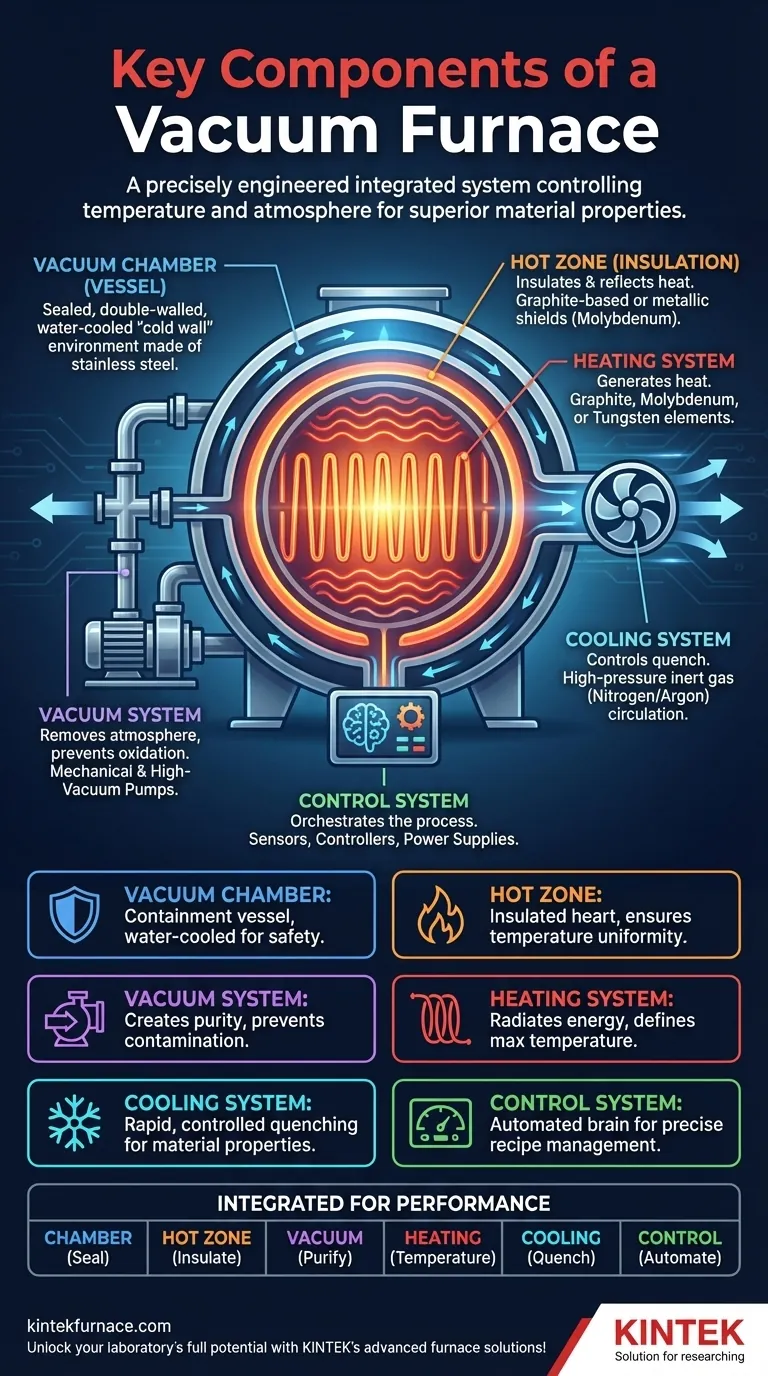
At its core, a vacuum furnace is an integrated system of six primary components working in concert. These include the sealed vacuum chamber that contains the workload, the heating system that generates the required temperature, the vacuum system that removes the atmosphere, the insulation or "hot zone" that contains the heat, the cooling system that controls the quench, and the control system that orchestrates the entire process.
A vacuum furnace is not merely a box that gets hot. It is a precisely engineered environment where each component plays a critical role in controlling temperature and atmosphere to achieve material properties that are impossible in a standard, open-air furnace.

The Core Structure: Chamber and Hot Zone
The physical structure of the furnace is designed for containment—of both the vacuum and the intense heat.
The Vacuum Chamber (Vessel)
The vacuum chamber is the outermost shell, providing the sealed environment necessary for the process. It is typically a double-walled, water-cooled vessel made of stainless or high-strength steel.
This "cold wall" design is crucial. Cooling water circulates between the walls, keeping the exterior of the furnace safe to touch and protecting the structural integrity of the chamber from the extreme internal temperatures.
The Hot Zone (Insulation)
Inside the chamber lies the hot zone, which is the insulated heart of the furnace. Its job is to reflect heat back towards the workload, ensuring temperature uniformity and protecting the cooled chamber walls.
Hot zones are commonly constructed from layers of graphite-based insulation (like carbon felt) for very high temperatures or metallic radiation shields (like molybdenum) for high-purity applications.
Creating the Environment: Vacuum and Heat
The two defining functions of the furnace—creating a vacuum and generating heat—are handled by dedicated systems.
The Vacuum System
This is the key differentiator from a conventional furnace. The vacuum system uses a series of pumps (e.g., mechanical "roughing" pumps and diffusion or turbomolecular "high-vacuum" pumps) to remove air and other gases from the chamber.
Removing the atmosphere prevents oxidation and contamination of the material being processed, which is the primary reason for using a vacuum furnace. The level of vacuum can be precisely controlled for different applications.
The Heating System
Heating elements are positioned within the hot zone to radiate energy onto the workload. The material used for these elements dictates the furnace's maximum operating temperature.
Common materials include graphite for temperatures up to and beyond 2200°C, or refractory metals like molybdenum and tungsten for high-purity processes that cannot tolerate carbon.
Managing the Process: Control and Cooling
Once the part is heated in a vacuum, the process must be precisely managed through its conclusion.
The Control System
The control system is the brain of the operation, consisting of sensors (thermocouples, vacuum gauges), controllers, and power supplies. It automates the entire heat-treat recipe.
This system precisely manages the heating ramp rate, soak time at temperature, vacuum level, and the final cooling or quenching sequence, ensuring process repeatability and quality.
The Cooling System
After the heating cycle is complete, the part must be cooled in a controlled manner. The cooling system is responsible for this critical step, which often determines the final material properties like hardness.
Most modern furnaces use a high-pressure gas quench. The system rapidly fills the chamber with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, which is then circulated by a high-power fan through the hot workload to cool it quickly.
Understanding Key Design Trade-offs
The specific components chosen for a furnace represent a series of engineering trade-offs tailored to its intended purpose.
Hot Wall vs. Cold Wall Design
While most industrial vacuum furnaces are cold wall designs (as described above) for their high-temperature capability and fast cycle times, hot wall designs also exist. In a hot wall furnace, the heating elements are outside the vacuum vessel (a retort), which gets hot itself. These are typically limited to lower temperatures.
Heating Element Selection
The choice between graphite and all-metal (molybdenum) heating elements is significant. Graphite is cost-effective and suitable for extremely high temperatures but can react with certain alloys. Molybdenum is cleaner and more inert but is more expensive and has a lower maximum temperature.
Pumping System Complexity
The required level of vacuum drives the complexity and cost of the pumping system. Basic heat treating may only require a simple mechanical pump, while advanced electronics or aerospace applications demand a multi-stage, high-vacuum system to achieve the necessary purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The configuration of a vacuum furnace must align directly with its intended process.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing (e.g., for medical or electronics): You need an all-metal hot zone and a high-performance vacuum system to eliminate any carbon contamination.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific material properties (e.g., hardening tool steels): A powerful and controllable gas quenching (cooling) system is the most critical component.
- If your primary focus is very high-temperature applications (>1300°C): A cold-wall design with robust graphite heating elements and insulation is essential.
Ultimately, these components work together as a single, finely-tuned instrument to transform materials in a way no other technology can.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Common Materials/Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Provides sealed environment | Stainless steel, water-cooled |
| Hot Zone | Insulates and contains heat | Graphite, molybdenum shields |
| Vacuum System | Removes atmosphere for purity | Mechanical and high-vacuum pumps |
| Heating System | Generates required temperature | Graphite, molybdenum, tungsten |
| Cooling System | Controls quenching process | High-pressure gas quench with fans |
| Control System | Automates and monitors process | Sensors, controllers, power supplies |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for high-purity processing, material property enhancement, or extreme temperature applications. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your heat treatment processes and drive innovation in your work!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















