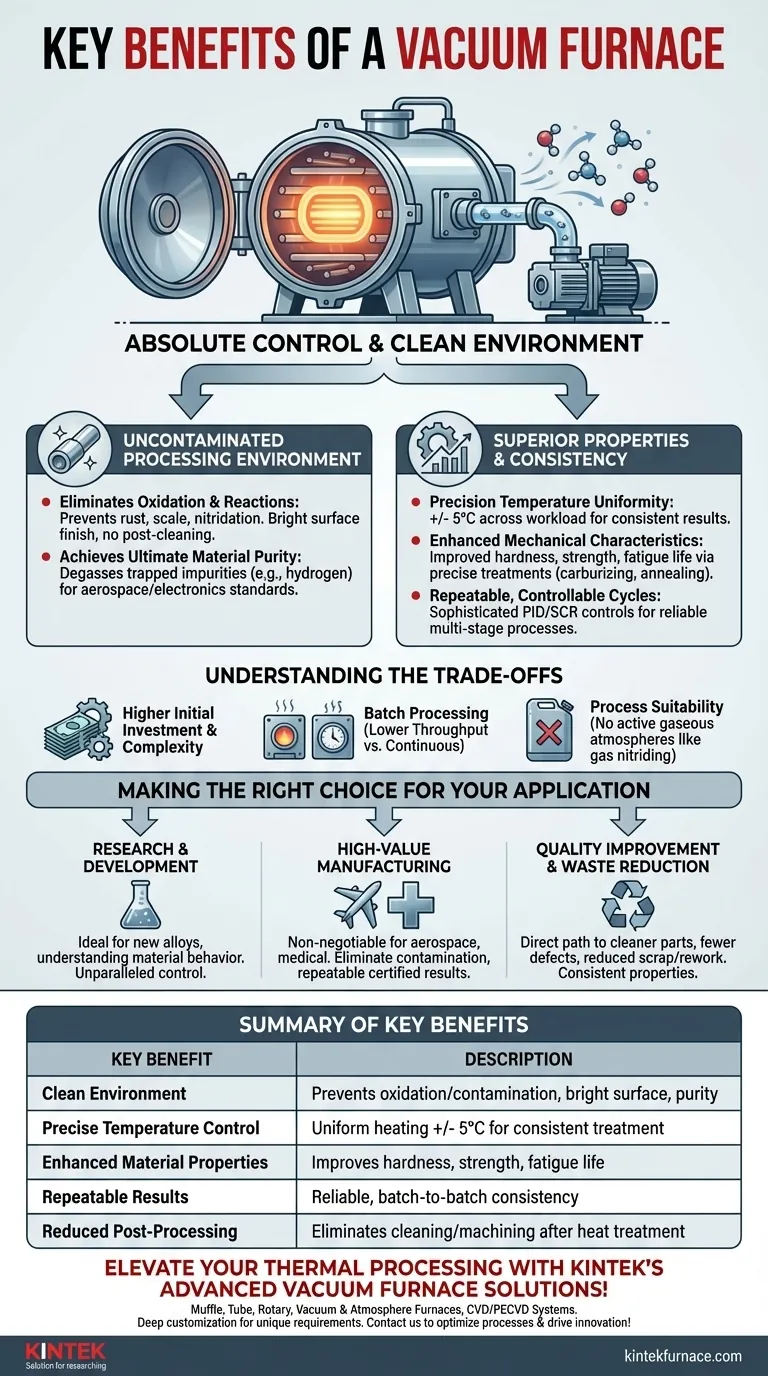
The fundamental benefit of a vacuum furnace is its ability to create an exceptionally clean and controllable environment for high-temperature processing. By evacuating the chamber of air and other reactive gases, it prevents oxidation and contamination, leading to superior material purity and enhanced mechanical properties. This precision makes it an indispensable tool for industries where material integrity is paramount.
While a vacuum furnace offers numerous advantages, they all stem from a single principle: absolute control. It replaces an unpredictable, reactive atmosphere with a stable, inert vacuum, giving engineers precise command over the final characteristics and quality of a material in a way that atmospheric furnaces cannot.

The Foundation: An Uncontaminated Processing Environment
A vacuum is not empty space; in this context, it is a highly controlled environment. The removal of atmospheric gases is the cornerstone of all other benefits.
Eliminating Oxidation and Reactions
By removing oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor, a vacuum furnace prevents unwanted chemical reactions on the material's surface at high temperatures. This means no oxidation (rust or scale), nitridation, or hydrogenation can occur.
The result is a bright, clean surface finish straight out of the furnace, eliminating the need for post-process cleaning or machining to remove a contaminated surface layer.
Achieving Ultimate Material Purity
For many advanced applications, even microscopic impurities can compromise performance. A vacuum furnace is essential for processes like degassing, where it pulls trapped gases like hydrogen out from within the material itself.
This level of purity ensures the material meets the stringent mechanical, thermal, and electrical specifications required in sectors like aerospace and electronics.
Unlocking Superior Material Properties and Consistency
A clean environment enables precise control, which in turn leads to highly predictable and enhanced material outcomes. The process becomes a science, not an approximation.
Precision Temperature Uniformity
Advanced vacuum furnaces deliver exceptional temperature uniformity, often within +/- 5°C across the entire workload. This is achieved through carefully designed heating elements and the lack of convective currents that exist in an atmosphere.
This uniformity ensures that every part in a batch, regardless of its position, receives the exact same thermal treatment, guaranteeing consistent results.
Enhanced Mechanical Characteristics
Heat treating in a vacuum allows for the development of superior material properties. Processes like vacuum carburizing, annealing, tempering, and quenching can be performed with incredible precision.
This control results in improved hardness, tensile strength, and fatigue life, as the material's microstructure is not compromised by surface impurities or reactions.
Repeatable, Controllable Cycles
Modern vacuum furnaces use sophisticated controls, such as independent PID loops and SCR power regulation, to manage heating and cooling rates with high fidelity.
This allows for complex, multi-stage thermal cycles to be programmed and executed perfectly every time, ensuring that results are repeatable from batch to batch. The system can even use partial pressure to carefully manage specific effects, like preventing the vaporization of chromium from steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Initial Investment and Complexity
Vacuum furnace systems represent a significant capital investment compared to many atmospheric furnaces. They are complex machines requiring specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance of vacuum pumps, seals, and control systems.
Throughput: Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Most vacuum furnaces are batch-type systems. While individual cycle times can be fast due to rapid heating and cooling, the overall throughput may be lower than continuous belt-style furnaces used for high-volume, low-cost parts.
Process Suitability
A vacuum environment is not suitable for all heat treatment processes. For example, processes that explicitly require an active gaseous atmosphere (like traditional gas nitriding) cannot be performed in a vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right thermal processing technology depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The unparalleled control over the environment and temperature makes a vacuum furnace ideal for developing new alloys and precisely understanding material behavior.
- If your primary focus is high-value manufacturing (e.g., aerospace, medical): The ability to eliminate contamination and achieve repeatable, certified results is non-negotiable and the core strength of vacuum technology.
- If your primary focus is improving quality and reducing waste: A vacuum furnace offers a direct path to cleaner parts, fewer surface defects, and more consistent properties, often justifying the investment through reduced scrap and rework.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum furnace technology is a strategic decision to prioritize control, quality, and repeatability in your thermal processes.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Clean Environment | Prevents oxidation and contamination by removing reactive gases, ensuring bright surface finish and material purity. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Achieves uniform heating within +/- 5°C, enabling consistent thermal treatment across all parts. |
| Enhanced Material Properties | Improves hardness, strength, and fatigue life through controlled processes like vacuum carburizing and annealing. |
| Repeatable Results | Uses advanced controls for reliable, batch-to-batch consistency in complex thermal cycles. |
| Reduced Post-Processing | Eliminates need for cleaning or machining after heat treatment, saving time and costs. |
Elevate your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or R&D, achieve superior material purity and repeatable results—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments



















