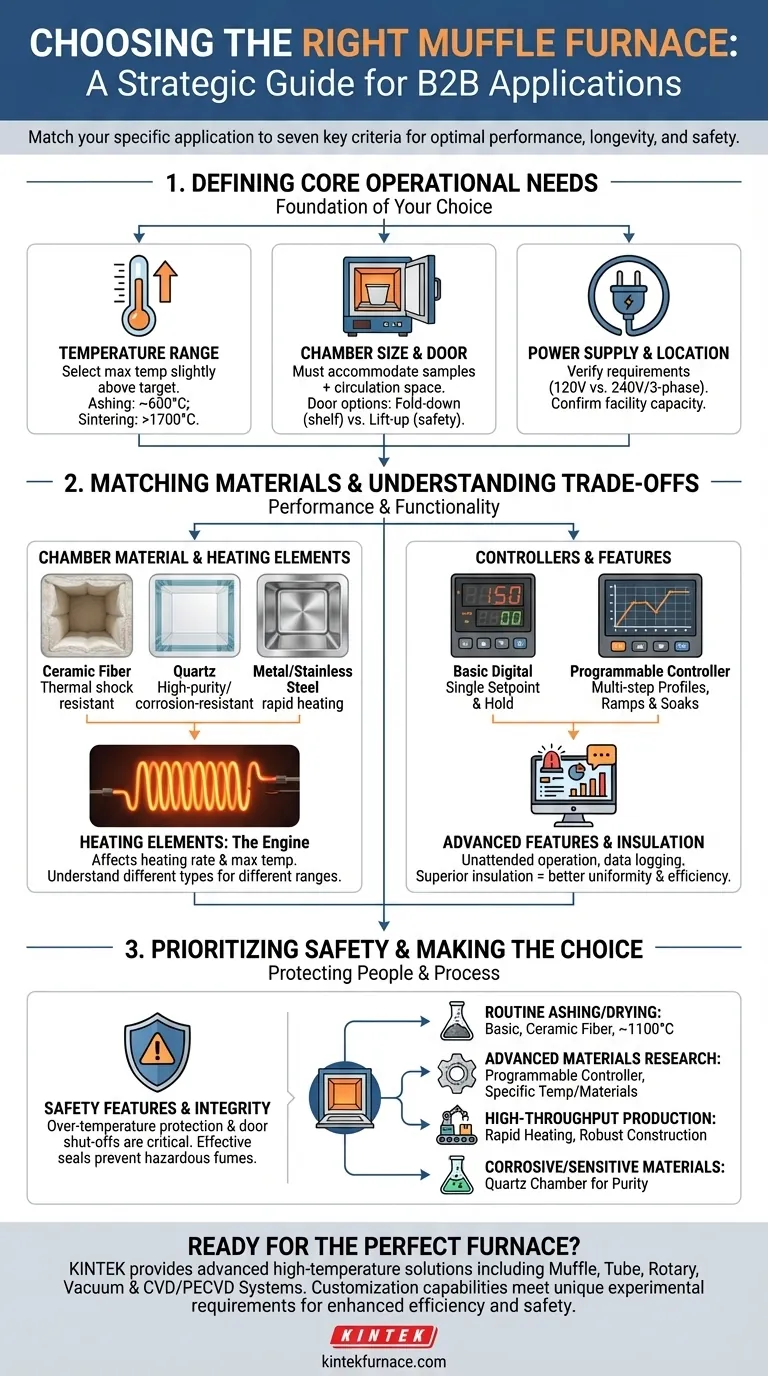
To choose the right muffle furnace, you must evaluate your specific application against seven key criteria: maximum operating temperature, chamber size, chamber material, heating element type, controller programmability, safety features, and power supply compatibility. These factors work together to determine the furnace's performance, longevity, and suitability for your work.
The goal is not to buy the furnace with the highest temperature or most features, but to select a tool precisely matched to your specific scientific or production requirements. A mismatch in any key area can lead to compromised results, safety hazards, and unnecessary expense.

Defining Your Core Operational Needs
Before evaluating furnace models, you must first define the non-negotiable parameters of your work. These foundational requirements will immediately narrow your options.
Temperature Range: The Non-Negotiable Starting Point
Your primary consideration is the maximum temperature required for your process. Always select a furnace with a maximum operating temperature at least slightly higher than your target, as running a furnace at its absolute limit for extended periods will shorten its lifespan.
Different applications demand vastly different temperature capabilities, from ashing organic samples (~600°C) to sintering advanced ceramics (>1700°C).
Chamber Size and Door Orientation
The internal chamber must be large enough to accommodate your samples or crucibles with adequate space for air circulation. Consider not just the volume but the dimensions.
Also, evaluate the door design. A fold-down door can serve as a convenient shelf for loading and unloading, while a lift-up door keeps the hot face away from the operator, improving safety.
Power Supply and Location
Verify the furnace's electrical requirements. Lab furnaces can range from standard 120V models that plug into any wall outlet to powerful 240V or three-phase units that require dedicated, high-amperage circuits installed by an electrician.
Confirming your facility's power capabilities beforehand prevents costly installation surprises.
Matching Materials to Your Application
The physical construction of the furnace chamber and its heating system directly impacts performance, durability, and what processes you can safely run.
Chamber Material: Balancing Reactivity and Durability
The material lining the heating chamber is critical.
Ceramic fiber bodies offer excellent insulation and good thermal shock resistance, making them a versatile choice for general heat treatment and ashing.
Quartz chambers provide high-purity, corrosion-resistant environments suitable for sensitive chemical reactions or semiconductor processing.
Metal bodies, often stainless steel, deliver excellent thermal conductivity for rapid heating and are well-suited for high-throughput production environments where chemical inertness is less of a concern.
Heating Elements: The Engine of Your Furnace
Heating elements are the consumable components that generate heat. Their material and design dictate the furnace's heating rate and maximum temperature.
While manufacturers handle the specific selection, understanding that different element types are used for different temperature ranges helps you appreciate why high-temperature furnaces are significantly more expensive.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing advanced features against cost and complexity. More is not always better.
Basic vs. Programmable Controllers
A basic digital controller allows you to set a single target temperature (setpoint) and hold it. This is perfectly adequate for simple processes like drying, ashing, or basic heat treating.
A programmable controller allows you to create complex multi-step thermal profiles with controlled heating rates (ramps), hold times (soaks), and cooling steps. This is essential for materials research, ceramics, and advanced metallurgy.
Software Features: Essential Tool or Unnecessary Complexity?
Advanced controllers may offer features like alarms, timers, data logging, or thermal gradient programming. These are invaluable for unattended operation, process validation in regulated industries (e.g., pharmaceuticals), or sophisticated research.
For basic, supervised tasks, these features can add unnecessary complexity and cost.
The Impact of High-Quality Insulation
Superior insulation does more than just protect the user. It directly translates to better temperature uniformity within the chamber, faster heat-up times, and significantly lower energy consumption.
A poorly insulated furnace will struggle to maintain a stable temperature and will cost more to operate over its lifetime.
Prioritizing Safety and Longevity
Safety features are not optional accessories; they are fundamental requirements for protecting the operator, the facility, and your samples.
Over-Temperature Protection and Failsafes
An over-temperature protection circuit is a critical safety feature. It uses a separate, independent sensor to monitor the furnace temperature and will automatically shut off power if it exceeds a preset safety limit, preventing catastrophic failure.
An automatic shut-off mechanism tied to the door opening is another key feature, protecting users from direct exposure to extreme heat and electrical components.
Door Seals and Structural Integrity
An effective door seal is crucial for maintaining a consistent internal atmosphere and preventing hazardous fumes from escaping into the lab. It also improves energy efficiency.
High-quality insulation and robust external construction ensure the furnace's outer surfaces remain at a safe temperature during operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be guided by a clear understanding of your primary application.
- If your primary focus is routine ashing or drying: A reliable furnace with a basic digital controller, ceramic fiber insulation, and a maximum temperature around 1100°C is a cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research: Prioritize a programmable controller for complex thermal cycles and select a furnace with the temperature and chamber materials appropriate for your experiments.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production: Focus on rapid heating rates, robust construction, and a chamber size optimized for your parts.
- If your primary focus is processing corrosive or sensitive materials: A furnace with a quartz chamber is likely necessary to prevent sample contamination and chamber degradation.
By systematically matching the furnace's capabilities to your specific needs, you ensure a safe, efficient, and successful investment.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Maximum operating temperature should exceed your process needs for longevity. |
| Chamber Size | Must accommodate samples with space for air circulation; consider door orientation. |
| Chamber Material | Choose ceramic fiber, quartz, or metal based on purity, durability, and application. |
| Heating Element | Type affects heating rate and temperature; varies by model and requirements. |
| Controller Type | Basic for simple tasks; programmable for complex thermal profiles and research. |
| Safety Features | Includes over-temperature protection and door shut-offs for operator safety. |
| Power Supply | Verify electrical requirements to match facility capabilities and avoid issues. |
Ready to find the perfect muffle furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring enhanced efficiency, safety, and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















