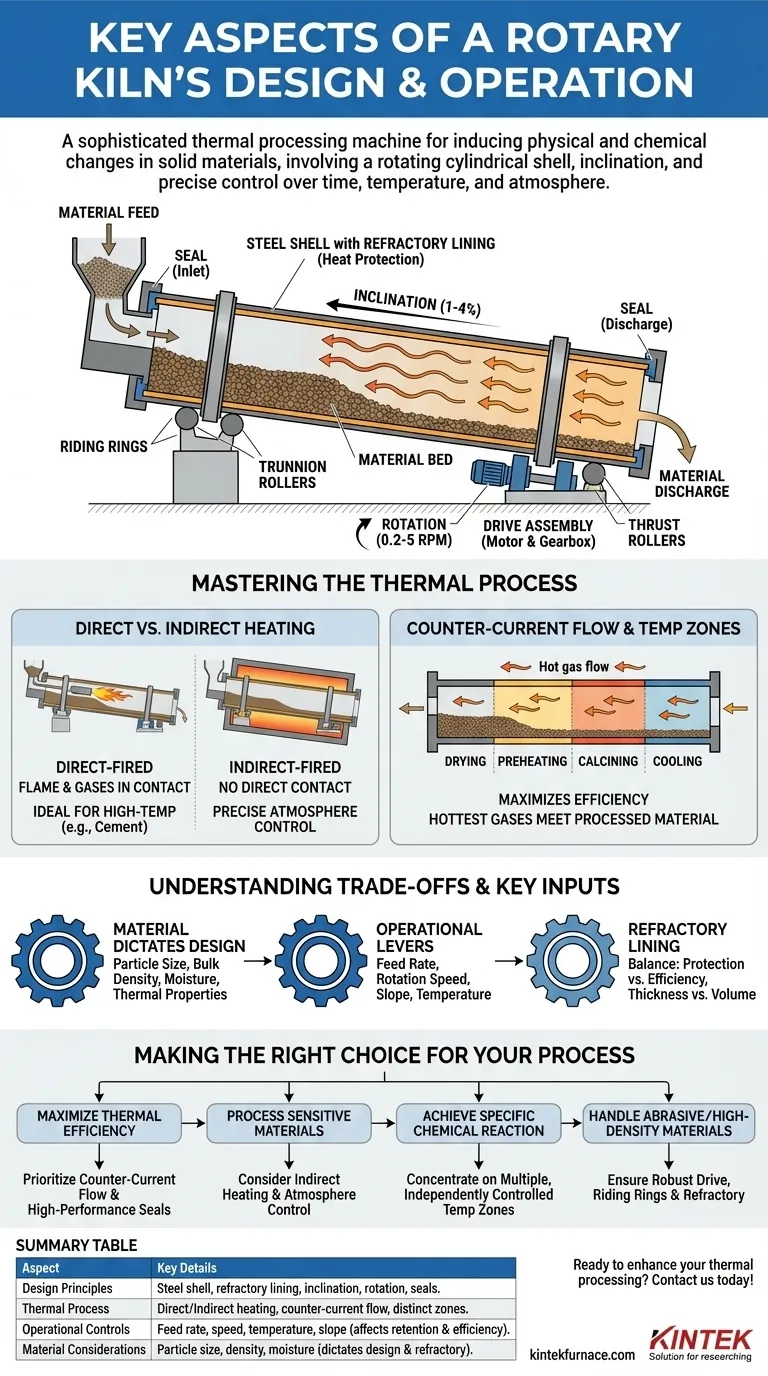
At its core, a rotary kiln is a sophisticated thermal processing machine designed to induce specific physical and chemical changes in solid materials. Its fundamental design consists of a large, rotating cylindrical shell lined with refractory material, which is slightly inclined to allow gravity to move material from the feed end to the discharge end. Operation hinges on precise control over material retention time, temperature profile, and internal atmosphere to achieve a desired transformation.
A rotary kiln is not merely a heated container; it is a dynamic system where the mechanical design (inclination, rotation) and the thermal process (heating method, temperature zones) are engineered in direct response to the specific chemical and physical properties of the material it is built to process.

The Core Design Principles
The physical structure of a rotary kiln is engineered for two primary purposes: containing extreme heat and controlling the movement of material through that heat.
The Kiln Body and Inclination
The main body, or shell, is a steel cylinder lined with heat-resistant refractory bricks. This lining is critical, as it protects the steel structure from the extreme internal process temperatures.
The entire assembly is mounted at a slight inclination, typically between 1% and 4% from the horizontal. This slope is the primary mechanism that advances material through the kiln, using gravity as a gentle but constant conveyor.
The Rotation System
The kiln is mounted on riding rings, which distribute its immense weight onto a series of support wheels or trunnion rollers.
A powerful drive assembly, usually an electric motor and gearbox, turns the kiln at a slow, controlled speed, generally between 0.2 and 5 revolutions per minute (RPM). Thrust rollers prevent the kiln from sliding horizontally due to its inclination.
The rotation speed is a critical operational lever. It controls how long the material stays in the kiln (retention time) and ensures the material tumbles, promoting uniform heat exposure.
Sealing and Atmosphere Control
Effective seals at the material inlet and discharge ends are essential. These seals prevent cold air from entering the kiln and hot gases from escaping.
This containment allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere, which is vital for many chemical reactions, improving thermal efficiency, and ensuring environmental compliance by managing exhaust gases.
Mastering the Thermal Process
The heart of the kiln's function is the application of heat. The method of heating and the flow of hot gases are fundamental design choices that dictate the kiln's efficiency and suitability for a given process.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
In a direct-fired kiln, a burner is located inside the shell (usually at the discharge end), and the flame and combustion gases are in direct contact with the material. This is common for high-temperature applications like cement manufacturing.
In an indirect-fired kiln, the rotating shell is enclosed within an external furnace or heated by external elements. The material never contacts the flame, which is ideal for processes requiring a specific atmosphere or where product contamination is a concern.
Counter-Current Gas Flow
For maximum thermal efficiency, most kilns use a counter-current flow system. Material enters the high end and moves down, while hot gas from the burner at the low end flows up and exits at the material feed end.
This design acts as a heat exchanger. The hottest gases encounter the most processed material, while the cooler gases encounter the cold, wet feed, efficiently preheating it before it reaches the main combustion zone.
Temperature Zones and Control
A kiln is not heated uniformly. It is designed with distinct temperature zones to perform different functions as the material travels its length, such as drying, preheating, calcining, and cooling.
Modern systems often feature multiple groups of heating elements or burners, each with separate temperature controls. This allows operators to create a precise temperature profile tailored to the specific reaction kinetics of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Inputs
The design of a rotary kiln is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It is a series of deliberate engineering compromises driven by the material itself.
The Material Dictates the Design
The properties of the feed material are the most critical input for kiln design. Particle size, bulk density, moisture content, and thermal properties dictate nearly every component choice.
For example, a high-density material requires a more robust drive system and support structure. A pelletized feed allows for higher gas velocities and thus a smaller kiln diameter compared to a fine powder, which could be blown out of the system.
Operational Levers and Their Impact
The key operational parameters—feed rate, rotation speed, kiln slope, and temperature—are all interconnected. Changing one will affect the others.
Increasing rotation speed, for instance, reduces material retention time. To achieve the same degree of processing, the operator might need to decrease the feed rate or increase the temperature, which has further implications for fuel consumption and refractory life.
Refractory Lining: Protection vs. Efficiency
The choice of refractory lining is a balance between durability and thermal efficiency. A thicker, more robust lining offers better protection for the steel shell against high heat and chemical attack.
However, a thicker lining also reduces the kiln's internal volume and can act as an insulator, slightly slowing heat transfer to the material. The right choice depends entirely on the process's peak temperature and the chemical corrosiveness of the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Optimizing a rotary kiln requires aligning its design and operational parameters with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing thermal efficiency: Prioritize a counter-current gas flow design with high-performance seals at both ends to minimize heat loss.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials: Consider an indirect heating system to avoid product contamination from combustion byproducts and enable precise atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific chemical reaction: Concentrate on a design with multiple, independently controlled temperature zones to precisely manage the material's heating curve and retention time.
- If your primary focus is handling abrasive or high-density materials: Ensure the drive system, riding rings, and refractory lining are specified to withstand high mechanical loads and wear.
Ultimately, a successful rotary kiln operation is achieved when the mechanical design and thermal process are perfectly harmonized with the properties of the material being transformed.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Design Principles | Steel shell with refractory lining, inclination (1-4%), rotation system (0.2-5 RPM), seals for atmosphere control |
| Thermal Process | Direct or indirect heating, counter-current gas flow, distinct temperature zones (drying, preheating, calcining, cooling) |
| Operational Controls | Feed rate, rotation speed, temperature, slope; affects retention time and efficiency |
| Material Considerations | Particle size, density, moisture; dictates design choices and refractory selection |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing with a custom rotary kiln solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your process efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















