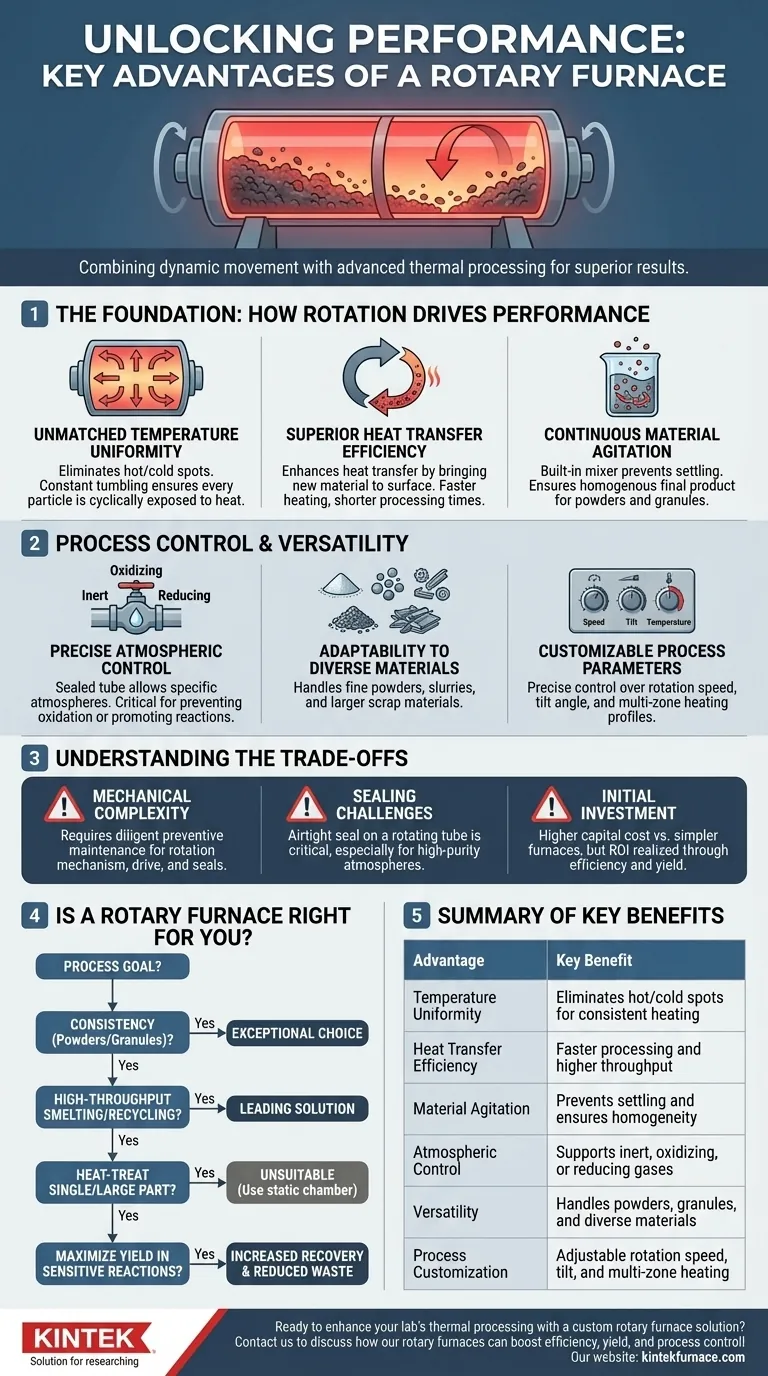
At its core, a rotary furnace excels by combining dynamic movement with thermal processing. Its primary advantages are superior heat uniformity, high efficiency, and exceptional process control, which stem directly from its ability to continuously tumble and mix materials while heating them in a tightly regulated environment.
The true value of a rotary furnace is not a single feature, but the synergy between them. The constant rotation ensures every particle is processed identically, which, when combined with precise atmospheric and temperature control, delivers a level of consistency and efficiency that static furnaces often cannot match.

The Foundation: How Rotation Drives Performance
The defining characteristic of a rotary furnace is its rotating cylindrical chamber. This simple mechanical action is the source of its most significant technical advantages.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The continuous tumbling of the material eliminates hot spots and cold spots. In a static furnace, material at the bottom or center can remain under-processed while material near the heat source is over-processed.
Rotation ensures every particle is cyclically exposed to the heat source and the furnace atmosphere, resulting in a highly uniform temperature distribution throughout the entire batch.
Superior Heat Transfer Efficiency
This constant movement dramatically enhances heat transfer. By continuously bringing new material to the surface, the furnace achieves faster and more efficient heating compared to static methods that rely solely on conduction and radiation through a stationary mass.
This leads directly to shorter processing times and higher throughput.
Continuous Material Agitation
For processes involving powders, granules, or mixed materials, the rotating action acts as a built-in mixer. This prevents sample settling and segregation, ensuring a homogenous final product.
This is critical for applications like catalyst roasting or sintering, where a consistent chemical reaction and physical structure are paramount.
Process Control and Versatility
Modern rotary furnaces are highly engineered systems that offer a level of control that makes them adaptable to a wide range of demanding applications.
Precise Atmospheric Control
Rotary furnaces are designed to operate with specific atmospheres. The sealed rotating tube allows for the introduction of inert, oxidizing, or reducing gases.
This capability is essential for preventing unwanted oxidation, promoting specific chemical reactions, or creating unique material properties during the heating process.
Adaptability to Diverse Materials
The design is inherently flexible, capable of handling everything from fine powders and slurries to larger scrap materials like battery plates for lead recovery.
This versatility makes them a valuable asset in industries ranging from chemical processing and metallurgy to recycling and scientific research.
Customizable Process Parameters
Operators have granular control over the process. Key parameters like rotation speed, tilt angle, and temperature can be precisely adjusted.
Advanced models feature multi-zone heating, allowing for different temperature profiles along the length of the tube, which enables highly sophisticated and optimized processing cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to making an objective decision.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotation mechanism, including the drive system and seals, adds mechanical complexity compared to a static furnace. These components require diligent preventive maintenance to ensure reliability and prevent downtime.
Sealing Challenges
Maintaining a perfectly airtight seal on a rotating tube is more challenging than on a static chamber. While modern designs are highly effective, seal integrity is a critical maintenance checkpoint, especially for processes requiring high-purity atmospheres.
Initial Investment
The sophisticated engineering, drive mechanics, and control systems typically result in a higher initial capital cost compared to simpler box or batch furnaces of a similar capacity. The return on investment is realized through higher throughput, improved yield, and greater efficiency.
Is a Rotary Furnace Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right furnace requires aligning its capabilities with your primary process goals.
- If your primary focus is process consistency for powders or granules: A rotary furnace is an exceptional choice, as its continuous mixing guarantees a homogenous result.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput smelting or recycling: The high thermal efficiency and capacity of a rotary furnace make it a leading solution.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating a single, large, or geometrically complex part: A rotary furnace is unsuitable; a static chamber or batch furnace would be the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is maximizing material yield in sensitive reactions: The combination of uniform heating and atmospheric control can significantly increase recovery and reduce waste.
Ultimately, a rotary furnace is a specialized tool engineered for processes where uniformity, efficiency, and control are the most critical drivers of success.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | Eliminates hot/cold spots for consistent heating |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | Faster processing and higher throughput |
| Material Agitation | Prevents settling and ensures homogeneity |
| Atmospheric Control | Supports inert, oxidizing, or reducing gases |
| Versatility | Handles powders, granules, and diverse materials |
| Process Customization | Adjustable rotation speed, tilt, and multi-zone heating |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with a custom rotary furnace solution? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our rotary furnaces can boost your efficiency, yield, and process control!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















