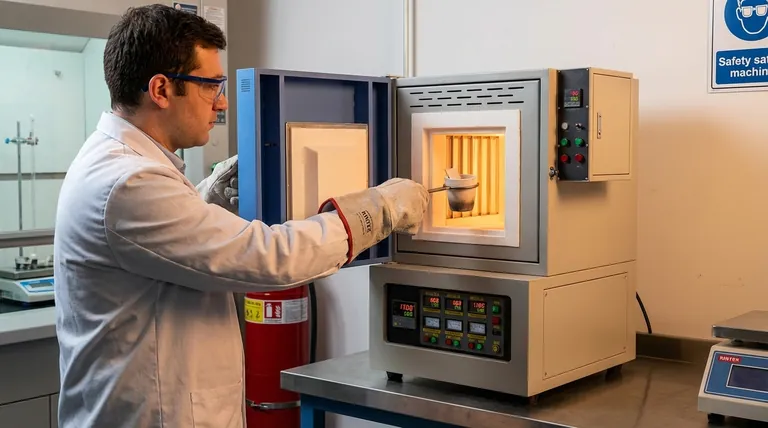
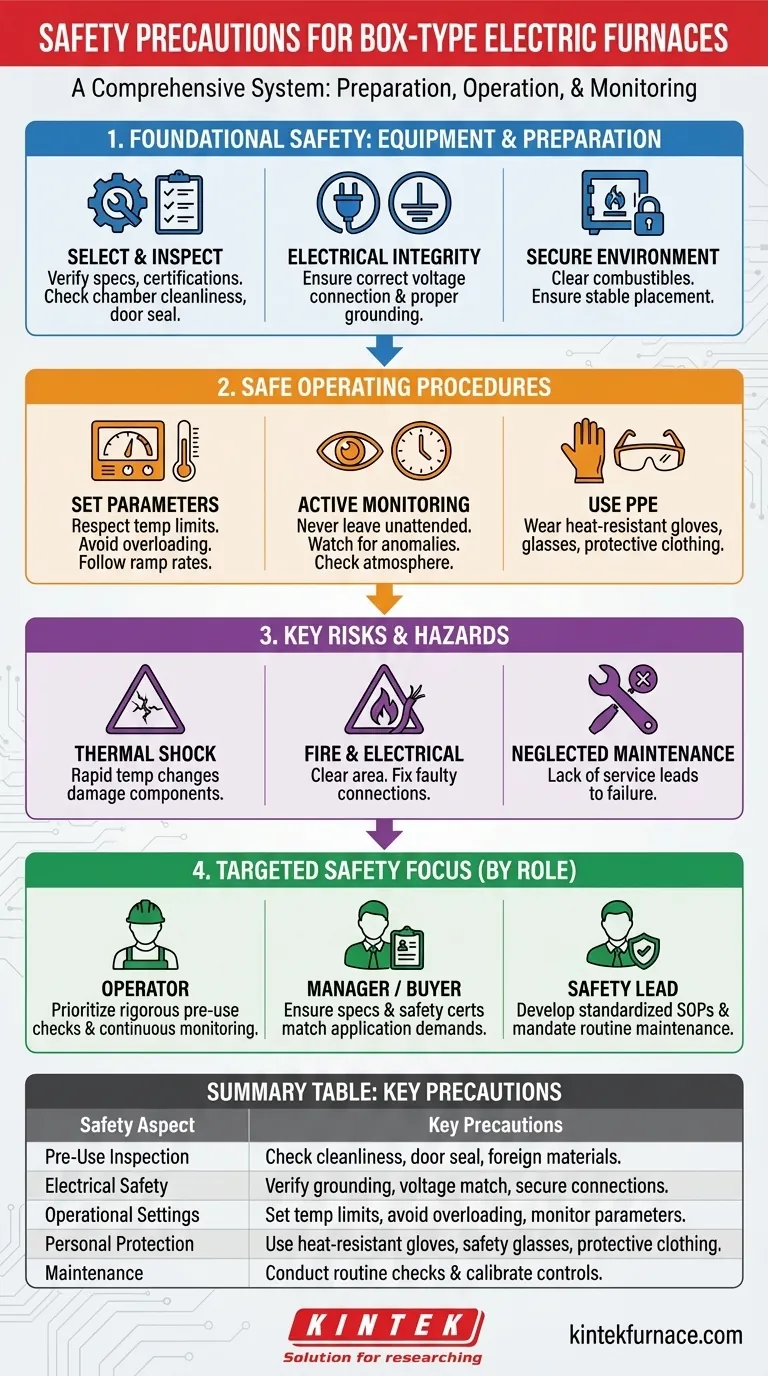
Operating a box-type electric furnace safely requires a systematic approach encompassing pre-use checks, correct operational settings, and diligent monitoring. Key precautions include verifying the furnace is clean, ensuring the power supply is properly connected and grounded, setting appropriate temperature limits to avoid overloading, and consistently observing the furnace's condition throughout its heating cycle.
True furnace safety is not a simple checklist; it is a comprehensive system. It begins with selecting the right equipment and extends through rigorous operator training, disciplined pre-use inspections, and active in-process monitoring.

Foundational Safety: Equipment and Preparation
Before you ever turn the furnace on, safety begins with the equipment itself and the environment around it. These foundational steps are the first line of defense against accidents.
The Role of Proper Furnace Selection
The safety of your operations is heavily influenced by the furnace you choose. When purchasing, verify that its heating elements, temperature control system, and insulation materials are suited for your specific application's temperature and atmospheric requirements.
Look for equipment with recognized safety certifications, as these indicate adherence to established design and manufacturing standards.
The Pre-Use Inspection is Non-Negotiable
Before every use, conduct a visual inspection. Check that the furnace chamber is clean and free of any foreign materials or residue from previous processes that could cause contamination or unexpected reactions at high temperatures.
Ensure the furnace door or lid forms a proper seal when closed to maintain thermal efficiency and control the internal atmosphere.
Ensuring Electrical Integrity
Confirm that the power supply is correctly connected and matches the furnace's voltage and phase requirements. An improper connection is a significant fire and electrical hazard.
Always verify that the furnace is properly grounded. A secure ground connection is critical for protecting operators from electric shock in the event of an electrical fault.
Safe Operating Procedures
With the foundational checks complete, safety shifts to correct operational protocols. Adhering to these procedures minimizes risk during the heating process.
Setting Correct Parameters
Program the temperature controller carefully. Never set a temperature that exceeds the maximum rating of the furnace, the heating elements, or the workpiece being heated.
Avoid overloading the furnace. Adhere to the manufacturer's guidelines for maximum load to ensure uniform heating and prevent damage to the equipment.
Active Monitoring During Operation
A furnace should never be left completely unattended. You must monitor temperature and atmosphere changes throughout the cycle. Be alert for any unexpected temperature spikes or sounds, which could indicate a problem with the controller or heating elements.
If your process involves controlled atmospheres, monitor gas flow and vacuum levels to prevent leaks or hazardous conditions.
The Importance of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Operators must use appropriate PPE when working near the furnace. This includes heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing to shield against extreme heat exposure when loading or unloading the furnace.
Understanding the Key Risks
Recognizing the potential hazards is as important as following procedures. A box furnace is a powerful tool, and its risks must be respected.
The Risk of Thermal Shock
Rapid heating or cooling can cause thermal shock, which can damage or crack both the workpiece and the furnace's internal components. Always follow recommended ramp rates for temperature changes.
Fire and Electrical Hazards
Combustible materials should never be stored near the furnace. Maintain a clear, unobstructed area around the unit at all times.
Neglecting electrical safety, such as using frayed power cords or ignoring faulty connections, is a leading cause of equipment failure and potential fires.
The Dangers of Neglected Maintenance
A lack of routine maintenance can lead to catastrophic failure. Regular service, including checking electrical connections and calibrating the temperature controller, is essential for safe, long-term operation.
Operator training is a form of preventative maintenance. Ensure all users are thoroughly trained on the specific operating procedures and emergency shutdown protocols for your unit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your safety focus will change slightly depending on your role. Use these guidelines to prioritize your actions.
- If your primary focus is routine operation: Prioritize rigorous pre-use checks and continuous in-process monitoring to catch issues before they escalate.
- If your primary focus is lab management or purchasing: Ensure the furnace's specifications and safety certifications are a perfect match for your application's demands.
- If your primary focus is team safety and training: Develop and enforce standardized operating procedures and mandate a non-negotiable schedule for routine maintenance.
Ultimately, a disciplined and informed approach transforms this powerful tool into a consistently safe and reliable asset.
Summary Table:
| Safety Aspect | Key Precautions |
|---|---|
| Pre-Use Inspection | Check for cleanliness, door seal, and foreign materials |
| Electrical Safety | Verify proper grounding, voltage match, and secure connections |
| Operational Settings | Set temperature limits, avoid overloading, and monitor parameters |
| Personal Protection | Use heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing |
| Maintenance | Conduct routine checks and calibrate temperature controls |
Ensure your laboratory operates safely and efficiently with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability allows us to precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing safety and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements and deliver tailored solutions for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace used for Ni-BN powder preheating? Achieve defect-free coating density.
- How is the thermal stability of KBaBi compounds evaluated? Discover Precise XRD & Heat Treatment Limits



















