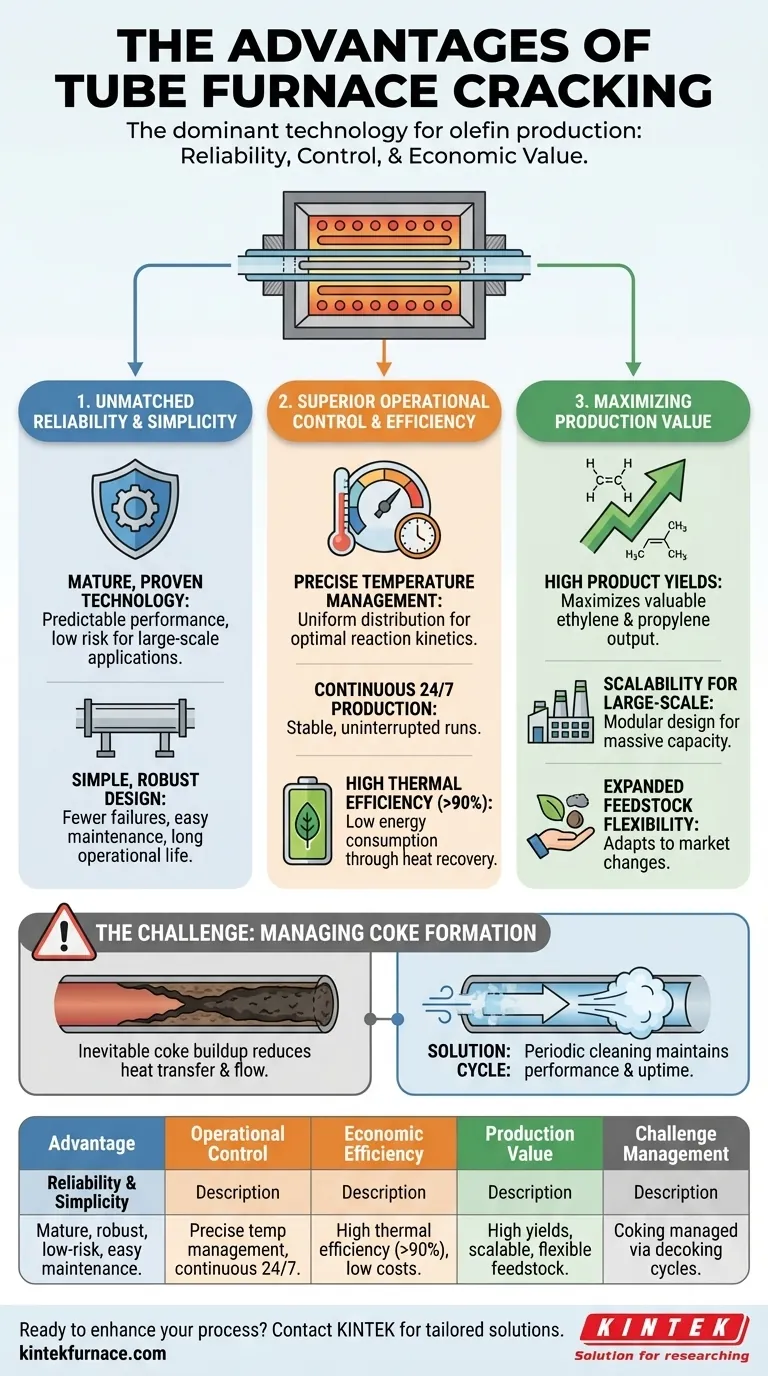
At its core, tube furnace cracking is the dominant technology for olefin production due to a powerful combination of mature design, operational efficiency, and high economic output. Its advantages stem from a simple and reliable structure that allows for precise control over the cracking process, leading to high yields of valuable products like ethylene and propylene while maintaining high thermal efficiency and the ability to scale for massive industrial production.
The true advantage of tube furnace cracking is not a single feature, but the systemic integration of reliability, control, and economic performance. This synergy has established it as the foundational process for the modern petrochemical industry.
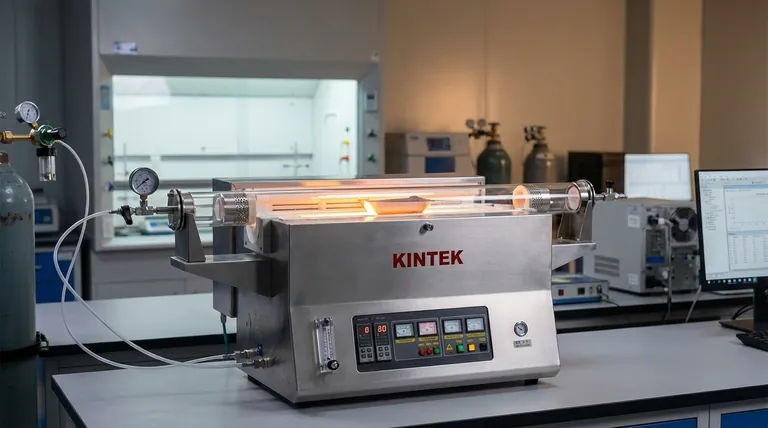

The Foundation: Unmatched Reliability and Simplicity
The long-standing success of tube furnace cracking is built on a design philosophy that prioritizes reliability and straightforward operation.
Mature, Proven Technology
This is not an experimental process. Tube furnace cracking is a highly mature and extensively refined technology, meaning its performance characteristics, operational challenges, and maintenance requirements are well-understood.
This maturity provides a high degree of predictability and reduces investment risk for large-scale industrial applications.
Simple and Robust Design
The fundamental structure of a tube furnace is simple: tubes are heated externally within a furnace box. This simplicity makes it easier to construct, operate, and maintain compared to more complex reactor designs.
This robust design contributes to long operational lifetimes and fewer points of catastrophic failure.
Superior Operational Control and Efficiency
Precise control over process variables is critical for maximizing desired products and minimizing waste. Tube furnaces excel in this area.
Precise Temperature Management
The furnace design allows for exceptional control over the process temperature profile. This includes uniform temperature distribution in the central heating zone and the ability to make fine adjustments.
This precise control is essential for managing reaction kinetics, ensuring the feedstock is "cracked" under optimal conditions to produce the desired molecules.
Designed for Continuous Production
Tube furnaces are engineered for continuous, 24/7 operation. Their ease of control, often managed remotely, allows for stable and uninterrupted production runs that are essential for commodity chemical manufacturing.
This capability is a primary driver of its economic viability in large-scale plants.
High Thermal and Energy Efficiency
Modern cracking furnaces achieve very high thermal efficiency, often exceeding 90%. This is accomplished through low power consumption and the strategic recovery of heat from both the hot cracked gas stream and the flue gas.
This focus on energy recovery significantly lowers operating costs and reduces the overall environmental footprint of the process.
Maximizing Production Value
The ultimate goal of cracking is to convert lower-value hydrocarbons into higher-value chemicals efficiently and at scale.
High Yields of Key Products
The process is optimized to deliver a high yield of ethylene and propylene, the building blocks for a vast array of plastics and chemicals. The resulting product stream also has a high concentration of these target molecules, simplifying downstream separation processes.
Scalability for Large-Scale Operations
A single plant can combine multiple cracking furnaces to achieve massive production capacity. This modular scalability allows producers to meet global demand by adding furnaces to an existing site.
Expanding Feedstock Flexibility
While traditionally designed for specific feedstocks like ethane or naphtha, technological progress has significantly expanded the range of raw materials that can be processed. This flexibility allows operators to adapt to market changes and select the most economically advantageous feedstock.
Understanding the Primary Operational Challenge: Coking
No technology is without its trade-offs. For tube furnace cracking, the primary operational challenge is not a design flaw but an inherent consequence of the chemical process itself.
The Inevitability of Coke Formation
Heating hydrocarbons to high temperatures inevitably causes side reactions that produce coke, a hard, solid form of carbon. This coke deposits on the inner walls of the furnace tubes.
Impact on Performance
Coke buildup acts as an insulator, reducing heat transfer from the furnace to the process fluid. It also constricts the tube diameter, increasing pressure drop and hindering flow.
Both effects reduce efficiency and can eventually force a shutdown if left unmanaged.
The Decoking Cycle
To maintain performance, furnaces must be taken offline periodically for decoking. During this process, the coke is burned off with steam and air. The frequency and duration of these decoking cycles are a critical factor in the overall plant availability and profitability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these advantages and challenges allows you to align the technology with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime and reliability: The mature, simple design offers proven performance, but you must budget for and engineer a robust strategy for managing the decoking cycle.
- If your primary focus is economic output: The combination of high product yields, exceptional thermal efficiency, and massive scalability makes this the unparalleled choice for commodity olefin production.
- If your primary focus is process control and versatility: The precise temperature management and growing feedstock flexibility provide significant operational levers to optimize production based on market conditions.
Ultimately, the tube furnace's blend of proven simplicity and high-efficiency performance makes it the enduring workhorse of the petrochemical world.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Reliability & Simplicity | Mature, robust design for predictable, low-risk operation with easy maintenance and long lifespan. |
| Operational Control | Precise temperature management and continuous production capabilities for stable, efficient processes. |
| Economic Efficiency | High thermal efficiency (>90%), energy recovery, and low operating costs for cost-effective production. |
| Production Value | High yields of ethylene and propylene, scalability for large-scale output, and feedstock flexibility. |
| Challenge Management | Inherent coking issue managed via decoking cycles to maintain performance and uptime. |
Ready to enhance your petrochemical processes with advanced tube furnace solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and industrial facilities with reliable high-temperature furnace systems. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can boost your efficiency and output!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















