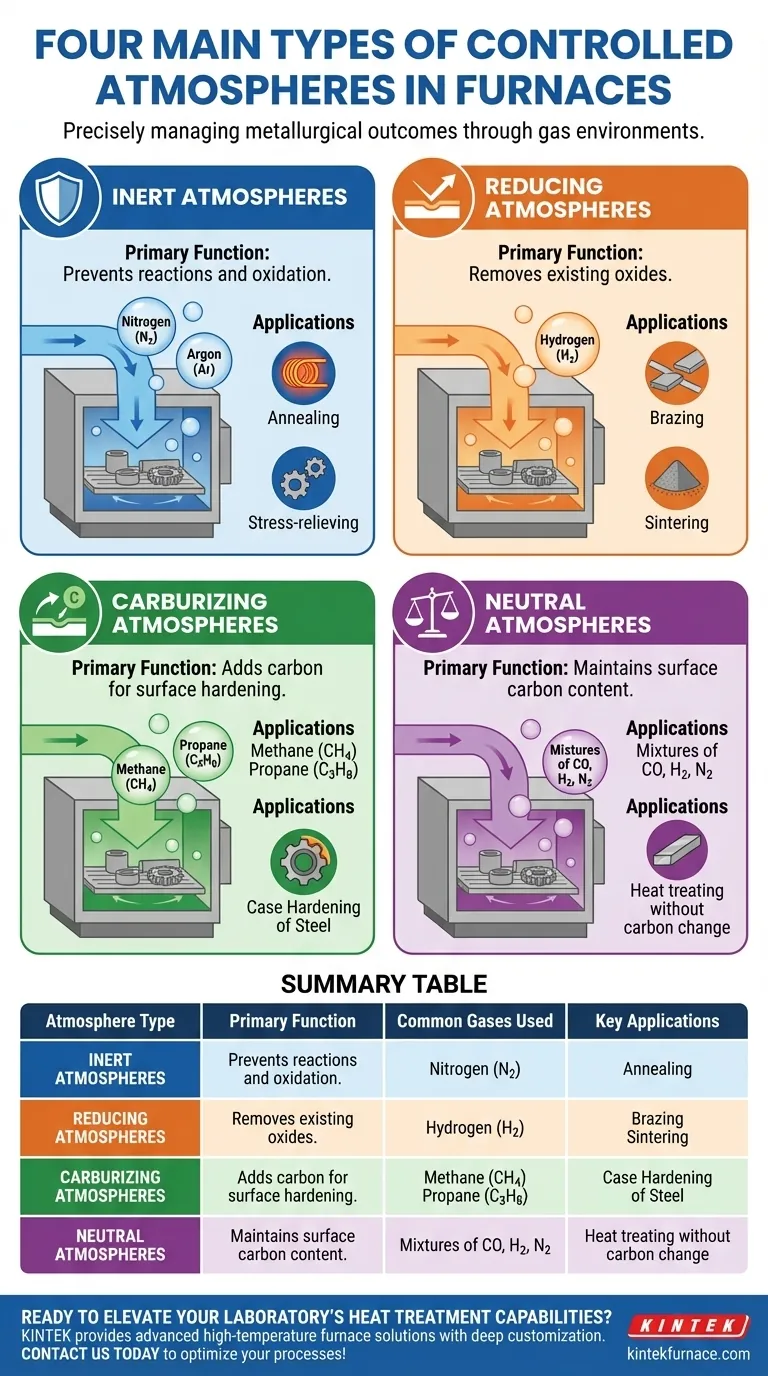
At its core, a controlled atmosphere furnace uses one of four main gas environments to precisely manage the outcome of a heat treatment process. These are inert atmospheres to prevent reactions, reducing atmospheres to remove oxides, carburizing atmospheres to add carbon for surface hardening, and neutral atmospheres to maintain the material's existing composition. Each type serves a distinct metallurgical purpose beyond simply heating the part.
Choosing the right furnace atmosphere is not just about protecting the material from air. It is an active engineering decision that directly manipulates the chemical and physical properties of the final component.

Protecting the Material: Inert & Neutral Atmospheres
The most common goal of a controlled atmosphere is to prevent unwanted chemical changes, primarily oxidation and scaling, that would occur if a part were heated in open air.
The Role of Inert Atmospheres
Inert atmospheres act as a protective shield. They use gases like nitrogen (N2) or argon (Ar), which are chemically non-reactive with the workpiece material at treatment temperatures.
The primary function is to displace oxygen. This prevents the formation of oxides (scale) on the material's surface, ensuring a clean finish for processes like annealing or stress-relieving.
The Challenge of a Neutral Atmosphere
A truly neutral atmosphere is more complex. Its goal is to heat a steel part without changing its surface carbon content—preventing both the addition of carbon (carburizing) and the loss of carbon (decarburizing).
Achieving this requires a delicate balance of gas mixtures, often containing carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), and nitrogen (N2), precisely matched to the steel's carbon potential at a specific temperature.
Actively Changing the Material: Reducing & Carburizing Atmospheres
In other applications, the atmosphere is intentionally reactive. It is used as a tool to actively change the surface chemistry of the material to achieve a desired property.
Reversing Oxidation with Reducing Atmospheres
Reducing atmospheres are designed to chemically remove oxides that are already present on a material's surface.
The most common reducing agent is hydrogen (H2). At high temperatures, hydrogen reacts with metal oxides (like iron oxide) to form pure metal and water vapor, which is then flushed from the furnace. This is critical for processes like brazing and sintering, where oxide-free surfaces are essential for metallurgical bonding.
Hardening Surfaces with Carburizing Atmospheres
Carburizing atmospheres are used to increase the carbon content on the surface of low-carbon steel parts. This process, known as case hardening, creates a hard, wear-resistant outer layer while maintaining a softer, tougher core.
These atmospheres introduce carbon-rich gases like methane (CH4) or propane (C3H8) into the furnace. At high temperatures, these gases decompose, allowing carbon atoms to diffuse into the steel's surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While powerful, each atmosphere type comes with its own set of considerations regarding cost, safety, and process control.
Cost vs. Purity
Argon is almost completely inert and ideal for highly reactive metals like titanium, but it is very expensive. Nitrogen is a far more cost-effective alternative for most applications but can form undesirable nitrides with certain metals at very high temperatures.
The Safety Factor: Handling Hydrogen
Hydrogen is an excellent reducing agent but is also highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. Furnaces using high concentrations of hydrogen require robust safety systems, leak detection, and careful operating procedures.
The Precision of Carburization
Controlling a carburizing process is a science. Improper control of gas composition, temperature, or time can lead to a case that is too shallow, too deep, or has excessive carbon, which can cause brittleness.
The Myth of a "Perfectly Neutral" Atmosphere
Maintaining a perfectly neutral atmosphere is difficult. Small fluctuations in gas flow or temperature can easily tip the balance, leading to unintended decarburization, which softens the material's surface and can compromise its fatigue life.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Goal
Your choice of atmosphere must be directly tied to the desired metallurgical outcome for your component.
- If your primary focus is preventing any surface reaction or discoloration: An inert atmosphere like nitrogen is your most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is hardening the surface of a low-carbon steel part: A carburizing atmosphere is necessary to introduce carbon for case hardening.
- If your primary focus is cleaning surface oxides to prepare for brazing or sintering: A reducing atmosphere containing hydrogen is required for a clean, active surface.
- If your primary focus is heat treating a steel part without altering its surface carbon: You need a precisely controlled neutral atmosphere matched to the material's carbon potential.
Ultimately, mastering furnace atmospheres means treating the gas not as a background condition, but as a critical ingredient in your material engineering process.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Primary Function | Common Gases Used | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert | Prevents reactions and oxidation | Nitrogen (N2), Argon (Ar) | Annealing, stress-relieving |
| Reducing | Removes existing oxides | Hydrogen (H2) | Brazing, sintering |
| Carburizing | Adds carbon for surface hardening | Methane (CH4), Propane (C3H8) | Case hardening of steel |
| Neutral | Maintains surface carbon content | Mixtures of CO, H2, N2 | Heat treating without carbon change |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's heat treatment capabilities? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can optimize your controlled atmosphere processes and deliver superior metallurgical results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance



















