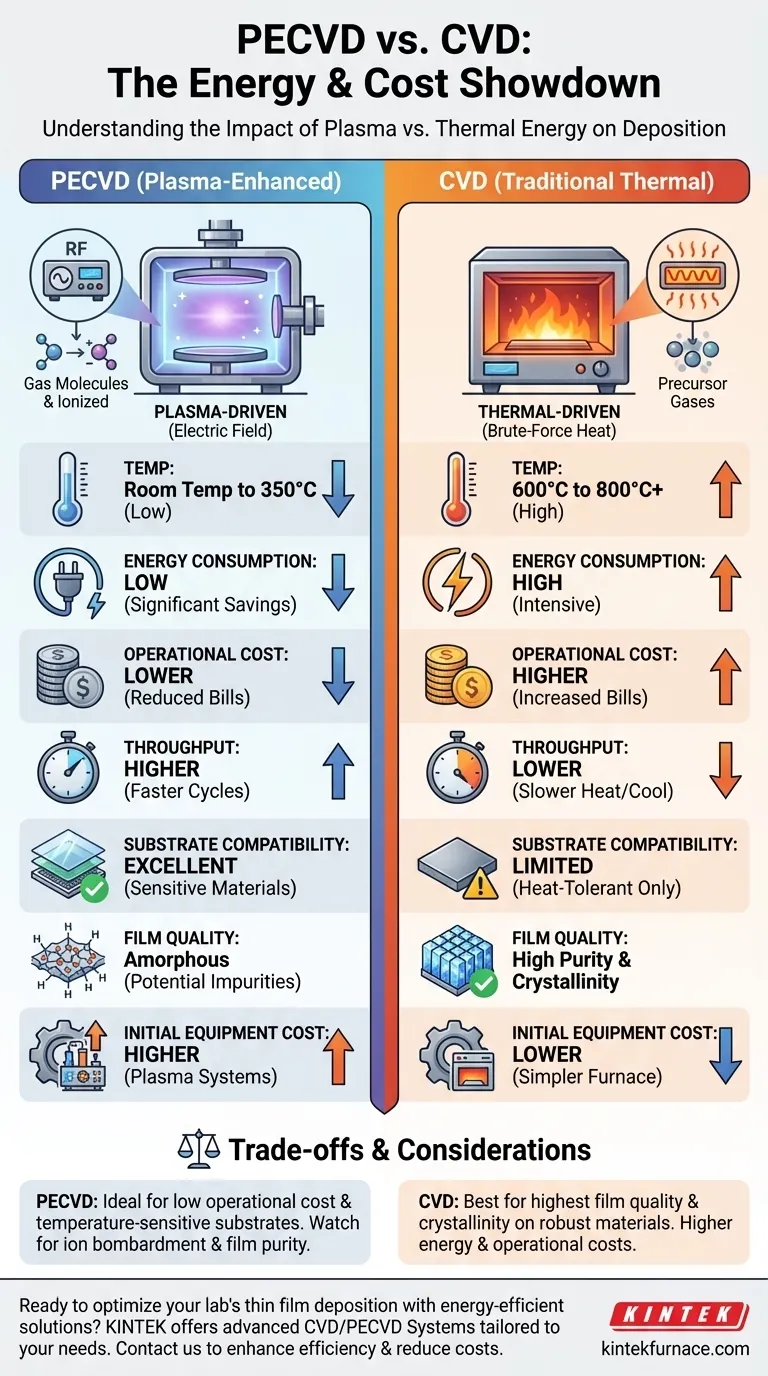
At its core, PECVD (Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition) is significantly more energy-efficient and has lower operational costs than traditional thermal CVD. This is because PECVD operates at much lower temperatures—often from room temperature to 350°C—by using an electric field to generate plasma, which provides the energy for the chemical reaction. In contrast, conventional CVD relies on intense heat, typically 600°C to 800°C or higher, leading to substantially greater energy consumption.
The choice between PECVD and CVD is not merely about cost, but about the fundamental energy source used for deposition. CVD uses brute-force thermal energy, while PECVD uses targeted plasma energy. This single difference dictates operating temperature, energy consumption, cost, and the types of materials you can work with.

The Fundamental Difference: Heat vs. Plasma
To understand the cost and energy implications, you must first understand how each process drives the necessary chemical reactions to form a thin film.
How Traditional CVD Works: The Thermal Approach
Conventional CVD functions like a high-temperature oven. Precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber, which is heated to extreme temperatures.
This thermal energy forces the gases to decompose and react on the surface of a substrate, depositing the desired thin film. The process is simple in concept but energy-intensive, as it requires heating the entire substrate and its immediate surroundings to very high temperatures.
How PECVD Works: The Plasma-Driven Approach
PECVD bypasses the need for extreme heat. Instead, it applies an electric field (typically radio frequency) to the precursor gases inside the chamber.
This field energizes the gas into a plasma, a highly reactive state of matter containing high-energy electrons, ions, and free radicals. These reactive species then drive the deposition reaction at a much lower substrate temperature, drastically reducing the overall thermal energy budget.
Translating Energy Source to Cost and Performance
The different energy mechanisms have direct, predictable consequences on operational efficiency, cost, and material capabilities.
Energy Consumption and Operational Costs
Because PECVD operates at significantly lower temperatures, its direct energy consumption is much lower than that of a high-temperature CVD furnace.
This directly translates to lower utility bills and reduced operational costs. The lower energy profile also results in a smaller environmental footprint, which is an increasingly important factor in modern manufacturing.
Throughput and Processing Time
PECVD systems can often achieve higher throughput and faster deposition cycles. The time required to heat and cool a high-temperature CVD system is a significant part of the total process time.
By eliminating this extensive thermal cycling, PECVD reduces overall processing time, further enhancing its cost-effectiveness, especially in high-volume production environments.
Substrate Compatibility: The Temperature Advantage
This is often the deciding factor. The high temperatures of traditional CVD can damage or destroy temperature-sensitive substrates, such as plastics, polymers, or complex semiconductor devices with pre-existing layers.
PECVD’s low-temperature nature makes it the only viable option for depositing films on these types of materials without causing thermal stress, warping, or irreversible damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While PECVD offers clear advantages in energy and cost, it is not universally superior. The choice involves critical trade-offs related to the process itself.
The Challenge of Ion Bombardment in PECVD
The same plasma that enables low-temperature deposition can also be a source of problems. In some PECVD configurations (direct PECVD), high-energy ions from the plasma can bombard the substrate surface.
This bombardment can cause physical damage to the growing film or the substrate itself, potentially affecting the material's electronic or optical properties. Advanced remote PECVD systems mitigate this by generating the plasma away from the substrate, but this adds to system complexity.
Film Quality and Purity
High-temperature thermal CVD often produces films with high purity and high crystallinity because the thermal energy allows atoms to settle into a stable, low-energy lattice structure.
PECVD films, being deposited at lower temperatures, can sometimes have a more amorphous (less ordered) structure or contain incorporated elements like hydrogen from the precursor gases. This is not inherently bad—amorphous silicon is critical for solar cells—but it is a key material difference.
Equipment Complexity and Initial Cost
A PECVD system requires a plasma generation stack, including an RF power supply and a matching network, which can increase the initial capital cost and complexity compared to a simpler thermal CVD furnace. While operational costs are lower, the initial investment for a PECVD system may be higher.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by your primary technical and business objectives.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational costs and energy on a heat-tolerant substrate: PECVD is generally the more cost-effective choice for high-volume production due to lower energy use and higher throughput.
- If your primary focus is depositing films on temperature-sensitive materials: PECVD is the definitive and often only viable option.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film crystallinity or purity for a robust substrate: Traditional high-temperature CVD may be required to achieve the desired material properties, despite its higher energy cost.
Ultimately, understanding the physics behind each method empowers you to select the process that best aligns with your material, substrate, and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PECVD | CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Room temp to 350°C | 600°C to 800°C or higher |
| Energy Consumption | Low (plasma-driven) | High (thermal-driven) |
| Operational Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Throughput | Higher (faster cycles) | Lower (slower heating/cooling) |
| Substrate Compatibility | Excellent for temperature-sensitive materials | Limited to heat-tolerant substrates |
| Film Quality | Amorphous, potential for impurities | High purity and crystallinity |
| Initial Equipment Cost | Higher (due to plasma systems) | Lower (simpler furnace) |
Ready to optimize your lab's thin film deposition with energy-efficient solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need cost-effective PECVD for low-temperature processes or high-purity CVD systems, we can tailor solutions to enhance your efficiency and reduce operational costs. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your specific application and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication



















