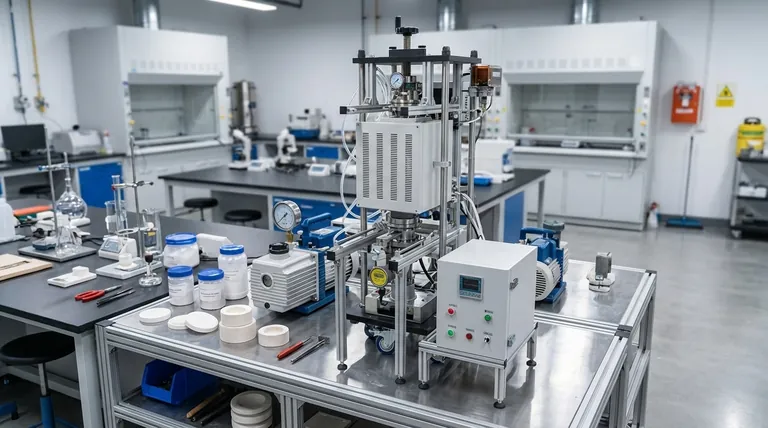
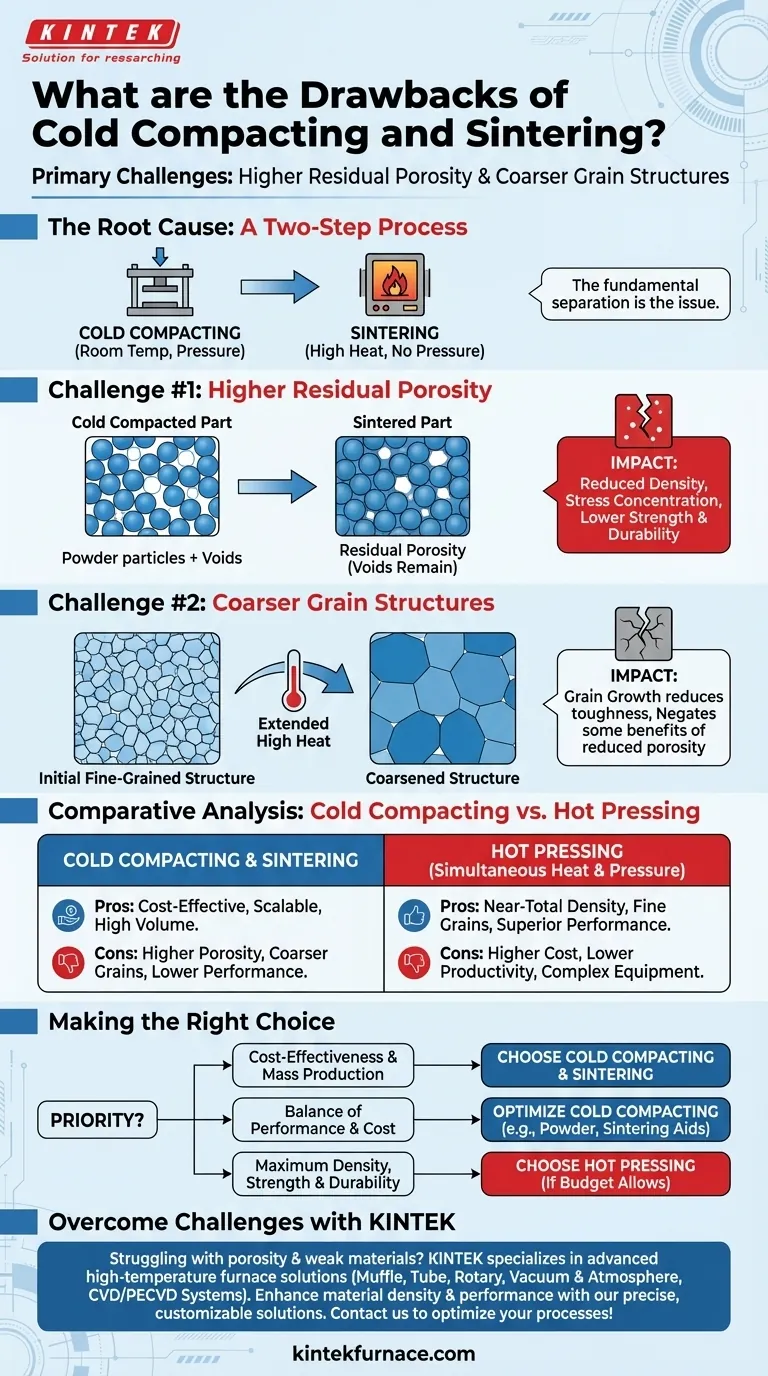
At its core, the primary drawbacks of cold compacting and sintering are higher residual porosity and the potential for coarser grain structures. These factors directly compromise the mechanical performance of the final part, reducing its strength and durability compared to components made through alternative methods like hot pressing.
The limitations of cold compacting and sintering are a direct trade-off for its primary benefits: cost-effectiveness and scalability. Understanding this trade-off is essential for selecting the right manufacturing process for your material and application.

The Root Cause: A Two-Step Process
The disadvantages of this method stem from the fundamental separation of its two main stages: compacting the material powder at room temperature and then heating it (sintering) without pressure.
The Problem of Porosity
When metal or ceramic powder is pressed at room temperature, tiny voids or pores inevitably remain between the particles. While the subsequent sintering step uses heat to bond the particles and shrink these voids, it often fails to eliminate them completely.
This residual porosity is the most significant disadvantage. These internal voids reduce the material's overall density and act as stress concentration points, making the component more susceptible to fracture under load.
The Impact on Mechanical Properties
The direct consequence of higher porosity is a reduction in mechanical strength and durability. A less dense part simply has less material in its cross-section to resist force, leading to lower tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and overall toughness.
The Sintering Dilemma: Heat vs. Grain Size
To combat porosity, engineers may increase the sintering temperature or extend the time the part is held at that temperature. However, this solution introduces another problem.
The Consequence of High Temperatures
Exposing the material to high heat for extended periods encourages grain growth. The individual crystalline grains within the material merge and grow larger, a process known as coarsening.
Why Coarser Grains Are a Drawback
For most engineering materials, a fine-grained microstructure is desirable. Smaller grains provide better strength and toughness. The coarser grain structures that result from aggressive sintering can therefore negate some of the benefits gained by reducing porosity, leading to a weaker final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cold Compacting vs. Hot Pressing
The drawbacks of cold compacting and sintering are best understood when compared to an alternative like hot pressing, where heat and pressure are applied simultaneously.
Where Cold Compacting Excels: Cost and Scale
Cold compacting is a simpler, faster, and more cost-effective process. The equipment is less complex, and because the steps are separate, they can be optimized for high-volume production. This makes it the superior choice for manufacturing large quantities of parts where ultimate performance is not the only consideration.
Where Hot Pressing Wins: Ultimate Performance
Hot pressing excels at producing parts with near-total density and extremely fine grain structures. Applying pressure during heating makes it much more effective at eliminating pores without requiring the high temperatures that cause grain growth. This results in superior mechanical properties but comes at the cost of lower productivity and significantly higher equipment and energy expenses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct process requires aligning its inherent characteristics with your project's most critical goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and mass production: Cold compacting and sintering is the clear and logical choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material density, strength, and durability: Hot pressing is the superior technical solution, provided the budget can support it.
- If you need a balance of good performance and reasonable cost: Optimizing the cold compacting and sintering process (e.g., powder selection, sintering aids) may offer the best compromise.
Ultimately, choosing a manufacturing method is about intentionally accepting a specific set of trade-offs to meet your most important objectives.
Summary Table:
| Drawback | Impact on Material |
|---|---|
| Higher Residual Porosity | Reduces density, increases stress concentration, and lowers tensile strength and fatigue resistance |
| Coarser Grain Structures | Decreases material toughness and overall mechanical performance due to grain growth during sintering |
Struggling with porosity and weak materials in your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions to overcome these challenges. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing material density and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your sintering and compacting processes for superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- How does a vacuum or protective atmosphere reduce oxidation in molten metals? Prevent Oxide Inclusions for Stronger Metals
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- What materials can be densified using a vacuum press and what are their applications? Unlock High-Performance Material Densification
- How does precise temperature control affect Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Master Titanium Hot Pressing Accuracy



















