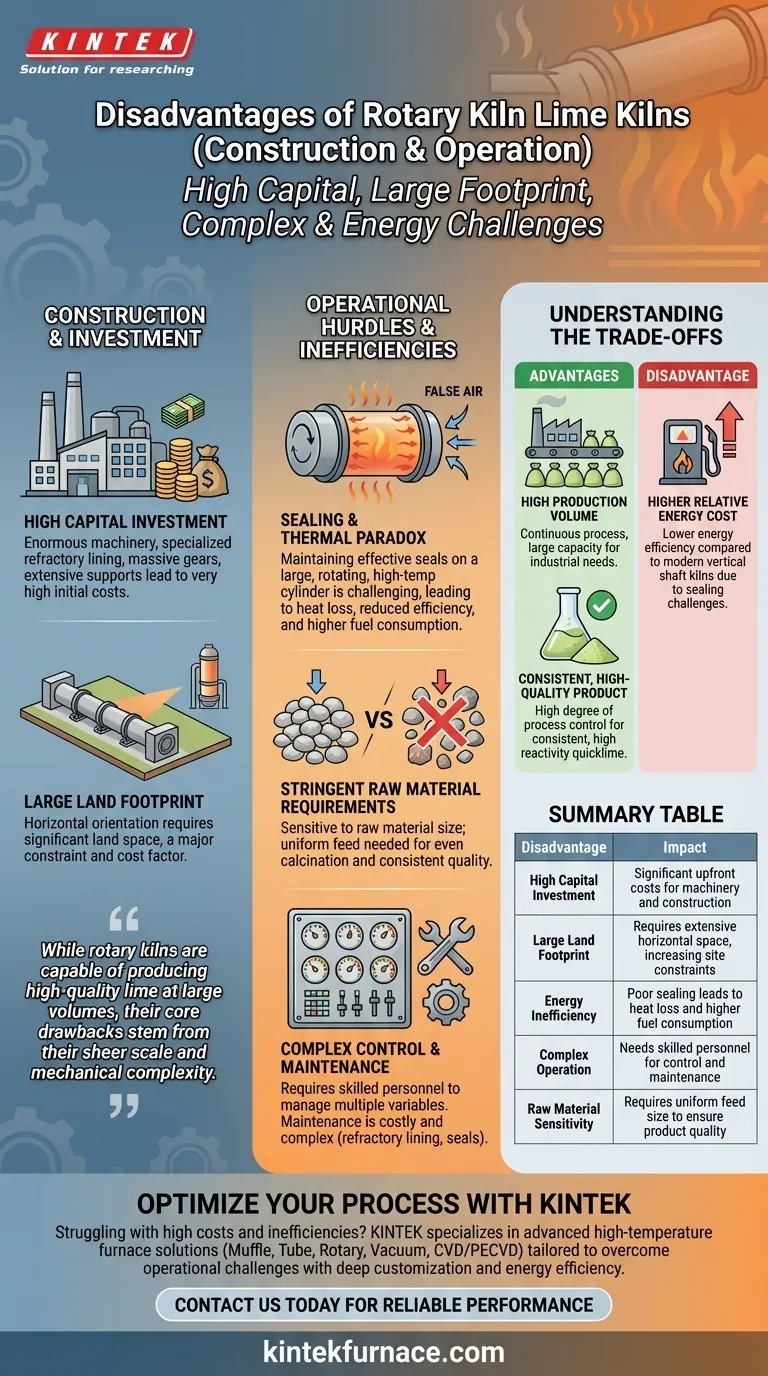
In terms of construction and operation, the primary disadvantages of rotary kiln lime kilns are their high capital investment, large physical footprint, complex operational demands requiring skilled personnel, and persistent challenges with energy efficiency due to sealing difficulties. These factors make them a significant long-term commitment in both capital and human resources.
While rotary kilns are capable of producing high-quality lime at large volumes, their core drawbacks stem from their sheer scale and mechanical complexity. These factors translate directly into high upfront costs, demanding operational oversight, and persistent challenges with energy efficiency.
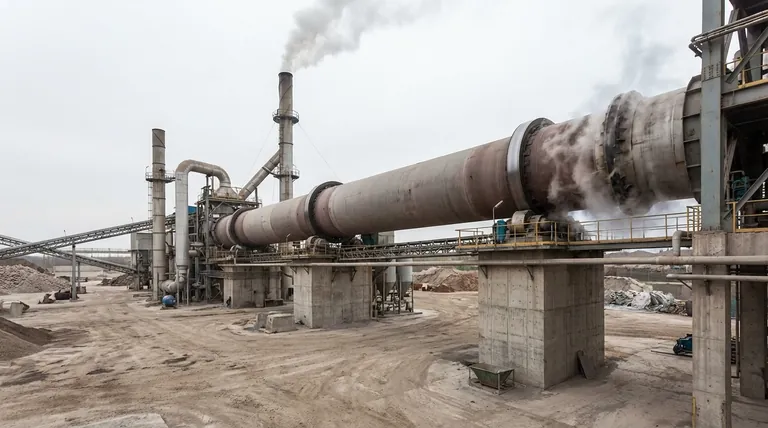

The Challenge of Scale: Construction and Investment
The physical design of a rotary kiln is the source of its most significant upfront disadvantages. Its horizontal orientation and massive size create substantial initial hurdles.
High Capital Investment
A rotary kiln is an enormous piece of industrial machinery. The long, heavy steel shell, specialized high-temperature refractory lining, massive gears, and extensive support structures (piers and rollers) all contribute to a very high initial construction cost.
Large Land Footprint
Unlike vertical kilns which build up, rotary kilns build out. Their long, cylindrical body requires a significant amount of horizontal land, which can be a major constraint and cost factor depending on the site location.
Operational Hurdles and Inefficiencies
Once constructed, the day-to-day operation of a rotary kiln presents a unique set of challenges that can impact profitability and reliability.
The Sealing and Thermal Efficiency Paradox
In theory, the long body of a rotary kiln provides an excellent zone for heat exchange. However, maintaining an effective seal at the feed and discharge ends of a massive, rotating, high-temperature cylinder is a major engineering challenge.
Poor sealing leads to heat loss and the ingress of "false air," which cools the kiln and reduces combustion efficiency. This directly increases fuel consumption per ton of lime produced, making energy costs a primary operational concern.
Stringent Raw Material Requirements
While rotary kilns can handle a range of limestone types, they are sensitive to the size of the raw material feed. To ensure even heating and complete calcination, the limestone particles must be of a relatively uniform and specific size.
Using a non-uniform feed can result in a mix of over-burnt and under-burnt product, reducing the overall quality and consistency of the final lime.
Complex Control and Maintenance
Operating a rotary kiln is not a simple task. It requires skilled technical personnel who can precisely manage multiple variables, including rotation speed, kiln slope, internal temperature profile, and fuel rate.
Improper operation can quickly lead to equipment failure or production accidents. Furthermore, maintenance is complex and costly, particularly the periodic replacement of the internal refractory lining and the upkeep of the kiln seals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology exists in a vacuum. The disadvantages of a rotary kiln must be weighed against its distinct advantages, which are primarily centered on production volume and product quality.
Advantage: High Production Volume
Rotary kilns are workhorses built for high-tonnage output. Their continuous process and large capacity make them suitable for industrial operations that require a massive and steady supply of lime, such as large steel mills or chemical plants.
Advantage: Consistent, High-Quality Product
When operated correctly, the high degree of process control allows rotary kilns to produce quicklime with very high and consistent activity (reactivity). The tumbling action ensures all material is evenly calcined, a critical factor for many chemical and metallurgical applications.
Disadvantage: Higher Relative Energy Cost
The trade-off for this high volume and quality is often energy efficiency. Compared to modern, well-sealed vertical shaft kilns, rotary kilns typically consume more fuel per ton of lime produced, primarily due to the sealing challenges mentioned earlier.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The decision to invest in a rotary kiln depends entirely on your specific production goals and operational capabilities.
- If your primary focus is maximum production volume and consistent, high-reactivity lime: A rotary kiln is a strong contender, provided you can manage the high capital and operational costs.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and lower capital investment: You should strongly evaluate modern vertical shaft kiln technologies, which often have a smaller footprint and lower fuel consumption.
- If you have a limited supply of skilled operators and maintenance personnel: The operational complexity of a rotary kiln may present a significant and ongoing challenge to your organization.
Ultimately, selecting the right kiln technology requires a clear-eyed assessment of your production goals against the long-term realities of capital, energy, and operational commitment.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Impact |
|---|---|
| High Capital Investment | Significant upfront costs for machinery and construction |
| Large Land Footprint | Requires extensive horizontal space, increasing site constraints |
| Energy Inefficiency | Poor sealing leads to heat loss and higher fuel consumption |
| Complex Operation | Needs skilled personnel for control and maintenance |
| Raw Material Sensitivity | Requires uniform feed size to ensure product quality |
Struggling with high costs and inefficiencies in your lime production? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems with deep customization to overcome operational challenges. Whether you're in metallurgy, chemicals, or other industries, our expertise ensures reliable, energy-efficient performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your process and reduce long-term commitments!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating



















