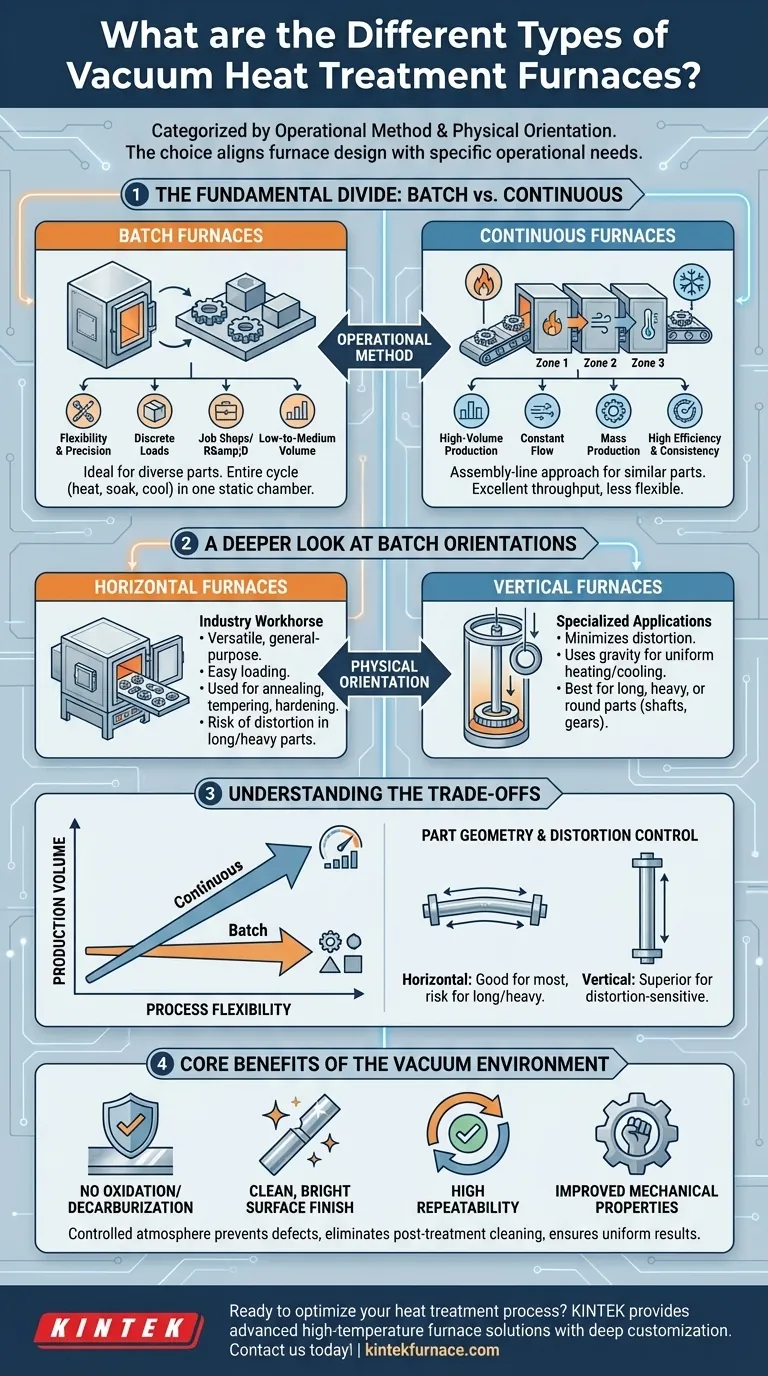
At its core, vacuum heat treatment furnaces are categorized by their operational method and physical orientation. The primary types are horizontal and vertical batch furnaces, designed for discrete loads, and continuous or semi-continuous furnaces, built for high-volume production lines. Each design is engineered to meet specific requirements for part geometry, production scale, and the desired metallurgical outcome.
The choice of a vacuum furnace is less about finding a single "best" type and more about aligning the furnace's design with your specific operational needs. The fundamental decision is between the flexibility of batch processing and the efficiency of continuous production, further refined by the part's geometry and handling requirements.

The Fundamental Divide: Batch vs. Continuous
The most significant distinction between vacuum furnace types is how they process materials—either in discrete groups (batch) or in a constant flow (continuous).
Batch Furnaces: For Flexibility and Precision
Batch furnaces process one distinct load of parts at a time. This makes them exceptionally versatile for handling a wide variety of part sizes, shapes, and material types.
They are the ideal choice for job shops, research and development, or production environments with diverse or low-to-medium volume requirements. The entire heat treatment cycle—heating, soaking, and cooling—is performed on the static load within the chamber.
Continuous Furnaces: For High-Volume Production
Continuous furnaces are designed for mass production of similar or identical parts. Parts move through a series of chambers, each dedicated to a specific stage of the heat treatment process.
This assembly-line approach delivers high throughput and excellent process consistency. However, it requires a significant initial investment and is less flexible for accommodating different part types or process cycles.
A Deeper Look at Furnace Orientations
Within the batch furnace category, the physical orientation—horizontal or vertical—plays a critical role in part handling and final quality.
Horizontal Furnaces: The Industry Workhorse
Horizontal vacuum furnaces are the most common type. Parts are loaded onto trays, baskets, or fixtures and moved horizontally into the heating chamber.
This configuration is a versatile, general-purpose solution suitable for a vast range of part shapes and sizes. Its ease of loading and robust design make it the default choice for many heat treatment applications like annealing, tempering, and hardening.
Vertical Furnaces: For Specialized Applications
Vertical furnaces load parts from the top or bottom. This design is specialized for parts where minimizing distortion is critical.
Long, slender parts (like shafts or landing gear), heavy components, or symmetrical, round parts (like rings and gears) benefit from being suspended or supported vertically. This orientation uses gravity to its advantage, ensuring uniform heating and cooling while preventing sagging or distortion that might occur in a horizontal furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right furnace involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single solution that is optimal for every scenario.
Production Volume vs. Process Flexibility
Continuous furnaces offer unmatched efficiency for high-volume, standardized production but are inflexible.
Batch furnaces provide maximum process flexibility, allowing you to run different parts and cycles one after another, but with lower overall throughput.
Part Geometry and Distortion Control
Horizontal furnaces are excellent for most applications but can lead to distortion in long or heavy parts that are not properly supported.
Vertical furnaces are the superior choice for distortion-sensitive parts, ensuring dimensional stability for critical components, though they are often more complex to load and integrate.
Core Benefits of the Vacuum Environment
Regardless of the furnace type, operating in a vacuum provides distinct advantages. The controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation and decarburization at high temperatures.
This results in a clean, bright surface finish and eliminates the need for post-treatment cleaning. The process also ensures high repeatability, uniform material properties, and improved mechanical performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice must be driven by your primary operational goal. Analyze your production needs against the strengths of each furnace type.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: A continuous furnace is the most efficient and consistent solution.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility for varied parts and lot sizes: A horizontal batch furnace offers the best balance of versatility and performance.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion in long, round, or heavy parts: A vertical batch furnace provides the necessary control for critical applications.
By matching the furnace architecture to your specific process and production goals, you can ensure optimal quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Furnaces | Flexible, processes discrete loads | Job shops, R&D, low-to-medium volume |
| Continuous Furnaces | High-throughput, consistent processing | Mass production of similar parts |
| Horizontal Furnaces | Versatile, easy loading | General-purpose applications, various shapes |
| Vertical Furnaces | Minimizes distortion, uses gravity | Long, heavy, or round parts |
Ready to optimize your heat treatment process? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today



















